The concept of exponents is a fundamental aspect of mathematics, and understanding the behavior of numbers when raised to various powers is crucial for a wide range of applications. One particular case that often sparks curiosity is 5 to the power of 0. At first glance, it might seem counterintuitive to consider raising a number to the power of zero, as our initial exposure to exponents usually involves positive integers. However, the rules of exponentiation are well-defined and consistent, even in cases that might seem unusual at first.
To approach this topic, let's start with the basics of exponentiation. When we say "5 to the power of n," we mean 5 multiplied by itself n times. For example, 5 to the power of 2 (5^2) is equal to 5 * 5 = 25. Extending this logic, 5 to the power of 3 (5^3) would be 5 * 5 * 5 = 125. The pattern is clear: as the exponent increases, the result grows rapidly. But what happens when the exponent is 0?
Key Points
- Understanding the concept of exponents and their application in mathematics.
- The definition and calculation of 5 to the power of 0.
- Exploring the mathematical rules and principles that apply to exponentiation, including the zero exponent rule.
- Applying the concept of 5 to the power of 0 in real-world scenarios and mathematical problems.
- Recognizing the importance of consistency in mathematical operations and the role of the zero exponent in maintaining this consistency.
Mathematical Principle Behind 5 to the Power of 0
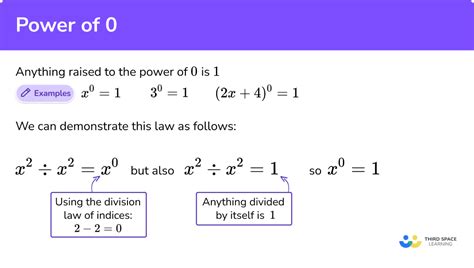
The principle behind any number raised to the power of 0 is rooted in the consistency of mathematical operations. To ensure that the rules of exponentiation hold true across all scenarios, including those involving zero and negative exponents, mathematicians have established that any number raised to the power of 0 equals 1. This principle is often referred to as the “zero exponent rule.” The reasoning behind this rule can be understood by considering the pattern of exponentiation and its inverse operation, division.
Understanding the Zero Exponent Rule
The zero exponent rule states that for any nonzero number x, x^0 = 1. This rule might seem arbitrary at first, but it is essential for maintaining consistency in mathematical operations, particularly when dealing with exponents. For instance, consider the equation x^m / x^n = x^(m-n), where m and n are exponents. If we let m = n, then x^m / x^n simplifies to x^0. According to the rule, x^0 should equal 1, which aligns with the idea that any number divided by itself equals 1.
| Exponent Rule | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Zero Exponent Rule | Any nonzero number raised to the power of 0 equals 1. |
| Product of Powers Rule | a^m * a^n = a^(m+n) |
| Quotient of Powers Rule | a^m / a^n = a^(m-n) |

Applications and Implications
Understanding and applying the concept of 5 to the power of 0 might seem abstract, but it has practical implications in various mathematical and real-world contexts. In algebra, for instance, recognizing that any number raised to the power of 0 equals 1 helps in simplifying expressions and solving equations. In computer science, this principle is fundamental in programming, where it affects how algorithms are designed and executed. Furthermore, in fields like physics and engineering, where mathematical models are crucial for describing and predicting the behavior of systems, the consistency provided by the zero exponent rule is indispensable.
Real-World Applications
In everyday applications, the concept might not be directly referenced as “5 to the power of 0,” but the underlying principle influences how we calculate and model real-world phenomena. For example, in finance, when calculating compound interest, the formula involves raising a number (the interest rate) to a power (the number of years). Understanding the behavior of exponents, including the zero exponent rule, is crucial for accurately predicting future values of investments.
In conclusion, the concept of 5 to the power of 0, and more broadly, any number raised to the power of 0, is a fundamental aspect of mathematics that underscores the consistency and logic of mathematical operations. By understanding and applying this principle, we can better appreciate the intricacies of mathematics and its widespread applications in various fields.
What is the zero exponent rule in mathematics?
+The zero exponent rule states that any nonzero number raised to the power of 0 equals 1. This rule is essential for maintaining consistency in mathematical operations, particularly in the context of exponentiation.
Why is the concept of 5 to the power of 0 important in mathematics?
+The concept of 5 to the power of 0, or any number to the power of 0, being equal to 1 is crucial because it ensures that the rules of exponentiation are consistent and applicable across all scenarios, including those involving zero and negative exponents.
Are there real-world applications of the concept of 5 to the power of 0?
+Yes, the concept has implications in various fields, including finance, where it affects calculations of compound interest, and in computer science, where it influences algorithm design. The principle also underpins mathematical models used in physics and engineering to describe and predict system behaviors.