Gravity, a fundamental force of nature, plays a crucial role in shaping our universe. From the falling of objects on Earth to the orbital motions of planets and stars, gravity's influence is omnipresent. One of the key aspects of gravity is its ability to accelerate objects, which is a direct consequence of its force. In this article, we will explore 5 ways gravity accelerates objects, highlighting the underlying physics and providing examples to illustrate each concept.
Key Points
- Gravity accelerates objects towards each other, as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation
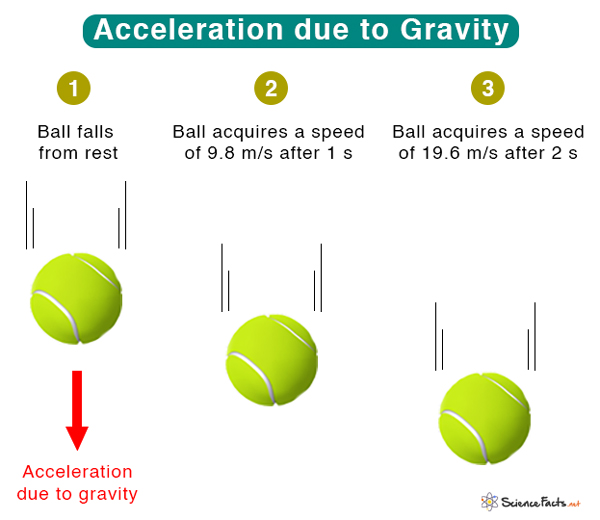
- The force of gravity causes objects to fall towards the ground, with an acceleration of 9.8 meters per second squared on Earth
- Gravity is responsible for the orbital motion of planets, moons, and stars, with acceleration directed towards the center of the orbit
- Tidal acceleration occurs when the gravitational force of one body causes the rotation of another body to slow down
- Gravitational waves are ripples in the fabric of spacetime produced by the acceleration of massive objects, such as black holes or neutron stars
Acceleration Due to Gravity on Earth
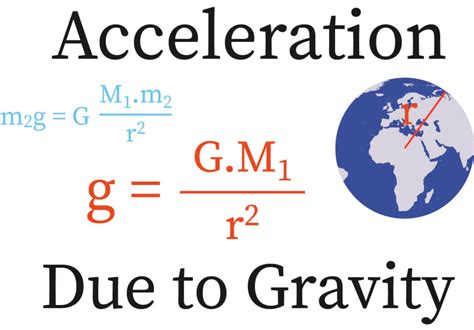
The most familiar example of gravity’s acceleration is the falling of objects towards the ground. On Earth, the acceleration due to gravity is approximately 9.8 meters per second squared (m/s^2). This means that if you drop an object from a certain height, its velocity will increase by 9.8 m/s every second, until it hits the ground. The force of gravity is responsible for this acceleration, and it is directed towards the center of the Earth.
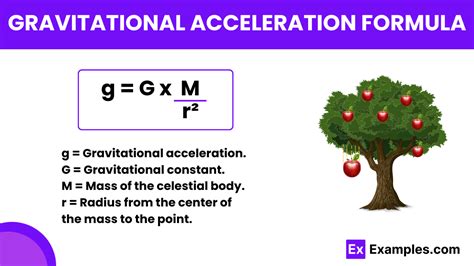
Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation
Newton’s law of universal gravitation states that every point mass attracts every other point mass by a force acting along the line intersecting both points. The force of gravity is proportional to the product of the two masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. This law provides a fundamental framework for understanding gravity’s acceleration, and it has been widely used to describe the motion of objects on Earth and in the universe.
| Object | Mass (kg) | Distance from Earth's Center (m) | Acceleration Due to Gravity (m/s^2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apple | 0.1 | 6.37 x 10^6 | 9.8 |
| Car | 1500 | 6.37 x 10^6 | 9.8 |
| Mountain | 10^12 | 6.37 x 10^6 | 9.8 |
Orbital Motion and Gravity
Gravity is also responsible for the orbital motion of planets, moons, and stars. The force of gravity provides the necessary centripetal force to keep these objects in orbit around each other. The acceleration due to gravity in orbital motion is directed towards the center of the orbit, and its magnitude depends on the mass of the central body and the distance from the orbiting object. For example, the Earth’s orbit around the Sun is an ellipse, with the Sun at one of the foci. The gravitational force of the Sun keeps the Earth in orbit, with an acceleration of approximately 0.006 m/s^2.
Tidal Acceleration
Tidal acceleration occurs when the gravitational force of one body causes the rotation of another body to slow down. This phenomenon is observed in the Earth-Moon system, where the Moon’s gravity causes the Earth’s rotation to slow down. As a result, the length of a day on Earth increases by about 1.78 milliseconds per century. Tidal acceleration is a consequence of the gravitational interaction between two bodies, and it has significant effects on the orbits and rotations of celestial bodies.
What is the difference between acceleration due to gravity and gravitational force?
+Acceleration due to gravity is the rate of change of velocity of an object under the influence of gravity, while gravitational force is the force that causes this acceleration. The gravitational force is proportional to the product of the masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them, while the acceleration due to gravity is independent of the object's mass.
How does gravity affect the motion of objects in the universe?
+Gravity affects the motion of objects in the universe by providing the necessary force to keep them in orbit, causing them to fall towards each other, and shaping the large-scale structure of the universe. Gravity is responsible for the formation of galaxies, stars, and planets, and it plays a crucial role in the evolution of the universe.
What is the relationship between gravity and gravitational waves?
+Gravitational waves are ripples in the fabric of spacetime produced by the acceleration of massive objects, such as black holes or neutron stars. Gravity is the force that causes these objects to accelerate, producing the gravitational waves. The detection of gravitational waves has provided new insights into the universe, allowing us to study cosmic phenomena in ways that were previously impossible.
In conclusion, gravity’s acceleration is a fundamental aspect of the universe, shaping the motion of objects on Earth and in the cosmos. From the falling of objects towards the ground to the orbital motion of planets and stars, gravity’s influence is omnipresent. By understanding the ways in which gravity accelerates objects, we can gain insights into the underlying physics of the universe and the behavior of celestial bodies. As we continue to explore the universe, the study of gravity’s acceleration will remain a vital area of research, with significant implications for our understanding of the cosmos and the laws of physics that govern it.