The 12 Tribes of Israel, also known as the Israelites, were the descendants of the 12 sons of Jacob, who is also known as Israel. Each tribe had its own unique characteristics, responsibilities, and destinies. Understanding the 12 Tribes of Israel is essential for grasping the history, culture, and religious significance of the Israelites. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide to the 12 Tribes of Israel, including their history, characteristics, and biblical significance.
Introduction to the 12 Tribes of Israel

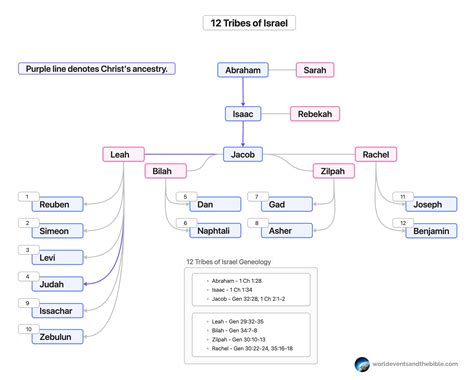
The 12 Tribes of Israel were the foundation of the Israelite nation. They were formed when Jacob, the grandson of Abraham, had 12 sons with his wives, Leah and Rachel, and their servants, Bilhah and Zilpah. Each son became the ancestor of a tribe, and their descendants formed the 12 Tribes of Israel. The tribes were:
- Reuben
- Simeon
- Levi
- Judah
- Dan
- Naphtali
- Gad
- Asher
- Issachar
- Zebulun
- Joseph
- Benjamin
Characteristics of Each Tribe
Each tribe had its own unique characteristics, strengths, and weaknesses. For example, the tribe of Judah was known for its leadership and bravery, while the tribe of Levi was known for its priestly duties and spiritual leadership. The tribe of Joseph was known for its wisdom and administrative skills. Understanding the characteristics of each tribe is essential for grasping their roles and contributions to the Israelite nation.
Key Points
- The 12 Tribes of Israel were the descendants of the 12 sons of Jacob.
- Each tribe had its own unique characteristics, strengths, and weaknesses.
- The tribes were formed when Jacob had 12 sons with his wives and servants.
- The tribe of Judah was known for its leadership and bravery.
- The tribe of Levi was known for its priestly duties and spiritual leadership.
The History of the 12 Tribes of Israel

The history of the 12 Tribes of Israel is complex and multifaceted. After the death of Jacob, the tribes were led by Moses, who received the Ten Commandments from God and guided the Israelites through the wilderness. The tribes eventually settled in the Promised Land, where they established a kingdom under the leadership of King Saul and later King David. The tribes were later divided into two kingdoms: the Kingdom of Israel and the Kingdom of Judah.
The Division of the Kingdoms
The division of the kingdoms occurred after the death of King Solomon, who had united the tribes under his rule. The Kingdom of Israel consisted of 10 tribes, while the Kingdom of Judah consisted of the tribes of Judah and Benjamin. The Kingdom of Israel was eventually conquered by the Assyrians, while the Kingdom of Judah was conquered by the Babylonians.
| Tribe | Characteristics | Destiny |
|---|---|---|
| Reuben | Firstborn son, leadership | Lost birthright due to disobedience |
| Simeon | Violent and aggressive | Scattered among other tribes |
| Levi | Priestly duties, spiritual leadership | Became the priestly tribe |
| Judah | Leadership, bravery | Became the dominant tribe, produced Jesus Christ |
| Dan | Wisdom, administrative skills | Settled in the north, eventually disappeared |
| Naphtali | Speed, agility | Settled in the north, eventually disappeared |
| Gad | Strength, courage | Settled in the east, eventually disappeared |
| Asher | Riches, prosperity | Settled in the north, eventually disappeared |
| Issachar | Wisdom, understanding | Settled in the center, eventually disappeared |
| Zebulun | Maritime trade, commerce | Settled in the west, eventually disappeared |
| Joseph | Wisdom, administrative skills | Became a dominant tribe, produced two tribes: Ephraim and Manasseh |
| Benjamin | Bravery, loyalty | Settled in the center, eventually disappeared |
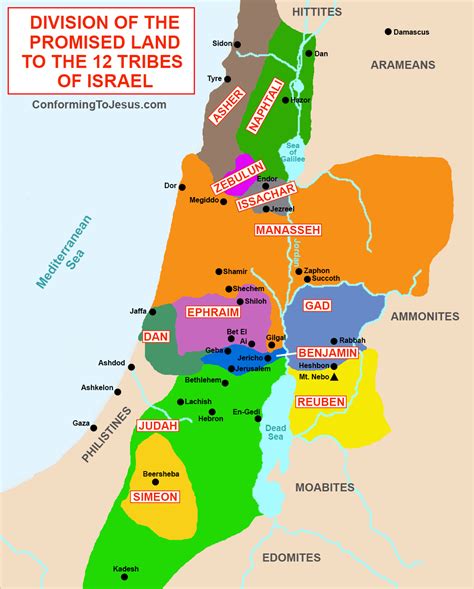
Biblical Significance of the 12 Tribes of Israel
The 12 Tribes of Israel have significant biblical implications. They were chosen by God to be His people, and they were given the responsibility of spreading His message to the world. The tribes were also given specific responsibilities, such as the tribe of Levi, which was responsible for the priestly duties. The tribes were also promised a land, the Promised Land, which they would inherit and settle.
The Promised Land
The Promised Land, also known as Canaan, was a land that God promised to the Israelites. It was a land of milk and honey, where the Israelites would settle and establish a kingdom. The Promised Land was also a land of spiritual significance, where the Israelites would worship God and fulfill their spiritual destinies.
What were the 12 Tribes of Israel?
+The 12 Tribes of Israel were the descendants of the 12 sons of Jacob, who is also known as Israel. Each tribe had its own unique characteristics, strengths, and weaknesses.
What was the significance of the 12 Tribes of Israel?
+The 12 Tribes of Israel played a crucial role in the history of the Israelite nation. Each tribe had its own unique characteristics, strengths, and weaknesses, which contributed to the richness and diversity of the nation.
What was the Promised Land?
+The Promised Land, also known as Canaan, was a land that God promised to the Israelites. It was a land of milk and honey, where the Israelites would settle and establish a kingdom.
Meta description suggestion: “Discover the history and significance of the 12 Tribes of Israel, including their characteristics, strengths, and weaknesses, and how they contributed to the richness and diversity of the Israelite nation.” (149 characters)