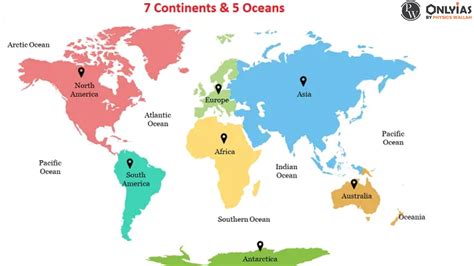
The world is a vast and diverse place, comprising 7 continents and 5 oceans that have been the subject of human fascination and exploration for centuries. Understanding the geography of our planet is essential for grasping the complex relationships between the environment, cultures, and economies that exist within it. In this article, we will delve into the details of each continent and ocean, exploring their unique characteristics, features, and significance in the global context.
Key Points
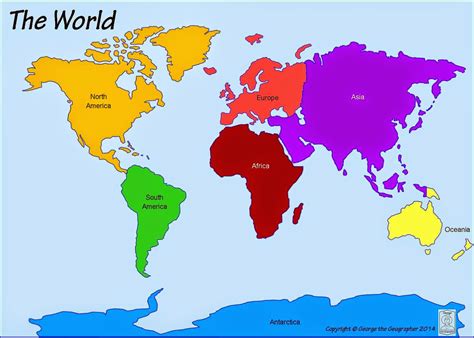
- The 7 continents are Africa, Antarctica, Asia, Australia, Europe, North America, and South America, each with its distinct geographical features and cultural identities.
- The 5 oceans are the Arctic, Atlantic, Indian, Pacific, and Southern Oceans, covering over 70% of the Earth's surface and playing a crucial role in the global ecosystem.
- Continents and oceans are not just geographical entities but also host a wide range of ecosystems, climates, and natural resources that support life on Earth.
- Understanding the geography of the continents and oceans is essential for addressing global challenges such as climate change, conservation, and sustainable development.
- The study of continents and oceans has significant implications for fields such as anthropology, biology, economics, and environmental science, among others.
Introduction to the 7 Continents
The 7 continents are the large, continuous areas of land on Earth, each with its unique set of geographical features, climates, and cultural identities. Africa, the second-largest continent, is home to 55 countries and a diverse range of ecosystems, from deserts to rainforests. Antarctica, the coldest and driest continent, is a frozen desert that supports a unique set of flora and fauna adapted to its extreme conditions. Asia, the largest continent, is a vast and populous region that encompasses a wide range of cultures, languages, and landscapes. Australia, an island continent, is known for its unique wildlife and coral reefs, while Europe, the smallest continent, is a region of rich cultural heritage and historical significance. North America and South America, the two American continents, are characterized by their diverse geography, from mountains to deserts, and their complex cultural identities shaped by indigenous, European, and African influences.
Geographical Features of the Continents
Each continent has its distinct geographical features, including mountains, rivers, deserts, and coastlines, which have shaped the history and development of human societies. The Himalayan mountain range in Asia, for example, is the highest and most rugged mountain range in the world, while the Amazon rainforest in South America is the largest tropical rainforest, supporting an incredible array of biodiversity. The Sahara Desert in Africa is the largest hot desert, covering over 9 million square kilometers, while the Great Barrier Reef in Australia is the largest coral reef system, stretching over 2,300 kilometers. The Grand Canyon in North America is one of the most iconic natural wonders, carved by the Colorado River over millions of years, while the Danube River in Europe is the second-longest river, flowing through 10 countries and supporting a rich cultural heritage.
| Continent | Geographical Feature | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Africa | Sahara Desert | Largest hot desert, covering over 9 million square kilometers |
| Asia | Himalayan mountain range | Highest and most rugged mountain range in the world |
| Australia | Great Barrier Reef | Largest coral reef system, stretching over 2,300 kilometers |
| Europe | Danube River | Second-longest river, flowing through 10 countries |
| North America | Grand Canyon | One of the most iconic natural wonders, carved by the Colorado River |
| South America | Amazon rainforest | Largest tropical rainforest, supporting an incredible array of biodiversity |

Introduction to the 5 Oceans
The 5 oceans, which cover over 70% of the Earth’s surface, are the largest and most influential ecosystems on the planet, playing a crucial role in regulating the climate, providing half of the oxygen we breathe, and serving as a source of food and livelihood for millions of people. The Arctic Ocean, the smallest and coldest ocean, is a frozen sea that supports a unique set of marine life adapted to its extreme conditions. The Atlantic Ocean, the second-largest ocean, is a vital trade route and a significant source of fish and other marine resources. The Indian Ocean, the warmest ocean, is a critical component of the global monsoon system, while the Pacific Ocean, the largest ocean, is a vast and diverse ecosystem that supports an incredible array of marine life, from coral reefs to deep-sea trenches. The Southern Ocean, which surrounds Antarctica, is a cold and nutrient-rich ocean that plays a crucial role in the global ocean circulation and carbon cycle.
Characteristics of the Oceans
Each ocean has its unique characteristics, including temperature, salinity, and marine life, which are shaped by factors such as latitude, depth, and ocean currents. The oceans are also home to a wide range of ecosystems, from coral reefs to deep-sea vents, which support an incredible array of biodiversity. The oceans play a critical role in regulating the climate, with the thermohaline circulation, for example, playing a key role in transporting heat and nutrients across the globe. The oceans are also a significant source of food and livelihood for millions of people, with the global fishing industry, for example, providing a vital source of protein for human consumption.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, the 7 continents and 5 oceans are complex and interconnected systems that support an incredible array of biodiversity and ecosystems. Understanding the geography of the continents and oceans is essential for addressing global challenges such as climate change, conservation, and sustainable development. As we move forward, it is critical that we continue to explore and learn more about the continents and oceans, developing effective strategies for conservation and sustainable management that balance human needs with environmental protection. By working together, we can ensure a healthy and thriving planet for future generations.
What are the 7 continents and 5 oceans, and why are they important?
+The 7 continents are Africa, Antarctica, Asia, Australia, Europe, North America, and South America, while the 5 oceans are the Arctic, Atlantic, Indian, Pacific, and Southern Oceans. They are important because they support an incredible array of biodiversity and ecosystems, regulate the climate, and provide a source of food and livelihood for millions of people.
What are some of the unique features of each continent and ocean?
+Each continent and ocean has its unique features, such as the Himalayan mountain range in Asia, the Amazon rainforest in South America, and the Great Barrier Reef in Australia. The oceans also have unique characteristics, such as temperature, salinity, and marine life, which are shaped by factors such as latitude, depth, and ocean currents.
Why is it important to study the continents and oceans, and what can we learn from them?
+Studying the continents and oceans is important because it can help us understand the complex relationships between the environment, cultures, and economies that exist within them. By learning more about the continents and oceans, we can develop effective strategies for conservation and sustainable management, address global challenges such as climate change, and promote sustainable development.
Meta description: Learn about the 7 continents and 5 oceans, their unique features, and importance in the global ecosystem. Discover the complex relationships between the environment, cultures, and economies that exist within them.