Converting volumes between different units is a common task in cooking, chemistry, and various other fields. One such conversion is from milliliters (mL) to cups. Understanding the relationship between these units is crucial for accurate measurements. Here, we will explore how to convert 200 milliliters to cups, considering the variations in cup sizes as they differ between the United States and the rest of the world.
Understanding Milliliters and Cups
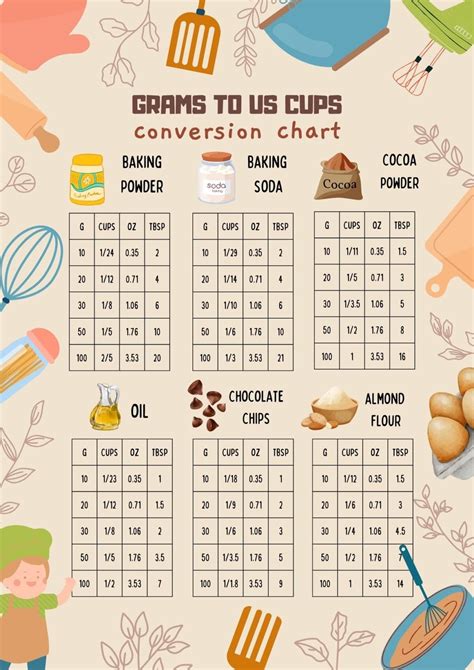
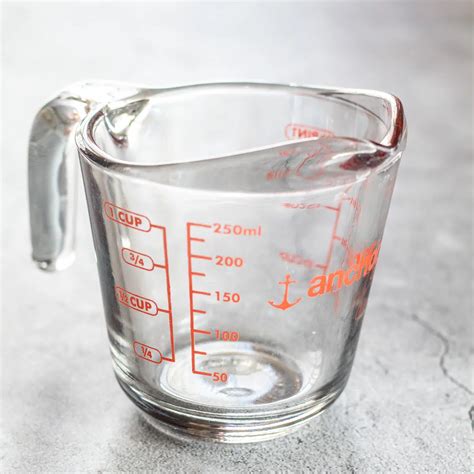
Milliliters are a metric unit of volume, where 1 liter equals 1,000 milliliters. Cups, on the other hand, are a unit of volume in the US customary and imperial systems of measurement. The size of a cup can vary; for instance, a US cup is approximately 236.6 milliliters, whereas a metric cup (used in most of the world) is 250 milliliters.
Conversion Factors
To convert milliliters to cups, we need to know the conversion factors. For a US cup, the conversion factor is about 236.6 mL per cup. For a metric cup, it is exactly 250 mL per cup. These conversion factors are essential for calculating volumes in different units.
| Measurement System | Conversion Factor (mL/cup) |
|---|---|
| US Customary | 236.6 |
| Metric | 250 |

Converting 200 Milliliters to Cups
To convert 200 milliliters into cups, we divide 200 by the conversion factor for the type of cup we are using.
Conversion to US Cups
For US cups: 200 mL / 236.6 mL/cup ≈ 0.846 cups.
Conversion to Metric Cups
For metric cups: 200 mL / 250 mL/cup = 0.8 cups.
Key Points
- 200 milliliters is approximately 0.846 US cups.
- 200 milliliters is exactly 0.8 metric cups.
- The conversion factor depends on the type of cup used (US or metric).
- Accuracy in measurement is crucial, especially in cooking and scientific applications.
- Understanding the differences between US and metric cups is vital for correct conversions.
These conversions highlight the importance of specifying the type of cup when converting volumes. Whether you're following a recipe or measuring chemicals, using the correct conversion factor ensures that your measurements are accurate and reliable.
Practical Applications
In practical terms, converting 200 milliliters to cups can be useful in a variety of situations. For example, if a recipe calls for 200 milliliters of liquid but you only have a measuring cup, knowing the equivalent in cups can be very helpful. Similarly, in scientific experiments, precise measurements are critical, and converting between units accurately can make a significant difference in the outcomes.
Technical Specifications
For technical applications, it’s also important to consider the precision of your measurements. Rounding errors can occur, especially when dealing with small volumes. Therefore, it’s essential to maintain consistency in the units used throughout a calculation or recipe to avoid potential errors.
What is the difference between a US cup and a metric cup?
+A US cup is approximately 236.6 milliliters, while a metric cup is exactly 250 milliliters. This difference is crucial for accurate conversions.
Why is it important to specify the type of cup when converting volumes?
+Specifying the type of cup (US or metric) is important because it directly affects the conversion factor used, which in turn affects the accuracy of the conversion.
How can I ensure accuracy when converting between milliliters and cups?
+To ensure accuracy, always use the correct conversion factor based on the type of cup you are using, and maintain consistency in the units throughout your calculations or recipes.
In conclusion, converting 200 milliliters to cups involves understanding the conversion factors for both US and metric cups. By applying these factors correctly, you can ensure accurate measurements for cooking, scientific experiments, or any other application where volume conversions are necessary. Remember, precision and consistency are key to achieving reliable results.



