The conversion of temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit is a fundamental concept in physics and chemistry, and is widely used in various fields such as meteorology, engineering, and everyday applications. In this article, we will explore the 20 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit conversion, and provide a comprehensive overview of the temperature conversion process.
Understanding the Celsius and Fahrenheit Scales
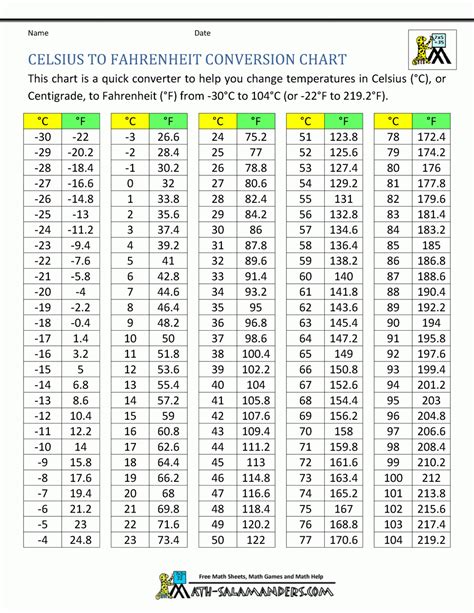
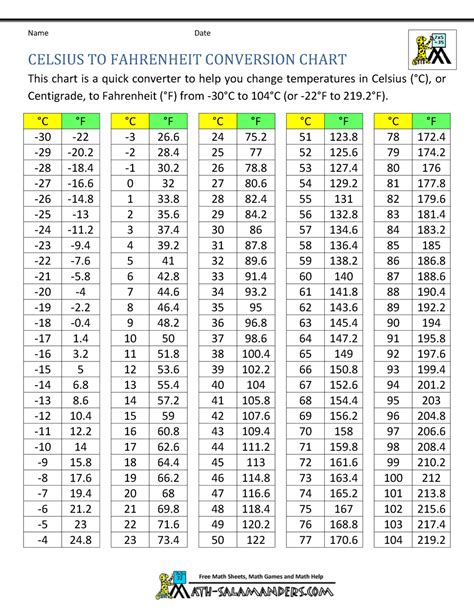
The Celsius scale, also known as the centigrade scale, is a temperature scale that is based on the freezing and boiling points of water. In this scale, the freezing point of water is defined as 0 degrees Celsius, and the boiling point is defined as 100 degrees Celsius. The Fahrenheit scale, on the other hand, is a temperature scale that is based on the freezing and boiling points of water, but with a different reference point. In the Fahrenheit scale, the freezing point of water is defined as 32 degrees Fahrenheit, and the boiling point is defined as 212 degrees Fahrenheit.
Conversion Formula and Process
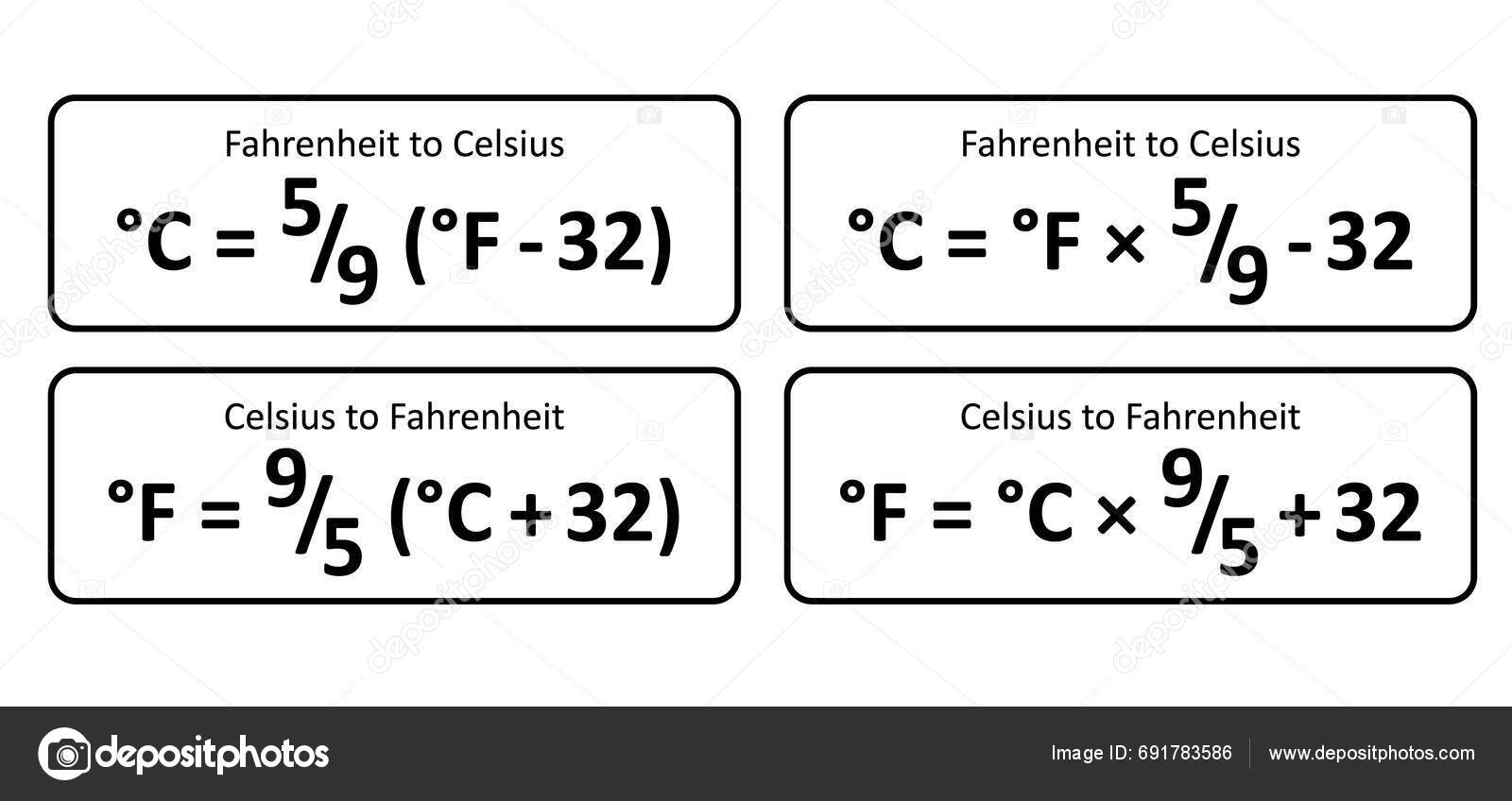
To convert 20 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit, we use the following formula: °F = (°C × 9⁄5) + 32. This formula can be applied to any temperature in Celsius to obtain the equivalent temperature in Fahrenheit. For example, to convert 20 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit, we multiply 20 by 9⁄5, which gives us 36, and then add 32 to get the final result.
| Temperature in Celsius | Temperature in Fahrenheit |
|---|---|
| 20°C | 68°F |
Key Points
Key Points
- The Celsius scale is based on the freezing and boiling points of water, with 0°C and 100°C respectively.
- The Fahrenheit scale is also based on the freezing and boiling points of water, but with 32°F and 212°F respectively.
- The conversion formula from Celsius to Fahrenheit is °F = (°C × 9⁄5) + 32.
- To convert 20°C to Fahrenheit, we use the formula to get 68°F.
- The conversion process can be reversed by subtracting 32 from the Fahrenheit temperature and then multiplying by 5⁄9.
Practical Applications and Examples
The conversion of temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit has numerous practical applications in various fields. For example, in meteorology, temperature forecasts are often reported in both Celsius and Fahrenheit to cater to different audiences. In engineering, temperature conversion is crucial in designing and operating systems that involve heat transfer, such as refrigeration and air conditioning systems.
In everyday applications, temperature conversion is useful when traveling to countries that use different temperature scales. For instance, if you're traveling from the United States to Europe, you may need to convert the temperature from Fahrenheit to Celsius to understand the local weather forecast.
Technical Specifications and Accuracy
The accuracy of temperature conversion depends on the precision of the measurement and the conversion formula used. In general, the conversion formula °F = (°C × 9⁄5) + 32 is accurate to within 0.1°C or 0.2°F. However, in some applications, such as in scientific research or industrial processes, higher accuracy may be required, and more complex conversion formulas or calibration procedures may be necessary.
What is the difference between Celsius and Fahrenheit scales?
+The Celsius scale is based on the freezing and boiling points of water, with 0°C and 100°C respectively, while the Fahrenheit scale is based on the freezing and boiling points of water, with 32°F and 212°F respectively.
How do I convert 20°C to Fahrenheit?
+To convert 20°C to Fahrenheit, use the formula °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32, which gives 68°F.
What are some practical applications of temperature conversion?
+Temperature conversion has numerous practical applications in fields such as meteorology, engineering, and everyday applications, such as traveling to countries that use different temperature scales.
In conclusion, the conversion of temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit is a fundamental concept that has numerous practical applications in various fields. By understanding the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales, and using the conversion formula °F = (°C × 9⁄5) + 32, we can easily convert temperatures between the two scales. Whether you’re a scientist, engineer, or simply a curious individual, mastering temperature conversion is an essential skill that can help you navigate the complexities of the physical world.



