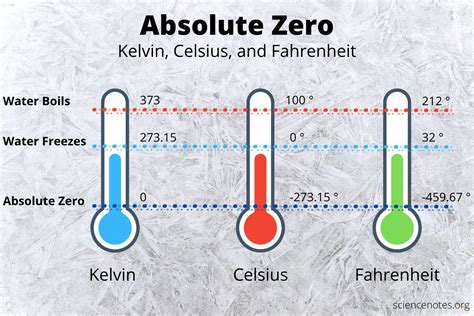
The concept of 0 Kelvin, also known as absolute zero, has long fascinated scientists and engineers alike. It represents the theoretical temperature at which all matter would have zero entropy, meaning that all molecular motion would cease. While it is impossible to achieve absolute zero by any finite number of processes, scientists have been able to get remarkably close. In this article, we will explore 5 ways that 0 Kelvin is significant, from its implications for quantum mechanics to its potential applications in advanced technologies.
Key Points
- The concept of 0 Kelvin is fundamental to the understanding of thermodynamics and the behavior of matter at extremely low temperatures.
- Scientists have developed innovative techniques to achieve temperatures very close to 0 Kelvin, with potential applications in fields such as quantum computing and materials science.
- 0 Kelvin has significant implications for our understanding of quantum mechanics and the behavior of particles at the atomic and subatomic level.
- Advanced technologies, such as superconducting materials and nanoscale devices, rely on the principles of low-temperature physics and the pursuit of 0 Kelvin.
- Research into 0 Kelvin has led to numerous breakthroughs in our understanding of the fundamental laws of physics and has the potential to drive future innovations in fields such as energy and transportation.
Theoretical Significance of 0 Kelvin
Theoretical models predict that at 0 Kelvin, all matter would be in its ground state, with all atoms and molecules having the minimum possible energy. This concept is fundamental to the understanding of thermodynamics and has significant implications for our understanding of the behavior of matter at extremely low temperatures. For instance, superfluidity and superconductivity are phenomena that occur at very low temperatures, where certain materials can exhibit zero viscosity and perfect conductivity, respectively.
Implications for Quantum Mechanics
0 Kelvin also has significant implications for our understanding of quantum mechanics. At such low temperatures, the behavior of particles at the atomic and subatomic level becomes even more pronounced, allowing for the study of quantum phenomena in greater detail. For example, quantum entanglement and quantum tunneling are phenomena that are more easily observable at very low temperatures, and have potential applications in fields such as quantum computing and cryptography.
| Temperature (Kelvin) | Physical Phenomenon |
|---|---|
| 4.2 K | Superfluidity of helium-4 |
| 2.17 K | Superconductivity of mercury |
| 0.01 K | Quantum entanglement and tunneling |

Practical Applications of Low-Temperature Physics
While it is impossible to achieve absolute zero, scientists have developed innovative techniques to achieve temperatures very close to 0 Kelvin. These techniques have numerous practical applications, from the development of superconducting materials and nanoscale devices to the advancement of quantum computing and materials science. For instance, superconducting materials can be used to create highly efficient power transmission lines, while nanoscale devices can be used to create ultra-sensitive sensors and detectors.
Advanced Technologies
Advanced technologies, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and particle accelerators, rely on the principles of low-temperature physics and the pursuit of 0 Kelvin. These technologies have numerous applications in fields such as medicine, energy, and transportation, and have the potential to drive future innovations in these areas. For example, MRI machines use superconducting magnets to create highly detailed images of the body, while particle accelerators use superconducting materials to accelerate particles to high speeds.
What is the significance of 0 Kelvin in thermodynamics?
+0 Kelvin represents the theoretical temperature at which all matter would have zero entropy, meaning that all molecular motion would cease. This concept is fundamental to the understanding of thermodynamics and has significant implications for our understanding of the behavior of matter at extremely low temperatures.
How do scientists achieve temperatures close to 0 Kelvin?
+Scientists use innovative techniques such as laser cooling, evaporative cooling, and magnetic cooling to achieve temperatures very close to 0 Kelvin. These techniques involve the use of highly advanced materials and equipment, and have numerous applications in fields such as quantum computing and materials science.
What are the potential applications of 0 Kelvin research?
+Research into 0 Kelvin has numerous potential applications, from the development of advanced technologies such as quantum computing and nanoscale devices to the advancement of our understanding of the fundamental laws of physics. These applications have the potential to drive future innovations in fields such as energy, transportation, and medicine.
In conclusion, the concept of 0 Kelvin is significant not only for its theoretical implications but also for its practical applications in advanced technologies. The pursuit of 0 Kelvin has driven innovation in fields such as cryogenics and materials science, and has the potential to drive future innovations in fields such as energy and transportation. As scientists continue to explore the properties of matter at extremely low temperatures, we can expect to see numerous breakthroughs in our understanding of the fundamental laws of physics and the development of new technologies that will shape our world.