Converting temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit is a common task in various fields, including science, engineering, and everyday life. The conversion process involves a simple formula, but understanding the underlying principles and the history behind these temperature scales can provide valuable insights. In this article, we will explore the conversion of 15 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit, delving into the details of the conversion process, the history of the temperature scales, and practical applications.
Understanding the Celsius and Fahrenheit Scales
The Celsius scale, previously known as the centigrade scale, is based on the freezing and boiling points of water. It sets the freezing point of water at 0 degrees Celsius and the boiling point at 100 degrees Celsius. This scale is widely used in most countries and in scientific applications due to its simplicity and the logical division of the temperature range between these two reference points.
The Fahrenheit scale, on the other hand, was developed earlier and sets the freezing point of water at 32 degrees Fahrenheit and the boiling point at 212 degrees Fahrenheit. Although it is less commonly used today, especially in scientific and international contexts, it remains in use in the United States and a few other countries for everyday applications.
Conversion Formula
To convert a temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit, the following formula is used: °F = (°C × 9⁄5) + 32. This formula adjusts the Celsius temperature to the Fahrenheit scale by first multiplying by 9⁄5 (which is equivalent to 1.8) to adjust for the different size of the degree units and then adding 32 to adjust for the difference in the zero points of the two scales.
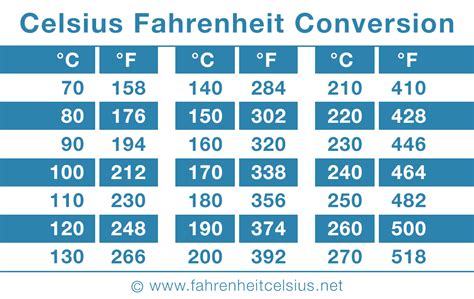
Applying this formula to convert 15 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit: °F = (15 × 9/5) + 32 = (15 × 1.8) + 32 = 27 + 32 = 59 degrees Fahrenheit.
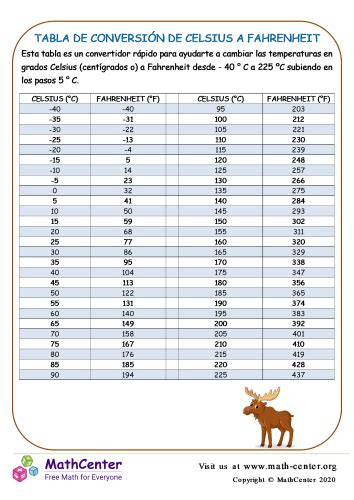
| Temperature Scale | 15 Degrees Celsius Equivalent |
|---|---|
| Celsius | 15°C |
| Fahrenheit | 59°F |
Key Points
- The Celsius scale is based on the freezing and boiling points of water, setting them at 0°C and 100°C, respectively.
- The Fahrenheit scale sets the freezing point of water at 32°F and the boiling point at 212°F.
- The formula to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit is °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32.
- 15 degrees Celsius is equivalent to 59 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Understanding both temperature scales is crucial for effective international communication, especially in scientific and engineering contexts.
Practical Applications and Considerations
In everyday life, the need to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit can arise in various situations, such as reading weather forecasts, setting oven temperatures for cooking, or understanding medical instructions. For instance, knowing that 15°C is equivalent to a mild 59°F can help in deciding what to wear on a day or in planning outdoor activities.
In scientific and engineering applications, precise temperature control is often critical. For example, in chemical reactions, the rate of reaction can be highly sensitive to temperature. Thus, accurate conversion between different temperature scales is essential to ensure that experiments are conducted under the correct conditions and that results are interpreted correctly.
Historical Context and Evolution
The development of temperature scales has a rich history, with early attempts to quantify heat and cold dating back to ancient civilizations. The Fahrenheit scale, developed by Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century, was one of the first standardized temperature scales. Later, the Celsius scale, introduced by Anders Celsius, offered a more intuitive and simpler division of the temperature range, leading to its widespread adoption in scientific and international contexts.
Today, with the increasing globalization of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields, the ability to work with and convert between different units and scales, including temperature scales, is more important than ever. This not only facilitates international collaboration but also ensures the accuracy and reliability of scientific and engineering work.
Why is it important to know how to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit?
+Knowing how to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit is important for effective communication in international and scientific contexts, as well as for practical applications in everyday life, such as cooking, weather forecasting, and medical care.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when converting between Celsius and Fahrenheit?
+Common mistakes include forgetting to add or subtract the appropriate offset (32 for Fahrenheit to Celsius conversions) and not using the correct multiplication factor (9/5 or 5/9). Double-checking calculations and using online conversion tools can help avoid these mistakes.
How does the conversion affect cooking and baking recipes?
+The conversion can significantly affect cooking and baking outcomes because temperature control is crucial in these processes. Incorrect conversions can lead to overcooking, undercooking, or ruining the dish. Always ensure to convert temperatures accurately when following recipes from different regions.
In conclusion, converting 15 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit, which equals 59 degrees Fahrenheit, is a straightforward process using the conversion formula. However, understanding the historical context, practical applications, and the importance of accurate conversions in various fields adds depth and relevance to this simple calculation. As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the ability to work seamlessly with different units and scales will continue to be a valuable skill in both professional and personal contexts.