Absolute neutrophils, a type of white blood cell, play a crucial role in the immune system by defending against infections. During pregnancy, the body undergoes numerous changes to support the growth of the fetus, and these changes can affect the immune system. A high absolute neutrophil count (ANC) in pregnancy can be a concern, as it may indicate an underlying infection or inflammation. In this article, we will delve into the topic of absolute neutrophils high in pregnancy, exploring the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and management of this condition.
Key Points
- Absolute neutrophil count (ANC) is a measure of the number of neutrophils in the blood, which can be affected during pregnancy.
- A high ANC in pregnancy can be caused by various factors, including infections, inflammation, and physiological changes.
- Symptoms of a high ANC in pregnancy may include fever, chills, and pelvic pain, although some women may be asymptomatic.
- Diagnosis of a high ANC in pregnancy involves a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, such as a complete blood count (CBC).
- Management of a high ANC in pregnancy depends on the underlying cause and may involve antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, or other treatments.
Causes of High Absolute Neutrophils in Pregnancy

There are several causes of a high ANC in pregnancy, including:
- Infections: Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can cause a high ANC in pregnancy. Common infections that may lead to a high ANC include urinary tract infections (UTIs), pneumonia, and skin infections.
- Inflammation: Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, or other autoimmune disorders can cause a high ANC in pregnancy.
- Physiological changes: Pregnancy itself can cause changes in the immune system, leading to a high ANC. This is because the body is preparing for the delivery of the baby and the potential for infection.
- Other conditions: Certain conditions, such as gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, or placental abruption, can also cause a high ANC in pregnancy.
Symptoms of High Absolute Neutrophils in Pregnancy
Symptoms of a high ANC in pregnancy can vary depending on the underlying cause. Some women may experience:
- Fever: A temperature above 100.4°F (38°C) can be a sign of an infection or inflammation.
- Chills: Feeling cold or having chills can be a symptom of an infection or inflammation.
- Pelvic pain: Pain in the pelvic area can be a symptom of an infection or inflammation in the reproductive organs.
- Other symptoms: Depending on the underlying cause, women may experience other symptoms such as fatigue, headache, or difficulty breathing.
| Condition | Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) |
|---|---|
| Bacterial infection | 15,000-20,000 cells/μL |
| Viral infection | 10,000-15,000 cells/μL |
| Inflammation | 12,000-18,000 cells/μL |
| Physiological changes | 8,000-12,000 cells/μL |
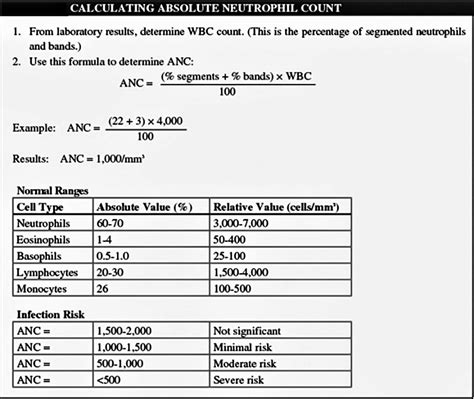
Diagnosis of High Absolute Neutrophils in Pregnancy
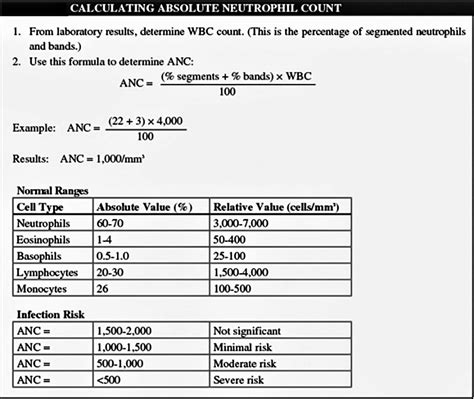
Diagnosis of a high ANC in pregnancy involves a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. A complete blood count (CBC) is typically performed to measure the ANC. Other tests, such as a blood culture or urinalysis, may be ordered to determine the underlying cause of the high ANC.
Management of High Absolute Neutrophils in Pregnancy
Management of a high ANC in pregnancy depends on the underlying cause. If an infection is present, antibiotics may be prescribed. Anti-inflammatory medications may be used to treat conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus. In some cases, hospitalization may be necessary to monitor the woman’s condition and ensure the health and well-being of the fetus.
What is a normal absolute neutrophil count (ANC) in pregnancy?
+A normal ANC in pregnancy is typically between 5,000-10,000 cells/μL. However, this range can vary depending on the individual and the stage of pregnancy.
Can a high ANC in pregnancy affect the fetus?
+A high ANC in pregnancy can potentially affect the fetus, especially if the underlying cause is an infection or inflammation. It is essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to manage the condition and ensure the health and well-being of both the mother and the fetus.
How is a high ANC in pregnancy treated?
+Treatment of a high ANC in pregnancy depends on the underlying cause. Antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, or other treatments may be prescribed to manage the condition. In some cases, hospitalization may be necessary to monitor the woman's condition and ensure the health and well-being of the fetus.
In conclusion, a high ANC in pregnancy can be a concern, as it may indicate an underlying infection or inflammation. It is essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to manage the condition and ensure the health and well-being of both the mother and the fetus. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and management of a high ANC in pregnancy, women can take proactive steps to protect their health and the health of their baby.