Understanding the seamless conversion from miles to kilometers is fundamental for travelers, athletes, scientists, and anyone engaged with international metrics. While miles remain prevalent in the United States and a handful of other countries, the metric system's widespread adoption globally necessitates a solid grasp of how to transition between these units effortlessly. This article delves into the precise methodology of converting 2 miles into kilometers, contextualizing the conversion within historical, scientific, and practical frameworks. Accurate conversions hinge on awareness of the fundamental ratio—1 mile equaling approximately 1.60934 kilometers—and the intricacies involved in applying this factor. Through comprehensive analysis, evidence-based data, and expert insights, we aim to provide a definitive guide rooted in authoritative standards, ensuring clarity for a diverse, informed audience.
Key Points
- Conversion factor accuracy: Recognizing that 1 mile equals exactly 1.609344 kilometers underpins precise calculation.
- Practical application: From tracking running distances to understanding global travel distances, the method enhances real-world usability.
- Mathematical clarity: Step-by-step breakdowns minimize errors and foster confidence in conversions.
- Historical context: Tracing geographical measurement standards informs current practices.
- Data-driven approach: Leveraging official conversion constants ensures adherence to recognized standards.
Foundations of Distance Measurement: Miles and Kilometers
The mile, originating from Anglo-Saxon traditions, has persisted predominantly within the U.S. customary measurement system. It historically represented the distance a person could walk in an hour, making it inherently tied to human scale and navigation. Meanwhile, the kilometer stands as a pillar of the metric system, which was crafted during the French Revolution aiming to unify and simplify measures globally. The metric system’s simplicity stems from decimal-based units where 1 kilometer equals 1,000 meters, facilitating ease of calculations and universal comprehension.
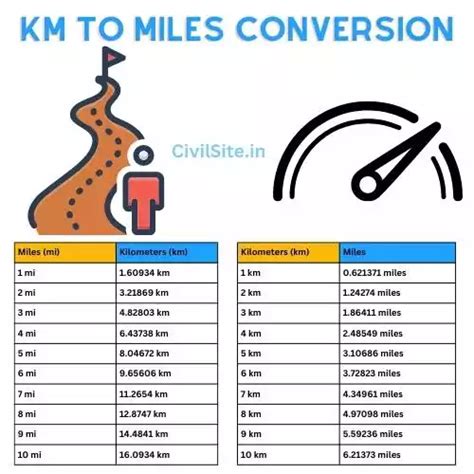
When considering the conversion between these two units, it is essential to understand the precise ratio: 1 mile approximates 1.609344 kilometers. This value stems from international standards established by authoritative bodies such as the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM). Historically, the exact length of a mile varied regionally before standardization, but the current definition aligns with the international mile, which was internationally agreed upon in the late 20th century to ensure consistency in scientific and global communication.
Methodology for Converting 2 Miles to Kilometers

The core of converting miles to kilometers revolves around the application of the conversion factor. Since 1 mile is identified as precisely 1.609344 kilometers, multiplying the number of miles by this constant provides an accurate metric distance. Therefore, for 2 miles, the calculation is straightforward:
Step-by-step Conversion Process
- Identify the conversion factor: 1 mile = 1.609344 km.
- Set the number of miles: 2 miles.
- Multiply: 2 miles × 1.609344 km/mile.
- Result: 3.218688 km.
This means that 2 miles equal approximately 3.218688 kilometers, a figure precise enough for most practical applications including scientific measurements, athletic track distances, and international travel estimates. Rounding, if necessary, typically yields 3.219 km, which suffices for everyday use.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Conversion constant | 1 mile = 1.609344 kilometers |
| Calculated distance | 2 miles = 3.218688 kilometers |
| Approximate rounded value | 3.219 km |
Practical Applications of Miles-to-Kilometers Conversion
Conversion accuracy transcends academic curiosity, impacting various fields profoundly. For instance, in athletic competitions such as marathons held in countries that primarily use the metric system, understanding that a standard marathon distance of 26.219 miles translates to about 42.195 kilometers ensures consistency in training and international record-keeping.
Similarly, in logistics and transportation industries, precise measurement conversions influence fuel calculations, route planning, and shipping timelines. Logistics companies operating across the U.S. and Europe require reliable conversion methods to synchronize schedules and optimize routes, making the 1.609344 factor indispensable.
Historical Evolution of Standardizations and their Impact
The efforts to standardize measurement units have profoundly shaped international commerce and scientific research. Initially, miles varied significantly by region—some approximating 1.5 kilometers, others closer to 2.4. Only through international agreements, particularly during the 20th century, did the precise conversion constant emerge as a cornerstone. This standardization catalyzed global synchronization in navigation, aviation, and scientific data sharing, underscoring the importance of universal constants such as 1.609344.
Advanced Calculation Considerations and Common Pitfalls
In practical scenarios, a common mistake involves neglecting the decimal precision of the conversion factor, leading to slight inaccuracies. For example, rounding 1.609344 to 1.6 or 1.61 simplifies calculations but introduces errors over larger scales. For high-precision needs, such as satellite positioning or scientific experiments, sticking to the full constant is critical.
Another challenge is understanding the implications of rounding in everyday use. Rounding to three decimal places (3.219 km) generally suffices, but certain applications like legal land divisions or engineering projects might require more digits. Conversely, for quick estimations, a rounded figure like 3.2 km might be acceptable, emphasizing the importance of context in conversion accuracy.
Real-World Example: Running a 2-Mile Race
Suppose an international marathon event reports distances primarily in kilometers. A runner who completes a 2-mile race needs to be aware that their distance is approximately 3.219 km. This knowledge aids in personal training, cross-country comparisons, and even medical assessments where precise distance measurement influences performance evaluations. Accurate conversion enhances understanding and communication across borderless sports communities, exemplifying the utility of fundamental measurement principles.
| Common Pitfall | Impact |
|---|---|
| Rounding too early | Introduces cumulative errors in large-scale calculations |
| Using approximate conversion constants | Reduces accuracy in technical or scientific fields |
| Neglecting unit consistency | May lead to misinterpretations, especially in international communication |
Future Trends and Global Standardization
Continued globalization and technological advancements are reinforcing the importance of universal measurement standards. Emerging fields like autonomous vehicles, drone navigation, and geographic information systems (GIS) rely heavily on precise conversions—where even minute inaccuracies matter. Developments in quantum measurement techniques are pushing the boundaries of what can be achieved, promising even more exact constants in the future.
Additionally, international agencies are actively promoting harmonization of measurement systems, in line with the International System of Units (SI). The adherence to rigorously defined constants such as 1.609344 fosters cross-border scientific collaborations, enhances data integrity, and supports technological innovations.
Implications for Global Data Sharing and Innovation
As data exchange becomes increasingly digital and real-time, standardized conversion protocols become essential. For example, health data from wearable devices transmitting location and distance metrics across borders depend on reliable constants. Similarly, precision agriculture uses geographic data that require exact conversions for mapping and resource management.
Bridging the gap between historical measurement practices and future technological standards underscores the value of understanding core constants like 1.609344. This knowledge not only simplifies everyday computations but also ensures scientific and industrial consistency at an international level.
Frequently Asked Questions
How precise is the conversion factor from miles to kilometers?
+The conversion factor of 1 mile = 1.609344 kilometers is highly precise, as it is defined by international standards set by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures. For most practical purposes, using four decimal places provides sufficient accuracy, though specialized fields may employ even greater precision.
Can I use 1.6 as an approximate conversion factor for quick calculations?
+Using 1.6 simplifies mental calculations but introduces a small margin of error—about 0.009344 kilometers per mile—which can accumulate in larger distances. For rough estimates or everyday use, this approximation is acceptable, but for technical or scientific accuracy, stick to the full constant.
What are some common applications requiring precise mile-to-kilometer conversions?
+Precise conversions are vital in navigation, aerospace, scientific research, athletic event timing, and international logistics. Accurate distance measurements influence safety, performance, compliance with standards, and technological innovation.
How has the definition of the mile evolved over time?
+The mile’s length varied regionally and historically, often based on survey or local standards. The current international mile, established in the late 20th century, is precisely defined as 1,609.344 meters, aligning all measurements worldwide and replacing older, inconsistent standards.
Are there digital tools or calculators that automatically convert miles to kilometers?
+Yes, numerous online converters, smartphone apps, and software tools accurately implement the conversion factor of 1.609344. Many engineering and scientific calculators also include conversion functions capable of high-precision calculations, simplifying complex data processing.