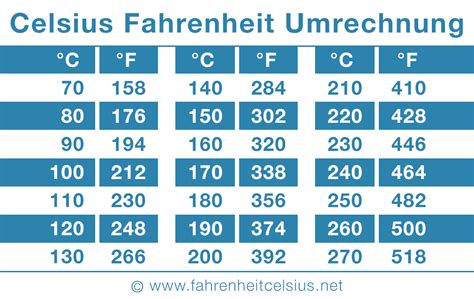
The temperature of 63 degrees Celsius is a significant threshold, often associated with specific physical and chemical transformations. In various domains, this temperature holds unique importance, whether it's in cooking, materials science, or environmental studies. To delve into the multifaceted nature of 63 degrees Celsius, let's explore five distinct ways this temperature manifests its relevance across different fields.
Key Points
- Cooking and Food Safety: Understanding the role of 63 degrees Celsius in ensuring food is cooked to a safe temperature.
- Materials Science: Exploring how 63 degrees Celsius affects the properties and behaviors of various materials.
- Environmental Studies: Analyzing the impact of temperatures around 63 degrees Celsius on ecosystems and climate change.
- Chemical Reactions: Discussing the significance of 63 degrees Celsius in initiating or accelerating specific chemical reactions.
- Biological Processes: Investigating how 63 degrees Celsius influences biological systems, including enzyme activity and microbial growth.
Cooking and Food Safety
In the realm of cooking, achieving a temperature of 63 degrees Celsius is crucial for ensuring that food, especially meat and poultry, is safe to eat. This temperature is significant because it is the minimum internal temperature required to kill harmful bacteria like Salmonella and E. coli. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), heating food to at least 63 degrees Celsius can significantly reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses. This principle is widely applied in commercial kitchens and is recommended for home cooking as well to prevent undercooked food from causing health issues.
Materials Science Perspective
From a materials science perspective, 63 degrees Celsius can have varying effects on different materials. For some plastics, this temperature may be near their glass transition temperature, affecting their flexibility and durability. In the context of electronics, temperatures around 63 degrees Celsius can influence the performance and lifespan of components. For instance, the efficiency of solar panels can decrease as the temperature increases beyond a certain threshold, with 63 degrees Celsius being a point of reference for evaluating thermal performance. Understanding these effects is crucial for designing and manufacturing electronic devices and systems intended for use in diverse environmental conditions.
| Material Type | Effects at 63°C |
|---|---|
| Certain Plastics | Approaching glass transition temperature, affecting flexibility |
| Solar Panels | Potential decrease in efficiency due to increased temperature |
| Electronic Components | Influence on performance and lifespan, depending on component type |
Environmental Studies and Climate Change

In the context of environmental studies, temperatures around 63 degrees Celsius can have profound effects on ecosystems. This temperature can be associated with the optimal growth conditions for certain microbial communities, influencing decomposition rates and nutrient cycling in soils. Furthermore, as global temperatures rise due to climate change, understanding how ecosystems respond to temperatures near 63 degrees Celsius can provide insights into potential future environmental shifts. For example, changes in microbial activity can affect greenhouse gas emissions, creating a feedback loop that exacerbates climate change.
Chemical Reactions and 63 Degrees Celsius
The temperature of 63 degrees Celsius is also significant in the context of chemical reactions. Many chemical processes are temperature-dependent, with 63 degrees Celsius being a critical point for the initiation or acceleration of specific reactions. In industrial processes, controlling temperature is essential for optimizing reaction rates, yields, and product quality. For instance, in the production of certain chemicals, heating the reactants to 63 degrees Celsius can be necessary to achieve the desired reaction kinetics without promoting unwanted side reactions.
Biological Processes and Temperature Sensitivity
In biological systems, enzymes and microbial growth are highly sensitive to temperature, with 63 degrees Celsius being a threshold that can significantly impact these processes. Enzymes, which are biological catalysts, have optimal temperature ranges within which they are most active. Temperatures above or below this optimum can reduce enzyme activity or even denature the enzyme, stopping the reaction. Similarly, microbial growth rates can be influenced by temperature, with 63 degrees Celsius potentially being near the optimal growth temperature for certain microorganisms or far beyond the tolerance of others.
What is the significance of 63 degrees Celsius in cooking?
+63 degrees Celsius is the minimum internal temperature required to ensure that food, especially meat and poultry, is safe to eat, as it can kill harmful bacteria like Salmonella and E. coli.
How does 63 degrees Celsius affect materials in electronics?
+Temperatures around 63 degrees Celsius can influence the performance and lifespan of electronic components, potentially decreasing the efficiency of devices like solar panels and affecting the durability of certain materials.
What role does 63 degrees Celsius play in environmental studies?
+63 degrees Celsius can be associated with optimal growth conditions for certain microbial communities, influencing ecosystem processes like decomposition and nutrient cycling, and can provide insights into potential future environmental shifts due to climate change.
In conclusion, the temperature of 63 degrees Celsius holds a multifaceted significance across various domains, from ensuring food safety and influencing material properties to impacting environmental processes and chemical reactions. Understanding the implications of this temperature is essential for advancing knowledge and practices in these fields, contributing to safer, more efficient, and more sustainable outcomes.