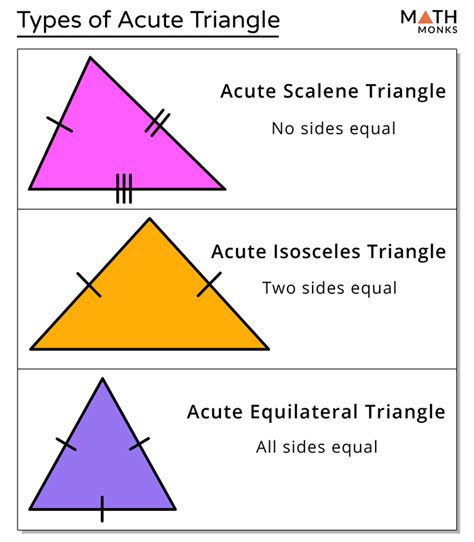
The study of triangles is a fundamental aspect of geometry, and among the various types of triangles, the acute isosceles triangle holds a significant place due to its unique properties and applications. An acute isosceles triangle is a triangle with two sides of equal length, and all angles are less than 90 degrees. This specific combination of characteristics makes the acute isosceles triangle an essential subject for exploration in both theoretical and practical geometry.
Understanding the acute isosceles triangle requires a grasp of basic geometric principles, including the definitions of acute angles, isosceles triangles, and the properties that distinguish these triangles from other types. An acute angle is an angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 degrees. An isosceles triangle is a triangle with at least two sides of equal length. When these conditions are combined in a single triangle, the result is an acute isosceles triangle, characterized by its two equal sides and three acute angles.
Key Points
- The acute isosceles triangle has two sides of equal length and all angles are less than 90 degrees.
- It is a specific type of triangle that combines the properties of isosceles and acute triangles.
- The sum of the angles in an acute isosceles triangle is always 180 degrees.
- Due to its symmetry, the acute isosceles triangle has a unique set of properties and applications.
- Understanding the acute isosceles triangle is crucial for advanced geometric and trigonometric studies.
Properties and Characteristics
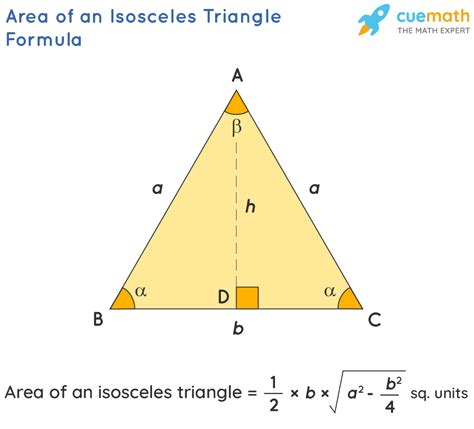
The acute isosceles triangle exhibits several key properties that make it a fascinating subject for study. One of the primary characteristics is its symmetry. Since two sides are of equal length, the triangle is symmetric about the line that passes through the vertex where the equal sides meet and is perpendicular to the base. This symmetry has implications for the triangle’s angles and side lengths, making it easier to calculate certain properties, such as the altitude to the base or the area of the triangle.
Another important property of the acute isosceles triangle is the relationship between its angles. Given that the triangle is acute, the largest angle must be less than 90 degrees. The sum of the angles in any triangle is 180 degrees. In an acute isosceles triangle, since two angles are equal (due to the two equal sides), the angles can be represented as x, x, and y, where x + x + y = 180 degrees, and both x and y are less than 90 degrees. This relationship can be used to find the angles of the triangle if one angle is known.
Calculating the Area and Perimeter
Calculating the area and perimeter of an acute isosceles triangle involves understanding its geometric properties. The area (A) of a triangle can be calculated using the formula A = 0.5 * base * height. For an acute isosceles triangle, the height can be found using the Pythagorean theorem if the length of the base and one of the equal sides is known. The perimeter (P) is the sum of all side lengths, which, for an acute isosceles triangle, can be represented as P = 2a + b, where ‘a’ is the length of the equal sides, and ‘b’ is the length of the base.
| Property | Formula |
|---|---|
| Area | A = 0.5 * base * height |
| Perimeter | P = 2a + b |
| Angle Sum | x + x + y = 180 degrees |

Applications and Real-World Examples
The acute isosceles triangle has numerous applications in real-world scenarios. In architecture, the triangle’s properties are utilized in the design of buildings and bridges, where stability and symmetry are crucial. The triangle’s shape is also found in nature, such as in the structure of certain molecules and in the geometry of mountain peaks. Furthermore, the acute isosceles triangle is a fundamental shape in engineering, particularly in the design of mechanical components and in the calculation of stresses and strains in materials.
In addition to its practical applications, the acute isosceles triangle plays a significant role in the development of geometric and trigonometric theories. It serves as a basic model for understanding more complex geometric shapes and is used in the derivation of various mathematical formulas and theorems. The study of the acute isosceles triangle, therefore, contributes to a deeper understanding of geometry and its applications, making it a vital part of mathematical education and research.
Historical Context and Evolutionary Developments
The study of triangles, including the acute isosceles triangle, has a rich history that dates back to ancient civilizations. Early mathematicians, such as the Greeks and Egyptians, recognized the importance of triangles in geometry and developed various theorems and formulas to describe their properties. Over time, as mathematical knowledge evolved, so did the understanding of the acute isosceles triangle, with contributions from mathematicians across different eras and cultures.
Today, the acute isosceles triangle remains a fundamental concept in geometry, with ongoing research and applications in various fields. Its study has led to a deeper understanding of geometric principles and has inspired new areas of mathematical inquiry. As mathematics continues to evolve, the acute isosceles triangle will likely remain a cornerstone of geometric studies, offering insights into the nature of shapes and their properties.
What is the primary characteristic of an acute isosceles triangle?
+The primary characteristic of an acute isosceles triangle is that it has two sides of equal length, and all angles are less than 90 degrees.
How is the area of an acute isosceles triangle calculated?
+The area of an acute isosceles triangle can be calculated using the formula A = 0.5 * base * height, where the height can be found using the Pythagorean theorem if necessary.
What are some real-world applications of the acute isosceles triangle?
+The acute isosceles triangle has applications in architecture, engineering, and nature, including the design of buildings, bridges, and mechanical components, as well as in the structure of molecules and mountain peaks.
In conclusion, the acute isosceles triangle is a geometric shape with unique properties and applications, making it a significant subject for study in mathematics and beyond. Its characteristics, including symmetry and acute angles, contribute to its importance in various fields, from architecture to engineering. As geometry and trigonometry continue to evolve, the acute isosceles triangle will remain a fundamental concept, offering insights into the nature of shapes and their properties, and inspiring new discoveries and applications.