To convert 86 degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius, we use the formula: °C = (°F - 32) × 5⁄9.
So, for 86°F: °C = (86 - 32) × 5⁄9 °C = 54 × 5⁄9 °C = 30
Therefore, 86°F is equal to 30°C.
This conversion is a fundamental aspect of understanding temperature scales, with Fahrenheit and Celsius being two of the most commonly used scales worldwide. The Fahrenheit scale is primarily used in the United States, while the Celsius scale is used in most other countries and in scientific applications due to its simplicity and direct relation to the freezing and boiling points of water.
Understanding the Conversion Formula
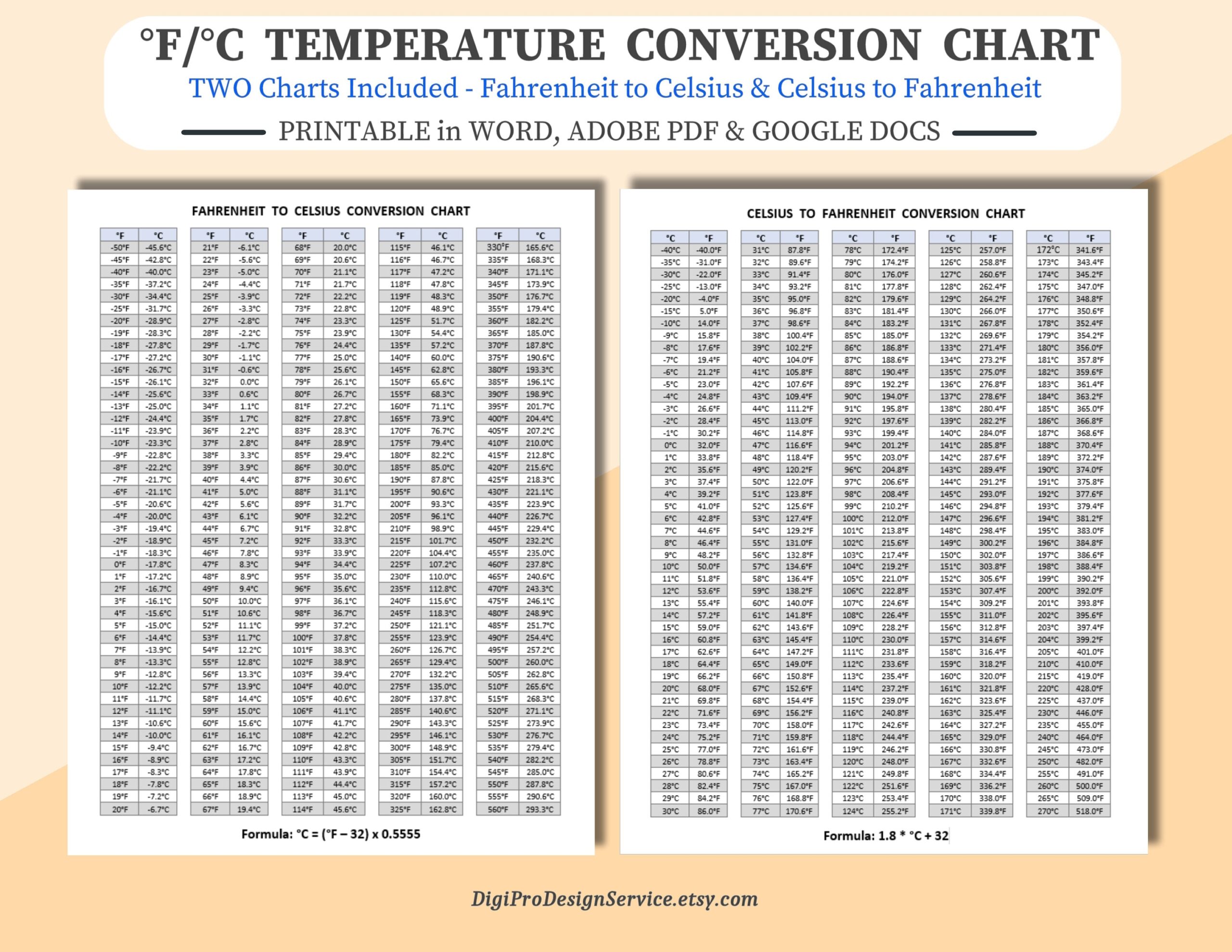
The formula to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius, (°F - 32) × 5⁄9, is derived from the differences in the zero points and the size of the degree units between the two scales. The freezing point of water is 32°F and 0°C, and the boiling point is 212°F and 100°C. This difference in zero points and the scale’s gradations necessitates the subtraction of 32 and then the multiplication by 5⁄9 to adjust for the different unit sizes.
Importance of Temperature Conversion
Temperature conversion is crucial in various fields, including science, engineering, and everyday applications. For scientists, converting between temperature scales is essential for comparing data and ensuring consistency across different experiments and studies. In engineering, precise temperature control and conversion are critical for designing and operating machinery, especially in fields like aerospace and automotive manufacturing.
| Temperature Scale | Freezing Point of Water | Boiling Point of Water |
|---|---|---|
| Fahrenheit | 32°F | 212°F |
| Celsius | 0°C | 100°C |

Key Points
- The conversion from Fahrenheit to Celsius involves subtracting 32 from the Fahrenheit temperature and then multiplying by 5/9.
- 86°F is equivalent to 30°C.
- Understanding temperature conversion is crucial for scientific research, engineering applications, and everyday use.
- The difference in zero points and the size of the degree units between the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales necessitates the specific conversion formula.
- Precise temperature control and conversion are critical in various fields, including aerospace, automotive manufacturing, and scientific experiments.
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the ability to convert between different units of measurement, including temperature scales, becomes more important. This skill is not just about knowing formulas, but also about understanding the practical implications of these conversions in real-world applications.
Why is it important to know how to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius?
+Knowing how to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius is important because it allows for the comparison and consistency of temperature measurements across different countries and applications, facilitating international collaboration and precise data interpretation.
What are the primary differences between the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales?
+The primary differences lie in their zero points and the size of their degree units. The Fahrenheit scale has a larger degree unit and different reference points (freezing point of water at 32°F and boiling point at 212°F) compared to the Celsius scale (freezing point at 0°C and boiling point at 100°C).
How does the conversion formula account for these differences?
+The conversion formula, (°F - 32) × 5⁄9, adjusts for the different zero points by subtracting 32 (the freezing point of water in Fahrenheit) and then scales the result by multiplying by 5⁄9 to account for the difference in degree unit sizes between the two scales.



