The law of supply is a fundamental concept in economics that describes the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity that suppliers are willing to sell. It states that, all else being equal, as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity supplied also increases. This is because higher prices make it more profitable for suppliers to produce and sell their products, thereby encouraging them to increase production. The law of supply is often graphically represented by a supply curve, which slopes upward from left to right, indicating the positive relationship between price and quantity supplied.
In order to understand the law of supply, it is essential to consider the factors that influence a supplier's decision to produce and sell a good or service. These factors include the cost of production, the price of related goods, and the level of technology used in production. For instance, if the cost of production decreases, suppliers may be willing to supply more of the good or service at each price level, leading to an increase in the supply curve. On the other hand, if the price of a related good increases, suppliers may shift their resources to producing the related good, leading to a decrease in the supply of the original good or service.
Key Points
- The law of supply states that, all else being equal, as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity supplied also increases.
- The supply curve slopes upward from left to right, indicating the positive relationship between price and quantity supplied.
- The law of supply is influenced by factors such as the cost of production, the price of related goods, and the level of technology used in production.
- A change in the cost of production can lead to a shift in the supply curve, either increasing or decreasing the quantity supplied at each price level.
- The law of supply has important implications for businesses and policymakers, as it helps to determine the optimal price and quantity of a good or service.
Understanding the Law of Supply
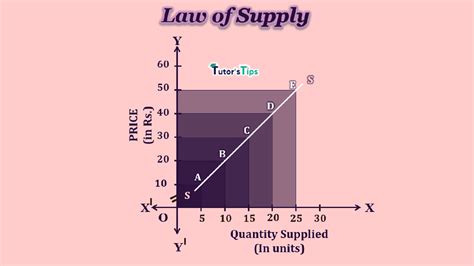
The law of supply can be understood by analyzing the behavior of suppliers in response to changes in price and other market conditions. When the price of a good or service increases, suppliers are incentivized to produce more, as they can earn higher profits. This leads to an increase in the quantity supplied, as suppliers try to take advantage of the higher price. On the other hand, when the price decreases, suppliers may reduce production, as the lower price makes it less profitable to produce and sell the good or service.
Factors Influencing the Law of Supply
There are several factors that can influence the law of supply, including the cost of production, the price of related goods, and the level of technology used in production. For example, if the cost of production decreases, suppliers may be willing to supply more of the good or service at each price level, leading to an increase in the supply curve. This can occur due to improvements in technology, which make production more efficient and reduce costs. On the other hand, if the price of a related good increases, suppliers may shift their resources to producing the related good, leading to a decrease in the supply of the original good or service.
| Factor | Effect on Supply |
|---|---|
| Decrease in cost of production | Increase in supply |
| Increase in price of related good | Decrease in supply |
| Improvement in technology | Increase in supply |
| Change in consumer preferences | Change in supply |
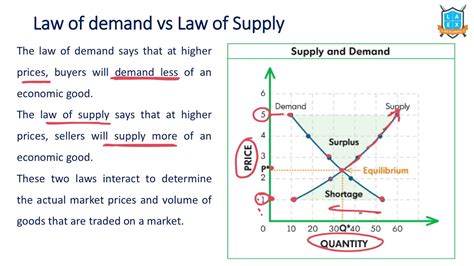
Implications of the Law of Supply
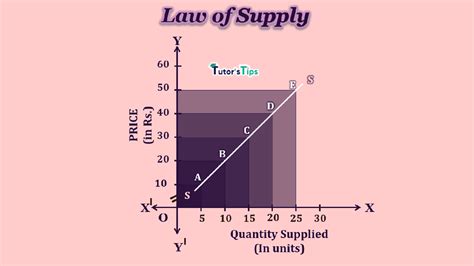
The law of supply has important implications for businesses and policymakers. By understanding how suppliers respond to changes in price and other market conditions, businesses can make informed decisions about production and pricing. For example, if a business expects an increase in demand for its product, it may increase production to meet the anticipated demand. On the other hand, if a business expects a decrease in demand, it may reduce production to avoid surplus inventory.
Policymakers can also use the law of supply to inform their decisions about taxation, regulation, and other economic policies. For instance, if a government imposes a tax on a good or service, it may decrease the supply of that good or service, as suppliers may be less willing to produce and sell it due to the increased cost. By understanding the law of supply, policymakers can anticipate the potential effects of their policies and make informed decisions about how to achieve their economic goals.
Real-World Applications of the Law of Supply
The law of supply has many real-world applications, from agriculture to manufacturing to services. For example, farmers may increase their production of crops in response to higher prices, while manufacturers may increase their production of goods in response to increased demand. Service providers, such as healthcare professionals or consultants, may also increase their supply of services in response to higher prices or increased demand.
In addition, the law of supply can be used to analyze the effects of economic policies, such as taxes or subsidies, on the supply of goods and services. For instance, a subsidy on a good or service may increase the supply of that good or service, as suppliers are incentivized to produce more due to the reduced cost. On the other hand, a tax on a good or service may decrease the supply, as suppliers may be less willing to produce and sell it due to the increased cost.
What is the law of supply?
+The law of supply states that, all else being equal, as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity supplied also increases.
What factors influence the law of supply?
+The law of supply is influenced by factors such as the cost of production, the price of related goods, and the level of technology used in production.
How does the law of supply affect businesses and policymakers?
+The law of supply has important implications for businesses and policymakers, as it helps to determine the optimal price and quantity of a good or service. By understanding the law of supply, businesses can make informed decisions about production and pricing, while policymakers can anticipate the potential effects of their policies and make informed decisions about how to achieve their economic goals.
In conclusion, the law of supply is a fundamental concept in economics that describes the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity that suppliers are willing to sell. By understanding the factors that influence the law of supply, businesses and policymakers can make informed decisions about production and pricing, which can have a significant impact on the overall economy. As the global economy continues to evolve, it is essential to consider the law of supply and its implications for businesses, policymakers, and individuals alike.