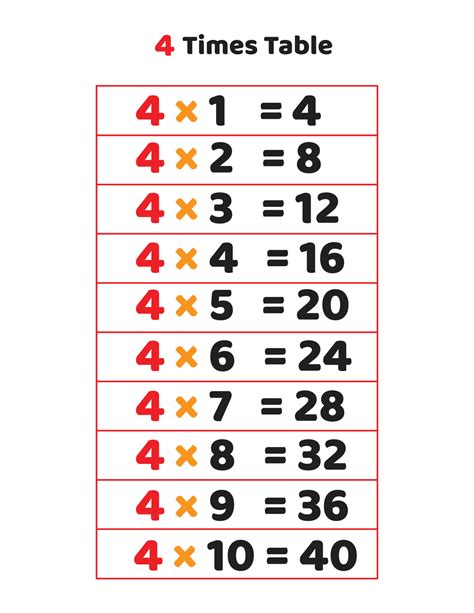
Calculating 4 times 8 is a basic arithmetic operation that can be performed in several ways. Understanding multiple methods for multiplication not only reinforces mathematical concepts but also helps in developing problem-solving skills. Here are four ways to calculate 4 times 8, each utilizing a different approach or tool.
Method 1: Traditional Multiplication
The traditional method of multiplication involves memorizing or using multiplication tables. For 4 times 8, you simply recall or look up the product. This method is quick and efficient for those familiar with multiplication tables.
Calculation: 4 × 8 = 32
This method relies on prior knowledge or quick reference, making it one of the fastest ways to perform simple multiplication tasks.
Variation: Using Arrays
An array can be used to visualize the multiplication process. Imagine having 4 rows of 8 items each. Counting all the items gives you the product of 4 and 8.
Array Visualization:
Row 1: ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● (8 items)
Row 2: ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● (8 items)
Row 3: ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● (8 items)
Row 4: ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● (8 items)
Total Items: 32
This visualization technique can help in understanding the concept behind multiplication.
Method 2: Repeated Addition
Another way to calculate 4 times 8 is by using repeated addition. This involves adding 8 together 4 times.
Calculation: 8 + 8 + 8 + 8 = 32
This method is helpful for those who are still learning multiplication tables or prefer a more basic arithmetic approach.
Variation: Using a Number Line
A number line can also be used to visualize repeated addition. Starting from 0, you would jump forward 8 units, 4 times, and end up at 32.
Number Line Visualization:
0 → 8 (first jump)
8 → 16 (second jump)
16 → 24 (third jump)
24 → 32 (fourth jump)
Final Position: 32
This method helps in understanding the concept of addition as the foundation of multiplication.
Method 3: Using Algebraic Expression
For those familiar with algebra, 4 times 8 can be represented as 4x, where x = 8. Solving for 4x gives the product.
Expression: 4x, where x = 8
Solution: 4x = 4 × 8 = 32
This approach introduces a more abstract way of thinking about multiplication, relating it to variable expressions.
Variation: Applying Distributive Property
The distributive property of multiplication over addition can also be applied. For example, breaking down 8 into 5 + 3, then multiplying.
Calculation: 4 × (5 + 3) = 4 × 5 + 4 × 3 = 20 + 12 = 32
This method shows how multiplication can be distributed and still yield the correct product.
Method 4: Calculator or Computational Tool
In today’s digital age, calculators and computational tools (like computers or smartphones) can instantly calculate 4 times 8.
Calculation: Input 4 × 8 into a calculator or computational tool.
Result: 32
This method is the quickest and most accurate for those with access to such tools, especially for more complex calculations.
Key Points
- Traditional multiplication relies on memorized tables or quick reference.
- Repeated addition involves summing a number a specified number of times.
- Algebraic expressions can represent multiplication problems.
- Calculators and computational tools provide instant calculation capabilities.
- Understanding multiple methods enhances problem-solving flexibility and reinforces mathematical concepts.
| Method | Description | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Multiplication | Using memorized tables | 32 |
| Repeated Addition | Adding 8 four times | 32 |
| Algebraic Expression | Solving 4x where x = 8 | 32 |
| Calculator/Computational Tool | Inputting 4 × 8 | 32 |
What is the most efficient way to calculate 4 times 8?
+The most efficient way typically involves using memorized multiplication tables or a calculator, as both methods yield immediate results.
How does repeated addition relate to multiplication?
+Repeated addition is the foundational concept behind multiplication. Multiplying two numbers is equivalent to adding one of the numbers a certain number of times, as specified by the other number.
Can algebra be used for simple multiplication problems?
+Yes, algebra can be applied to simple multiplication problems by representing one of the factors as a variable and solving for the product.