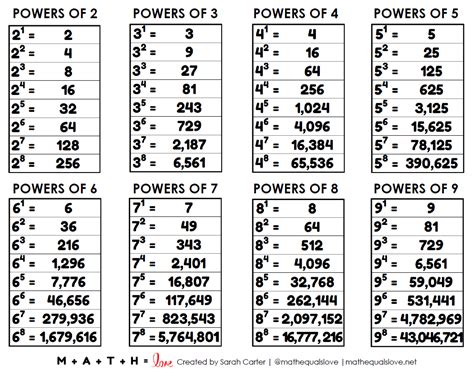
The concept of exponentiation is a fundamental aspect of mathematics, and understanding the power of 2 is crucial in various fields, including computer science, physics, and engineering. In this article, we will delve into the world of exponentiation, focusing on 4 to the power of 2, and explore its significance, applications, and mathematical representations.
Understanding Exponentiation
Exponentiation is a mathematical operation that involves raising a number, known as the base, to a certain power, known as the exponent. In the case of 4 to the power of 2, the base is 4, and the exponent is 2. This operation is denoted as 4^2, and it represents the result of multiplying 4 by itself 2 times. In mathematical terms, 4^2 = 4 × 4 = 16.
Mathematical Representation
The mathematical representation of exponentiation is based on the concept of repeated multiplication. For example, 4^2 can be represented as 4 × 4, 4^3 as 4 × 4 × 4, and so on. This representation is essential in understanding the properties and applications of exponentiation. The formula for exponentiation is a^b = a × a ×… × a (b times), where a is the base and b is the exponent.
| Base | Exponent | Result |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | 2 | 16 |
| 4 | 3 | 64 |
| 4 | 4 | 256 |
Applications of 4 to the Power of 2

The concept of 4 to the power of 2 has numerous applications in various fields. In computer science, exponentiation is used in algorithms, data structures, and cryptography. For example, the RSA algorithm, which is widely used for secure data transmission, relies on the concept of exponentiation. In physics, exponentiation is used to describe the behavior of particles and forces, such as the exponential decay of radioactive materials.
Computer Science Applications
In computer science, 4 to the power of 2 is used in various applications, including data compression, encryption, and digital signatures. The concept of exponentiation is also used in machine learning algorithms, such as neural networks, where it is used to calculate the output of neurons. The use of exponentiation in computer science has led to significant advancements in fields such as artificial intelligence, cryptography, and data analysis.
Key Points
- 4 to the power of 2 represents the result of multiplying 4 by itself 2 times, which equals 16.
- Exponentiation is a fundamental concept in mathematics, with numerous applications in computer science, physics, and engineering.
- The concept of 4 to the power of 2 is crucial in understanding exponential growth and scaling, which is essential in various fields.
- The mathematical representation of exponentiation is based on the concept of repeated multiplication.
- The use of exponentiation in computer science has led to significant advancements in fields such as artificial intelligence, cryptography, and data analysis.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, 4 to the power of 2 is a fundamental concept in mathematics, with numerous applications in various fields. The understanding of exponentiation is crucial in understanding exponential growth and scaling, which is essential in fields such as computer science, physics, and engineering. As technology continues to advance, the importance of exponentiation will only continue to grow, leading to new discoveries and innovations in various fields.
What is the result of 4 to the power of 2?
+The result of 4 to the power of 2 is 16, which represents the result of multiplying 4 by itself 2 times.
What are the applications of 4 to the power of 2 in computer science?
+The applications of 4 to the power of 2 in computer science include data compression, encryption, digital signatures, and machine learning algorithms.
What is the significance of exponentiation in mathematics?
+Exponentiation is a fundamental concept in mathematics, representing the result of repeated multiplication. It is essential in understanding exponential growth and scaling, which is crucial in various fields, including computer science, physics, and engineering.