The conversion of temperature from one scale to another is a fundamental concept in physics and chemistry, and it has numerous practical applications in our daily lives. One such conversion is from Fahrenheit to Celsius, where 67 degrees Fahrenheit is equivalent to a specific temperature in Celsius. To understand this conversion, it is essential to delve into the basics of temperature measurement and the differences between the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales.
Key Points
- The Fahrenheit scale is defined such that the freezing point of water is 32 degrees Fahrenheit and the boiling point is 212 degrees Fahrenheit.
- The Celsius scale, on the other hand, defines the freezing point of water as 0 degrees Celsius and the boiling point as 100 degrees Celsius.
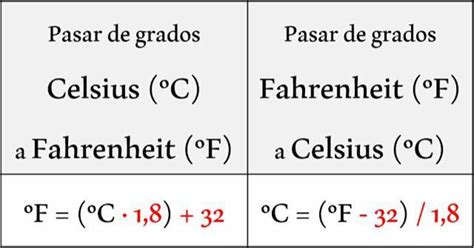
- The conversion from Fahrenheit to Celsius can be achieved using the formula: Celsius = (Fahrenheit - 32) * 5/9.
- For 67 degrees Fahrenheit, applying the conversion formula yields the equivalent temperature in Celsius.
- This conversion is crucial in various scientific, medical, and everyday applications where temperature precision is vital.
Understanding the Fahrenheit and Celsius Scales
The Fahrenheit scale was introduced by Gabriel Fahrenheit in 1724, and it was widely used until the Celsius scale, introduced by Anders Celsius in 1742, became more commonly accepted in the scientific community and beyond. The Celsius scale is also known as the centigrade scale because it divides the temperature range between the freezing and boiling points of water into 100 equal parts.
Conversion Formula and Application
To convert 67 degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius, we apply the conversion formula: Celsius = (Fahrenheit - 32) * 5⁄9. Substituting 67 for Fahrenheit, we get Celsius = (67 - 32) * 5⁄9. Performing the arithmetic, we first subtract 32 from 67, which equals 35, and then multiply by 5⁄9, which gives us 19.44 degrees Celsius. Therefore, 67 degrees Fahrenheit is equivalent to approximately 19.44 degrees Celsius.
| Temperature Scale | Temperature Value |
|---|---|
| Fahrenheit | 67 |
| Celsius | 19.44 |
Practical Applications and Importance

The conversion between Fahrenheit and Celsius has numerous practical applications. In scientific research, precise temperature control and measurement are crucial for the validity and reproducibility of experiments. In medicine, understanding body temperature in both scales can help in diagnosing and treating conditions, as normal body temperature is approximately 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit or 37 degrees Celsius. In everyday life, knowing the equivalent temperatures can help in cooking, where recipes may list temperatures in one scale, and the cook needs to adjust according to their thermometer’s scale.
Challenges and Considerations
One of the challenges in converting temperatures is ensuring accuracy, especially in applications where small differences in temperature can have significant effects. Additionally, the choice of scale can sometimes depend on regional preferences or the context of the application. For instance, in the United States, Fahrenheit is more commonly used in everyday applications, whereas in most other parts of the world, Celsius is the preferred scale.
Why is it important to know how to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius?
+Knowing how to convert between these two scales is important for a variety of reasons, including scientific research, medical applications, cooking, and everyday conversation, especially when interacting with people from different countries where one scale might be more commonly used than the other.
What is the formula to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius?
+The formula to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius is: Celsius = (Fahrenheit - 32) * 5/9. This formula allows for accurate conversion between the two temperature scales.
What is 67 degrees Fahrenheit in Celsius?
+67 degrees Fahrenheit is equivalent to approximately 19.44 degrees Celsius, as calculated using the conversion formula.
In conclusion, understanding and applying temperature conversions, such as from 67 degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius, is a fundamental aspect of working with temperatures in various contexts. The ability to accurately convert between different scales enhances communication, ensures precision in scientific and medical applications, and facilitates everyday tasks that involve temperature measurement.



