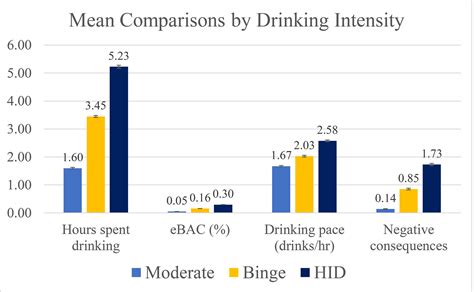
Dividing numbers is a fundamental operation in mathematics, and understanding the various ways to divide a number can be both intriguing and useful. The number 108, in particular, offers several interesting division possibilities due to its unique factors. In this article, we will explore 9 different ways to divide 108, highlighting the factors and the resulting quotients in each case.
Key Points
- Understanding the factors of 108
- Dividing 108 by its factors
- Exploring the results of each division
- Applying mathematical principles to real-world scenarios
- Recognizing the importance of division in problem-solving
Introduction to Dividing 108
To begin dividing 108, it’s essential to identify its factors. The factors of 108 are the numbers that can divide 108 without leaving a remainder. By prime factorization, we find that 108 = 2^2 * 3^3. This means the factors of 108 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18, 27, 36, 54, and 108. Now, let’s explore 9 ways to divide 108 using these factors.
Division 1: 108 Divided by 1
Dividing 108 by 1 results in 108. This is the simplest division, as any number divided by 1 equals itself.
Division 2: 108 Divided by 2
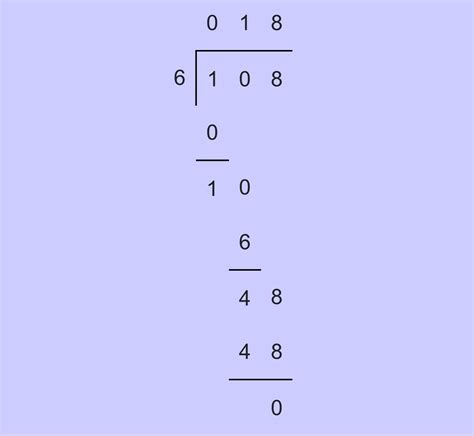
When we divide 108 by 2, we get 54. This division is straightforward and demonstrates the basic principle of dividing by a prime factor.
Division 3: 108 Divided by 3
Dividing 108 by 3 gives us 36. This division showcases another prime factor of 108 and how it reduces the original number.
Division 4: 108 Divided by 4
The result of dividing 108 by 4 is 27. This illustrates the division by a composite factor, which is a product of prime factors.
Division 5: 108 Divided by 6
Dividing 108 by 6 yields 18. This division combines the factors of 2 and 3, demonstrating how multiple prime factors can be used in division.
Division 6: 108 Divided by 9
When we divide 108 by 9, we obtain 12. This division highlights the use of a factor that is itself a product of prime factors, specifically 3^2.
Division 7: 108 Divided by 12
The result of dividing 108 by 12 is 9. This showcases a division by a factor that combines both 2 and 3, demonstrating the flexibility in choosing factors for division.
Division 8: 108 Divided by 18
Dividing 108 by 18 gives us 6. This division demonstrates the use of a larger factor to reduce the original number significantly.
Division 9: 108 Divided by 27
Finally, dividing 108 by 27 results in 4. This division illustrates the use of a factor that is a product of prime factors, specifically 3^3, to achieve a small quotient.
| Division | Divisor | Quotient |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 108 |
| 2 | 2 | 54 |
| 3 | 3 | 36 |
| 4 | 4 | 27 |
| 5 | 6 | 18 |
| 6 | 9 | 12 |
| 7 | 12 | 9 |
| 8 | 18 | 6 |
| 9 | 27 | 4 |

Conclusion and Future Implications

In conclusion, dividing 108 in 9 different ways illustrates the complexity and versatility of mathematical operations. By understanding the factors of a number and how they can be used in division, we can approach problems from multiple angles and develop a deeper appreciation for the underlying principles of mathematics. As we continue to explore and apply these principles, we may uncover new insights and methods that can be used to tackle more complex challenges in the future.
What are the factors of 108?
+The factors of 108 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18, 27, 36, 54, and 108.
Why is understanding the factors of a number important?
+Understanding the factors of a number is crucial because it allows for the division of the number in various ways, which can be applied to solve complex mathematical problems and real-world scenarios.
Can the method of dividing a number by its factors be applied to other numbers?
+Yes, the method of dividing a number by its factors can be applied to any number, as long as the factors of that number are known. This approach enhances the understanding of mathematical operations and their applications.