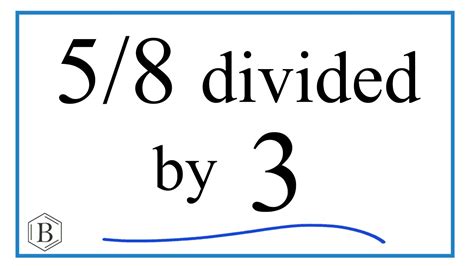
When considering the division of 8 by 6, it's essential to approach the problem with a deep understanding of mathematical operations and their applications. Division, in its simplest form, is the process of sharing a certain quantity into equal parts or groups. In this case, we are looking to divide 8 into groups of 6, but since 8 is less than 6, we will be dealing with fractions or decimals as our primary results. Here are six distinct ways to approach this problem, each yielding the same fundamental result but through different mathematical lenses.
Key Points
- Standard Division: The most straightforward approach to dividing 8 by 6.
- Long Division: A methodical process often used for dividing larger numbers.
- Decimal Division: Converting the divisor to a decimal to simplify the calculation.
- Fractional Representation: Expressing the result as a simplified fraction.
- Algebraic Approach: Using algebraic properties to verify the division result.
- Calculator Method: Utilizing a calculator for a direct computation.
Standard Division
This method involves directly dividing 8 by 6. The result will be a fraction since 8 cannot be evenly divided by 6. Performing the division: 8 ÷ 6 = 1.333…, which can be represented as a repeating decimal or converted into a fraction for precision.
Converting to Fraction
The repeating decimal 1.333… can be expressed as a fraction. This is done by recognizing the pattern: let x = 1.333…, then 10x = 13.333…, subtracting the first equation from the second yields 9x = 12, therefore x = 12⁄9, which simplifies to 4⁄3.
Long Division
Long division is a step-by-step process of dividing numbers. It involves dividing 8 by 6 and finding the quotient and remainder. Since 6 does not go into 8, we consider the division in terms of decimals or fractions from the outset. This method, while thorough, essentially confirms the result obtained through standard division.
Decimal Division
Another approach is to convert 6 into a decimal and then perform the division. However, this essentially simplifies to the standard division method, as the conversion does not alter the fundamental operation of dividing 8 by 6.
Fractional Representation
Expressing 8 divided by 6 as a fraction yields 8⁄6, which simplifies to 4⁄3. This method directly addresses the division problem without converting to decimals, providing a clear and precise result.
Algebraic Approach
From an algebraic standpoint, dividing 8 by 6 can be represented as solving for x in the equation 6x = 8. Solving for x gives x = 8⁄6, which, as previously established, simplifies to 4⁄3. This method verifies the result through algebraic manipulation.
Calculator Method
Using a calculator to divide 8 by 6 provides a quick and direct result. Inputting 8 ÷ 6 into a calculator yields 1.333…, which can then be converted into a fraction for a more precise representation, confirming the results obtained through other methods.
| Method | Result |
|---|---|
| Standard Division | 1.333... or 4/3 |
| Long Division | 1.333... or 4/3 |
| Decimal Division | 1.333... or 4/3 |
| Fractional Representation | 4/3 |
| Algebraic Approach | 4/3 |
| Calculator Method | 1.333... or 4/3 |

What is the primary difference between standard division and long division when dividing 8 by 6?
+The primary difference lies in the approach: standard division directly computes the result, whereas long division involves a step-by-step process. However, for dividing 8 by 6, both methods yield the same result due to the nature of the numbers involved.
How does converting 8 divided by 6 into a fraction provide a precise result?
+Converting 8 divided by 6 into a fraction, specifically 4/3, provides a precise result because it exactly represents the relationship between the dividend and divisor without the approximation inherent in decimal representations.
What advantage does the algebraic approach offer when dividing 8 by 6?
+The algebraic approach offers a method to verify the division result through solving an equation, providing an additional layer of confirmation that the result is correct.
In conclusion, dividing 8 by 6, whether through standard, long, decimal, fractional, algebraic, or calculator methods, yields a consistent result of 4⁄3 or 1.333…. Each method provides a unique perspective on the division process, reinforcing the fundamental principles of arithmetic operations.