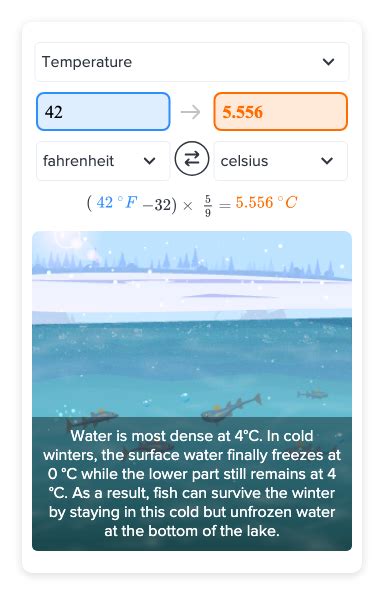
Converting 42 degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius is a common temperature conversion task. Understanding the relationship between Fahrenheit and Celsius scales is essential for various applications, including science, engineering, and everyday weather forecasting. The Fahrenheit scale, developed by Gabriel Fahrenheit, and the Celsius scale, introduced by Anders Celsius, are two different ways to measure temperature, with the Celsius scale being more widely used in scientific and international contexts.
Introduction to Temperature Conversion

Temperature conversion between Fahrenheit and Celsius can be achieved through a simple mathematical formula. The formula to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius is: (C = \frac{5}{9}(F - 32)), where (C) is the temperature in Celsius and (F) is the temperature in Fahrenheit. This formula allows for the direct conversion of temperatures from one scale to the other, facilitating communication and calculation across different systems.
Converting 42°F to Celsius
To convert 42 degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius, we use the conversion formula: (C = \frac{5}{9}(42 - 32)). Calculating this gives: (C = \frac{5}{9}(10) = \frac{50}{9}). Therefore, 42°F is equivalent to approximately 5.56°C when rounded to two decimal places.
| Temperature in Fahrenheit | Temperature in Celsius |
|---|---|
| 42°F | 5.56°C |
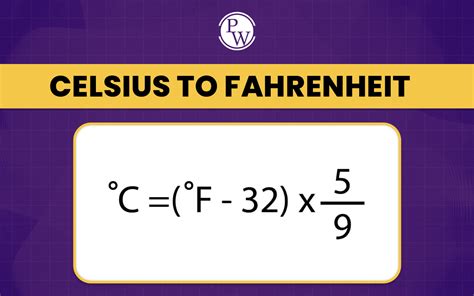
Alternative Conversion Methods
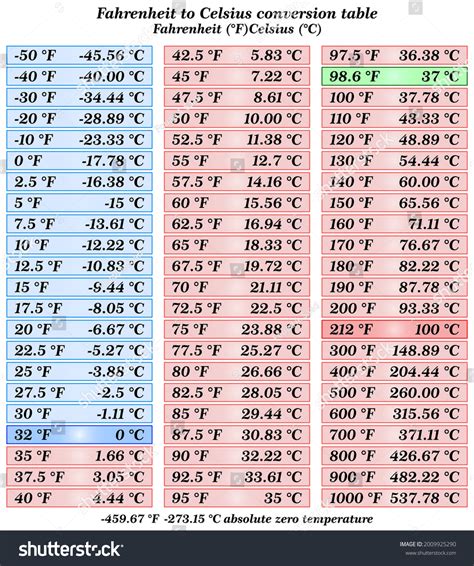
Besides the direct formula, there are other ways to approach temperature conversions, including the use of conversion charts or online calculators. These tools can be particularly useful for quick conversions or when dealing with a range of temperatures. However, understanding the underlying formula provides a deeper grasp of the temperature relationship and allows for conversions to be performed manually when necessary.
Practical Applications of Temperature Conversion
The ability to convert temperatures between Fahrenheit and Celsius is crucial in various fields. For example, in cooking, recipes often specify temperatures in one scale or the other, and being able to convert between them ensures that dishes are prepared correctly. In science and engineering, accurate temperature measurements and conversions are critical for experiments, calculations, and design specifications.
Key Points
- The conversion formula from Fahrenheit to Celsius is C = \frac{5}{9}(F - 32).
- 42°F is equivalent to approximately 5.56°C.
- Temperature conversion is essential in science, engineering, and everyday applications.
- Understanding the conversion formula allows for manual calculations and a deeper understanding of temperature relationships.
- Alternative methods, such as conversion charts and online calculators, can also be used for convenience and speed.
Conclusion and Further Considerations
In conclusion, converting 42 degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius involves a straightforward application of the conversion formula. This process not only yields the equivalent temperature in Celsius but also highlights the importance of understanding temperature scales and their conversions in various contexts. As technology and global communication continue to advance, the ability to convert between different units of measurement, including temperature, remains a vital skill.
Why is it important to know how to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius?
+Knowing how to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius is important because it facilitates communication and calculation across different systems, particularly in scientific, engineering, and international applications.
What is the formula to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius?
+The formula to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius is C = \frac{5}{9}(F - 32), where C is the temperature in Celsius and F is the temperature in Fahrenheit.
How do I convert 42°F to Celsius using the formula?
+To convert 42°F to Celsius, substitute F = 42 into the formula C = \frac{5}{9}(F - 32), which yields C = \frac{5}{9}(42 - 32) = \frac{5}{9}(10) = \frac{50}{9}, or approximately 5.56°C.
Meta Description: Learn how to convert 42 degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius using a simple formula and understand the importance of temperature conversion in various applications.