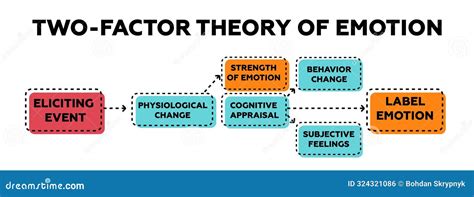
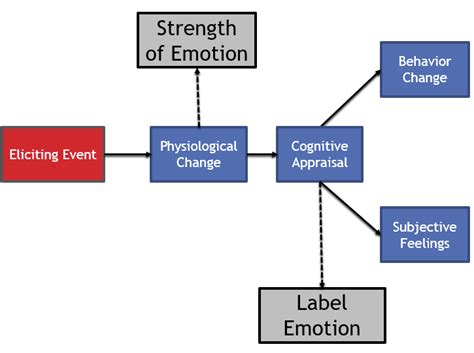
The 2 Factor Theory of Emotion, also known as the Schachter-Singer theory, is a psychological model that attempts to explain the complex and multifaceted nature of human emotions. Developed by psychologists Stanley Schachter and Jerome Singer in 1962, this theory posits that emotions result from a combination of two factors: physiological arousal and cognitive appraisal. In essence, the theory suggests that emotions are not solely the product of internal physiological states or external stimuli, but rather the result of an interaction between the two.
Understanding the 2 Factors

The first factor, physiological arousal, refers to the body’s physical response to a stimulus, such as increased heart rate, blood pressure, or respiration. This arousal can be caused by a variety of factors, including external stimuli, internal states, or even random fluctuations in physiological activity. The second factor, cognitive appraisal, refers to the process by which an individual interprets and evaluates the meaning of the arousal. This appraisal is influenced by various factors, including past experiences, cultural norms, and personal beliefs.
Cognitive Appraisal and Emotion
Cognitive appraisal plays a crucial role in determining the type of emotion experienced. For example, if an individual is aroused and interprets the arousal as a result of a threatening stimulus, they are likely to experience fear or anxiety. On the other hand, if the same arousal is attributed to a positive stimulus, such as a pleasant surprise, the individual may experience joy or excitement. This highlights the importance of cognitive appraisal in shaping emotional experiences.
| Emotion | Physiological Arousal | Cognitive Appraisal |
|---|---|---|
| Fear | Increased heart rate, blood pressure | Interpretation of arousal as threat |
| Joy | Increased heart rate, smiling | Interpretation of arousal as positive stimulus |
| Anxiety | Increased respiration, sweating | Interpretation of arousal as uncertainty or doubt |

Key Points
- The 2 Factor Theory of Emotion proposes that emotions result from a combination of physiological arousal and cognitive appraisal.
- Physiological arousal refers to the body's physical response to a stimulus, while cognitive appraisal refers to the interpretation and evaluation of the arousal.
- Cognitive appraisal plays a crucial role in determining the type of emotion experienced, as it influences how the individual interprets the meaning of the arousal.
- The theory highlights the importance of considering both biological and psychological factors when understanding human emotions.
- The 2 Factor Theory of Emotion has implications for various fields, including psychology, neuroscience, and education.
Implications and Applications
The 2 Factor Theory of Emotion has significant implications for various fields, including psychology, neuroscience, and education. For example, understanding the role of cognitive appraisal in shaping emotional experiences can inform the development of interventions aimed at managing anxiety or promoting emotional well-being. Additionally, the theory highlights the importance of considering both biological and psychological factors when understanding human emotions, which can inform the development of more effective treatments for emotional disorders.
Criticisms and Limitations
While the 2 Factor Theory of Emotion provides a useful framework for understanding human emotions, it is not without its limitations. One criticism is that the theory oversimplifies the complex and multifaceted nature of human emotions, which can involve multiple factors and processes. Additionally, the theory has been criticized for its lack of empirical support, as some studies have failed to replicate the findings of Schachter and Singer’s original study.
What is the main difference between the 2 Factor Theory of Emotion and other theories of emotion?
+The main difference between the 2 Factor Theory of Emotion and other theories of emotion is its emphasis on the interaction between physiological arousal and cognitive appraisal in shaping emotional experiences. This distinguishes it from other theories, such as the James-Lange theory, which posits that emotions result solely from physiological responses.
How does the 2 Factor Theory of Emotion explain the experience of emotions in everyday life?
+The 2 Factor Theory of Emotion explains the experience of emotions in everyday life by highlighting the role of cognitive appraisal in shaping emotional experiences. According to the theory, emotions result from the interaction between physiological arousal and cognitive appraisal, which influences how individuals interpret and evaluate the meaning of the arousal. This can help explain why different people may experience different emotions in response to the same stimulus, as their cognitive appraisals may differ.
What are the implications of the 2 Factor Theory of Emotion for the treatment of emotional disorders?
+The 2 Factor Theory of Emotion has significant implications for the treatment of emotional disorders, as it highlights the importance of considering both biological and psychological factors when understanding human emotions. This can inform the development of more effective treatments, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, which targets cognitive appraisals and helps individuals manage their emotional responses to different stimuli.
Meta Description: “Discover the 2 Factor Theory of Emotion, a psychological model that explains how emotions result from a combination of physiological arousal and cognitive appraisal. Learn about the implications and applications of this theory in understanding human emotions.” (149 characters)