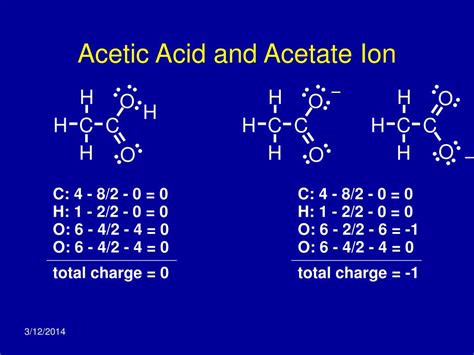
The acetate ion, a crucial component in various chemical reactions, plays a significant role in understanding the principles of chemistry. With a charge of -1, the acetate ion is a conjugate base of acetic acid, which is a weak organic acid. The charge on the acetate ion is a result of the loss of a proton (H+) from acetic acid, leading to the formation of a negatively charged ion. In this article, we will delve into the 5 ways acetate ion charge works, exploring its properties, applications, and the underlying chemical principles.
Key Points
- The acetate ion has a charge of -1, resulting from the loss of a proton from acetic acid.
- The charge on the acetate ion influences its reactivity, solubility, and interaction with other ions.
- Acetate ions play a crucial role in various biological processes, including metabolism and energy production.
- The acetate ion is used in various industrial applications, such as the production of plastics, textiles, and pharmaceuticals.
- Understanding the charge on the acetate ion is essential for predicting its behavior in different chemical reactions and applications.
Understanding the Charge on Acetate Ion

The charge on the acetate ion is a result of the dissociation of acetic acid in water. When acetic acid (CH3COOH) is dissolved in water, it partially dissociates into acetate ions (CH3COO-) and hydrogen ions (H+). The acetate ion has a charge of -1, which is due to the loss of a proton from the acetic acid molecule. This negative charge affects the reactivity, solubility, and interaction of the acetate ion with other ions and molecules.
Reactivity of Acetate Ion
The charge on the acetate ion influences its reactivity in various chemical reactions. As a negatively charged ion, the acetate ion is more reactive than the neutral acetic acid molecule. The acetate ion can participate in nucleophilic substitution reactions, where it acts as a nucleophile and donates a pair of electrons to form a new bond. The charge on the acetate ion also affects its ability to form complexes with metal ions, which is important in various biological and industrial processes.
Biological Applications of Acetate Ion
Acetate ions play a crucial role in various biological processes, including metabolism and energy production. In cells, acetate ions are produced as a byproduct of fatty acid metabolism and can be used as a source of energy. The acetate ion is also involved in the synthesis of cholesterol and other important biomolecules. Understanding the charge on the acetate ion is essential for predicting its behavior in different biological processes and applications.
| Biological Process | Role of Acetate Ion |
|---|---|
| Fatty acid metabolism | Produced as a byproduct and used as a source of energy |
| Cholesterol synthesis | Involved in the synthesis of cholesterol and other important biomolecules |
| Energy production | Used as a source of energy in cells |
Industrial Applications of Acetate Ion
The acetate ion is used in various industrial applications, including the production of plastics, textiles, and pharmaceuticals. The charge on the acetate ion affects its solubility and interaction with other ions and molecules, making it an important component in various industrial processes. For example, acetate ions are used as a solvent in the production of polyvinyl acetate (PVA), a common plastic used in adhesives and coatings.
Charge-Dependent Properties of Acetate Ion
The charge on the acetate ion influences its physical and chemical properties, including its solubility, conductivity, and reactivity. The negative charge on the acetate ion makes it more soluble in water than the neutral acetic acid molecule. The charge on the acetate ion also affects its conductivity, making it a good conductor of electricity in aqueous solutions.
What is the charge on the acetate ion?
+The charge on the acetate ion is -1, resulting from the loss of a proton from acetic acid.
What are the biological applications of the acetate ion?
+Acetate ions play a crucial role in various biological processes, including metabolism and energy production. They are produced as a byproduct of fatty acid metabolism and can be used as a source of energy.
What are the industrial applications of the acetate ion?
+The acetate ion is used in various industrial applications, including the production of plastics, textiles, and pharmaceuticals. The charge on the acetate ion affects its solubility and interaction with other ions and molecules, making it an important component in various industrial processes.
In conclusion, the charge on the acetate ion is a critical factor in understanding its properties, applications, and behavior in different chemical reactions and biological processes. By recognizing the role of the acetate ion and its charge-dependent properties, researchers and industries can develop new strategies for manipulating these processes and improving human health and industrial applications.