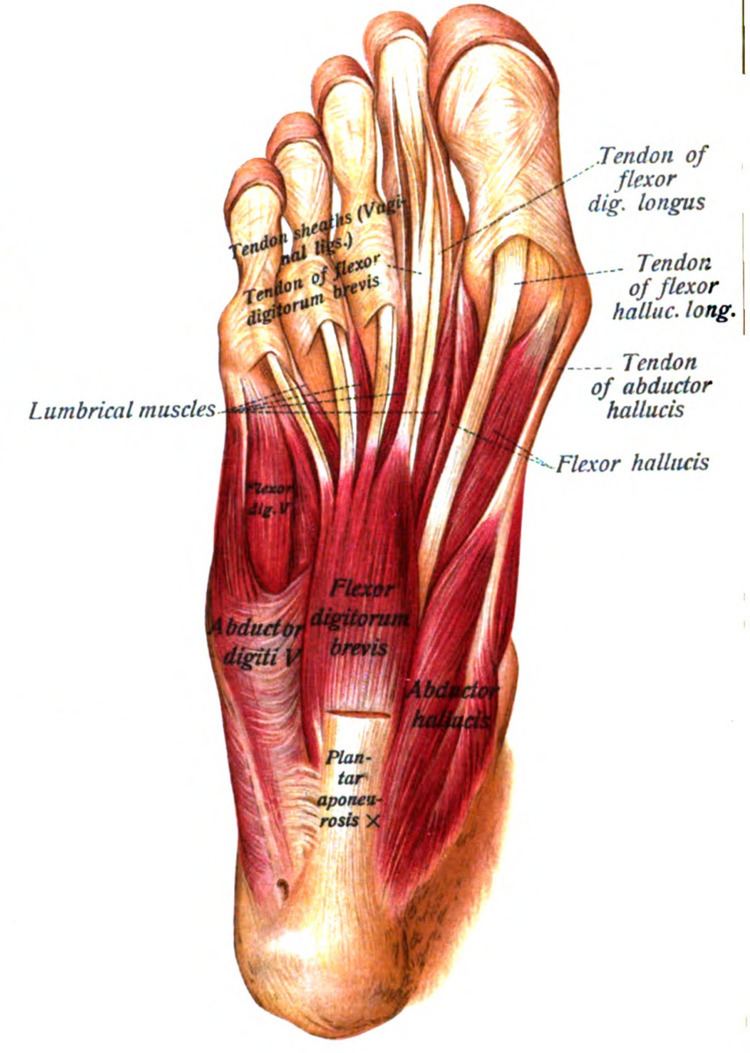
The abductor hallucis muscle, located in the medial aspect of the foot, plays a crucial role in the movement and stability of the first toe, also known as the hallux. This muscle is one of the intrinsic muscles of the foot, meaning it originates and inserts within the foot itself, as opposed to the extrinsic muscles that originate in the lower leg. The abductor hallucis muscle is essential for balance, gait, and the performance of daily activities that require foot movement and stability.
The anatomy of the abductor hallucis muscle is characterized by its fan-shaped structure, with its base originating from the medial process of the calcaneus bone, the medial tubercle of the talus, and the medial aspect of the plantar aponeurosis. The muscle then converges to form a tendon that inserts into the medial aspect of the base of the proximal phalanx of the first toe. This anatomical arrangement allows the muscle to abduct the hallux, moving it away from the midline of the body, and to assist in flexion of the metatarsophalangeal joint.
Key Points
- The abductor hallucis muscle is crucial for the balance and movement of the first toe.
- It originates from the medial process of the calcaneus, the medial tubercle of the talus, and the plantar aponeurosis.
- The muscle inserts into the medial aspect of the base of the proximal phalanx of the first toe.
- Its primary function is to abduct the hallux and assist in its flexion.
- Damage or dysfunction of the abductor hallucis can lead to issues with gait and balance.
Function and Importance
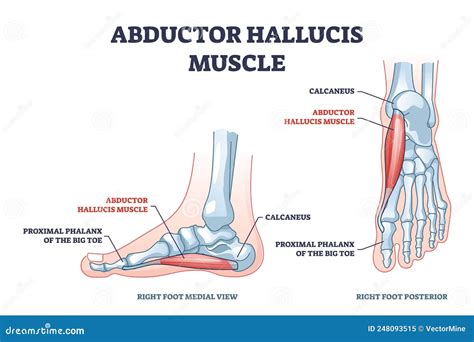
The abductor hallucis muscle works in concert with other intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the foot to facilitate a wide range of movements, including toe spreading, flexion, and extension. Its role in stabilizing the medial arch of the foot during weight-bearing activities is also critical. The muscle’s function is closely tied to the maintenance of proper gait mechanics, and its dysfunction can lead to various pathologies, including hallux valgus (a condition where the big toe angles toward the second toe) and metatarsalgia (pain in the ball of the foot).
Clinical Significance
Clinically, the abductor hallucis muscle is significant due to its involvement in several foot and ankle pathologies. For instance, weakness or paralysis of this muscle can result in a weakened ability to abduct the hallux, potentially leading to gait abnormalities. Moreover, the muscle’s proximity to the medial plantar nerve makes it susceptible to nerve compression, which can cause pain and sensory disturbances in the medial aspect of the foot. Diagnosis of abductor hallucis muscle issues often involves clinical examination, including strength testing and gait analysis, as well as imaging studies such as MRI to assess muscle and tendon integrity.
| Muscle Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Abduction of the Hallux | Movement of the big toe away from the midline of the body. |
| Flexion Assistance | Aids in the flexion of the metatarsophalangeal joint. |
| Medial Arch Support | Contributes to the stabilization of the medial arch during weight-bearing activities. |

Training and Rehabilitation
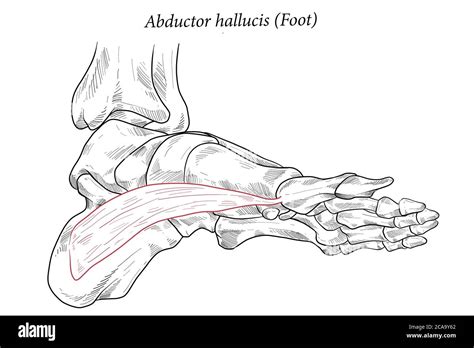
Training and rehabilitation of the abductor hallucis muscle are crucial for individuals suffering from related injuries or conditions. Exercises aimed at strengthening the muscle, such as toe spreads and resisted hallux abduction, can help improve its function. Additionally, physical therapy interventions focusing on foot and ankle mobilization, as well as gait retraining, are beneficial in restoring normal function and reducing the risk of future complications. The use of orthotic devices to support the medial arch and correct biomechanical abnormalities can also be an effective component of a comprehensive treatment plan.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing injuries and conditions affecting the abductor hallucis muscle involves adopting strategies that reduce stress and strain on the foot. Wearing properly fitting shoes that provide adequate support to the arch and toe box can help distribute pressure more evenly. Engaging in regular foot exercises to maintain strength and flexibility, as well as incorporating activities that promote balance and proprioception, can also be beneficial. Furthermore, avoiding repetitive activities that put excessive stress on the foot and taking regular breaks to rest and stretch can help mitigate the risk of overuse injuries.
What is the primary function of the abductor hallucis muscle?
+The primary function of the abductor hallucis muscle is to abduct the hallux, or big toe, and assist in its flexion, playing a crucial role in balance, gait, and foot mechanics.
How does the abductor hallucis muscle contribute to foot stability?
+The abductor hallucis muscle contributes to foot stability by supporting the medial arch of the foot, particularly during weight-bearing activities, and facilitating balanced movement of the toes.
What are common symptoms of abductor hallucis muscle dysfunction?
+Common symptoms of abductor hallucis muscle dysfunction include pain in the medial aspect of the foot, weakness or difficulty in abducting the big toe, and alterations in gait mechanics that can lead to other foot and ankle pathologies.
In conclusion, the abductor hallucis muscle is a vital component of the foot’s intrinsic musculature, playing a significant role in the movement, stability, and overall function of the foot. Understanding its anatomy, function, and clinical significance is essential for the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of related pathologies. Through a combination of strengthening exercises, orthotic support, and preventive strategies, individuals can reduce their risk of abductor hallucis muscle dysfunction and maintain optimal foot health.