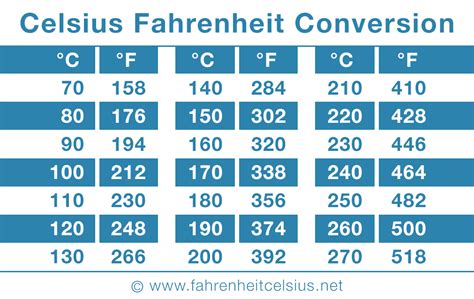
Converting temperature from Fahrenheit to Celsius is a fundamental process in various fields, including science, engineering, and everyday applications. To convert 103 degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius, we use the formula: Celsius = (Fahrenheit - 32) * 5/9. Applying this formula, we subtract 32 from 103, which equals 71. Then, we multiply 71 by 5/9, resulting in 39.44 Celsius. Therefore, 103 degrees Fahrenheit is equivalent to approximately 39.44 degrees Celsius.
Understanding the Conversion Process

The conversion from Fahrenheit to Celsius involves a simple mathematical operation. The formula, as mentioned, is straightforward: (C = (F - 32) \times \frac{5}{9}), where (C) is the temperature in Celsius and (F) is the temperature in Fahrenheit. This formula is derived from the fact that the freezing point of water is 32 degrees Fahrenheit and 0 degrees Celsius, and the boiling point of water is 212 degrees Fahrenheit and 100 degrees Celsius.
Applying the Formula to Different Scenarios
Beyond converting 103 Fahrenheit to Celsius, understanding how to apply the formula is crucial for various applications. For instance, converting room temperature, which is often around 72 degrees Fahrenheit, to Celsius involves the same process: (C = (72 - 32) \times \frac{5}{9}), which simplifies to (C = 40 \times \frac{5}{9}), resulting in approximately 22.22 degrees Celsius.
| Temperature in Fahrenheit | Equivalent in Celsius |
|---|---|
| 32 | 0 |
| 103 | 39.44 |
| 212 | 100 |

Key Points
- The formula to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius is C = (F - 32) \times \frac{5}{9}.
- 103 degrees Fahrenheit is equivalent to approximately 39.44 degrees Celsius.
- The conversion process is linear and applies to all temperatures.
- Understanding the conversion is crucial for international communication and scientific applications.
- Both Fahrenheit and Celsius scales have their uses and preferences in different parts of the world.
Practical Applications of Temperature Conversion
In everyday life, converting between Fahrenheit and Celsius might seem like a trivial matter, but it has significant implications in fields like meteorology, where weather forecasts are often reported in Celsius in many parts of the world but in Fahrenheit in the United States. Moreover, in scientific research, especially in fields like chemistry and physics, temperatures are often reported in Celsius due to its simpler and more intuitive scale for many applications.
Historical Context of Temperature Scales
The development of temperature scales dates back to the early 18th century, with Gabriel Fahrenheit introducing his scale in 1724 and Anders Celsius proposing his scale in 1742. The Celsius scale, initially called the centigrade scale, was based on the freezing and boiling points of water, making it a more logical and simpler system for scientific use.
Why do different countries use different temperature scales?
+The use of different temperature scales in various countries is largely a matter of historical and cultural preference. The United States, for example, has retained the Fahrenheit scale for everyday applications, while most other countries have adopted the Celsius scale for both scientific and everyday use.
Is there a move towards a single global temperature standard?
+While there is a trend towards globalization and standardization in many areas, the use of temperature scales remains diverse. However, in scientific and international communications, the Celsius scale is predominantly used, suggesting a de facto standardization in these contexts.
In conclusion, converting temperatures between Fahrenheit and Celsius is a straightforward process with significant implications for communication and application across different fields and geographical locations. Understanding and applying the conversion formula is essential for anyone dealing with temperatures in their professional or personal life, ensuring clarity and precision in a world where both scales coexist.