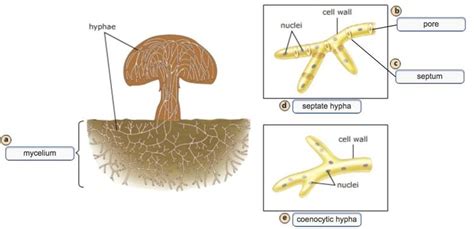
Fungi are a group of organisms that play a vital role in the ecosystem, and their importance cannot be overstated. With over 100,000 known species, fungi can be found in almost every habitat, from the freezing tundra to the hottest deserts. They are a diverse group of organisms that have evolved to occupy a wide range of ecological niches, and their roles in the ecosystem are equally diverse. In this article, we will explore two of the most important roles that fungi play in the ecosystem: decomposition and symbiosis.
Key Points
- Fungi play a crucial role in decomposing organic matter and recycling nutrients
- Symbiotic relationships between fungi and other organisms are essential for the health and survival of many plant and animal species
- Fungi have evolved to occupy a wide range of ecological niches, from decomposers to symbionts
- The role of fungi in the ecosystem is often overlooked, but it is essential for maintaining ecosystem balance and promoting biodiversity
- Further research is needed to fully understand the complex relationships between fungi and other organisms in the ecosystem
Decomposition: The Unsung Heroes of the Ecosystem
Fungi are one of the primary decomposers of organic matter in the ecosystem. They play a crucial role in breaking down dead plants and animals, and recycling nutrients back into the soil. This process is essential for maintaining ecosystem balance and promoting biodiversity. Without fungi, dead organic matter would accumulate, and the ecosystem would become stagnant. Fungi are able to break down complex organic molecules into simpler compounds, which can then be used by other organisms. This process is facilitated by the production of enzymes, which are specialized proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. For example, the enzyme cellulase breaks down cellulose, a tough, fibrous molecule found in plant cell walls.
The Importance of Fungal Enzymes
Fungal enzymes are highly specialized and play a critical role in the decomposition process. They are able to break down a wide range of organic molecules, from simple sugars to complex polymers. The production of enzymes is a key factor in the ability of fungi to decompose organic matter, and it is essential for their survival. Fungi have evolved to produce a wide range of enzymes, each with its own specific function. For example, the enzyme lacase is involved in the breakdown of lignin, a complex molecule found in plant cell walls. The production of enzymes is tightly regulated, and fungi are able to adjust their enzyme production in response to changes in their environment.
| Enzyme | Function |
|---|---|
| Cellulase | Breaks down cellulose |
| Lacase | Breaks down lignin |
| Protease | Breaks down proteins |

Symbiosis: The Hidden Relationships

In addition to their role in decomposition, fungi also form symbiotic relationships with other organisms. Symbiosis is a close, long-term relationship between two or more organisms, in which one or both organisms benefit. Fungi form symbiotic relationships with a wide range of organisms, from plants to animals. These relationships are often mutually beneficial, and they play a critical role in maintaining ecosystem balance. For example, fungi form symbiotic relationships with plant roots, providing them with essential nutrients in exchange for carbohydrates. This relationship is known as mycorrhizal symbiosis, and it is essential for the health and survival of many plant species.
The Importance of Mycorrhizal Symbiosis
Mycorrhizal symbiosis is a critical component of many ecosystems. It allows plants to access essential nutrients, such as phosphorus and nitrogen, which are often in short supply. In return, plants provide fungi with carbohydrates, which are produced during photosynthesis. This relationship is mutually beneficial, and it is essential for the health and survival of many plant species. Mycorrhizal symbiosis also plays a critical role in maintaining ecosystem balance. By providing plants with essential nutrients, fungi help to promote plant growth and diversity. This, in turn, helps to maintain ecosystem balance and promote biodiversity.
What is the role of fungi in decomposition?
+Fungi play a crucial role in decomposing organic matter and recycling nutrients back into the soil. They produce enzymes that break down complex organic molecules into simpler compounds, which can then be used by other organisms.
What is mycorrhizal symbiosis?
+Mycorrhizal symbiosis is a symbiotic relationship between fungi and plant roots. Fungi provide plants with essential nutrients, such as phosphorus and nitrogen, in exchange for carbohydrates produced during photosynthesis.
Why are fungi important in the ecosystem?
+Fungi are important in the ecosystem because they play a crucial role in decomposing organic matter and recycling nutrients. They also form symbiotic relationships with other organisms, which helps to maintain ecosystem balance and promote biodiversity.
In conclusion, fungi play a vital role in the ecosystem, and their importance cannot be overstated. They are a diverse group of organisms that have evolved to occupy a wide range of ecological niches, and their roles in the ecosystem are equally diverse. From decomposition to symbiosis, fungi are essential for maintaining ecosystem balance and promoting biodiversity. Further research is needed to fully understand the complex relationships between fungi and other organisms in the ecosystem, but it is clear that fungi are a critical component of many ecosystems.