Converting between different units, formats, or systems is a fundamental aspect of various fields, including science, engineering, and data analysis. The ability to accurately convert between different forms enables seamless communication, ensures precision in calculations, and facilitates problem-solving. In this article, we will explore three essential ways to convert, focusing on unit conversions, data format conversions, and system conversions, highlighting their importance, methods, and applications.
Key Points
- Understanding the basics of unit conversion, including the use of conversion factors and dimensional analysis.
- Recognizing the importance of data format conversions in maintaining data integrity and usability across different platforms.
- Appreciating the role of system conversions in enabling compatibility and interoperability between different systems and technologies.
- Identifying the challenges and considerations associated with each type of conversion, such as precision, context, and compatibility.
- Exploring real-world applications and examples of conversions in various fields, including physics, computer science, and engineering.
Unit Conversions

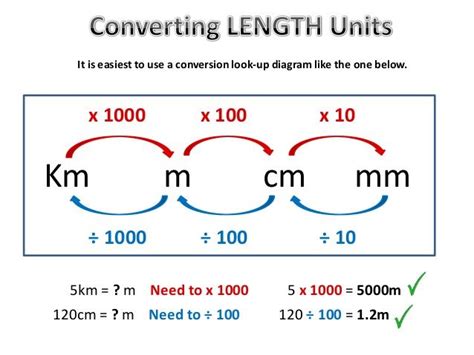
Unit conversions are a critical aspect of scientific and engineering calculations, as they allow for the expression of quantities in different units. This is particularly important in international collaborations, where different countries may use different systems of measurement. The most common method of unit conversion involves the use of conversion factors, which are ratios of equivalent quantities. For example, to convert meters to feet, one can use the conversion factor 1 meter = 3.2808 feet. Dimensional analysis is another powerful technique for unit conversions, where the units of the initial and final quantities are analyzed to determine the appropriate conversion factors.
Conversion Factors and Dimensional Analysis
Conversion factors are derived from the definitions of units and the relationships between them. They can be used to convert between units within the same system (e.g., meters to kilometers) or between different systems (e.g., meters to feet). Dimensional analysis, on the other hand, involves canceling out units to arrive at the desired unit. This method is particularly useful for complex conversions involving multiple steps. For instance, to convert joules (a unit of energy) to watts (a unit of power), one must understand the relationship between energy, power, and time, highlighting the importance of dimensional analysis in ensuring the correctness of the conversion.
| Unit | Conversion Factor |
|---|---|
| Meters to Feet | 1 meter = 3.2808 feet |
| Grams to Pounds | 1 gram = 0.00220462 pounds |
| Joules to Calories | 1 joule = 0.239005736 calories |
Data Format Conversions
Data format conversions refer to the process of transforming data from one format to another, ensuring compatibility and usability across different platforms and applications. This is increasingly important in the digital age, where data is shared, processed, and analyzed in various formats. Common data format conversions include text to CSV, JSON to XML, and image format conversions like JPEG to PNG. Each conversion requires an understanding of the source and target formats, as well as the potential for data loss or corruption during the conversion process.
Text and Image Conversions
Text conversions, such as converting plain text to rich text format, involve preserving the integrity of the text data while adapting it to the new format. Image conversions, on the other hand, can be more complex due to the variety of image formats and the potential for quality loss during conversion. For example, converting a JPEG image to a PNG format may require considerations regarding compression, color depth, and transparency, to ensure that the resulting image meets the required standards.
System Conversions
System conversions involve transitioning from one system or technology to another, often driven by the need for compatibility, efficiency, or innovation. This can include conversions between different operating systems, database systems, or software applications. System conversions require careful planning, as they can impact performance, security, and user experience. A key aspect of system conversions is ensuring data integrity and minimizing downtime during the transition process.
Challenges and Considerations
Each type of conversion—whether unit, data format, or system—comes with its own set of challenges and considerations. Precision and accuracy are paramount in unit conversions to ensure that calculations are correct. Data format conversions must consider the potential for data loss and the importance of maintaining data integrity. System conversions require careful planning to minimize disruptions and ensure compatibility. Understanding these challenges and taking a nuanced approach to conversions can help mitigate risks and ensure successful outcomes.
What are the key considerations for unit conversions in scientific calculations?
+Key considerations include understanding the conversion factors, applying dimensional analysis correctly, and ensuring that the units are appropriately canceled out to avoid calculation errors.
How do data format conversions impact data usability and compatibility?
+Data format conversions are crucial for ensuring that data can be used across different platforms and applications. They impact data usability by making it accessible in the required format and compatibility by ensuring that the data can be processed and analyzed as intended.
What are the main challenges associated with system conversions, and how can they be mitigated?
+The main challenges include ensuring data integrity, minimizing downtime, and maintaining compatibility. These can be mitigated through careful planning, testing, and phased implementation of the conversion process.
In conclusion, conversions—whether unit, data format, or system—are fundamental to various aspects of science, technology, and engineering. Understanding the principles, methods, and challenges associated with each type of conversion is essential for accurate calculations, data integrity, and system compatibility. By approaching conversions with a nuanced perspective and careful consideration of the underlying principles and potential impacts, professionals can ensure successful outcomes and contribute to advancements in their respective fields.



