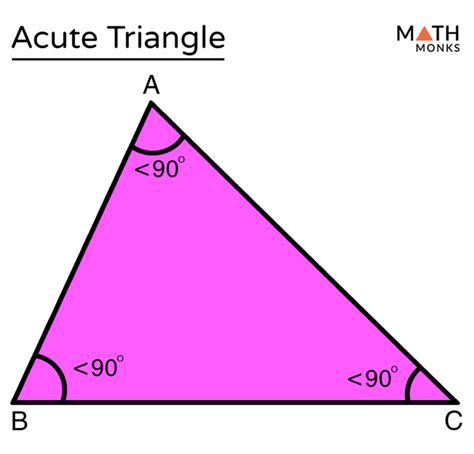
An acute triangle is a type of triangle where all three angles are less than 90 degrees. This classification is based on the measure of the angles within the triangle, which distinguishes it from right triangles (where one angle is exactly 90 degrees) and obtuse triangles (where one angle is greater than 90 degrees). The definition of an acute triangle is fundamental in geometry and is crucial for understanding various properties and theorems related to triangles.
Understanding the concept of an acute triangle begins with the basic properties of triangles and angles. In any triangle, the sum of the three interior angles is always 180 degrees. For a triangle to be classified as acute, each of its angles must measure less than 90 degrees, and the sum of these angles must still equal 180 degrees. This constraint implies that the largest angle in an acute triangle is less than 90 degrees, distinguishing it from other types of triangles.
Key Points
- An acute triangle has all three angles less than 90 degrees.
- The sum of the interior angles of any triangle, including acute triangles, is 180 degrees.
- Acute triangles are distinct from right triangles and obtuse triangles based on their angle measurements.
- Understanding acute triangles is essential for geometry and has applications in various fields, including architecture, engineering, and design.
- The properties of acute triangles, such as their side lengths and angle relationships, can be analyzed using geometric principles and theorems.
Properties of Acute Triangles
Acute triangles exhibit several unique properties that are significant in geometric studies. One of the critical properties is that the square of the longest side of an acute triangle is less than the sum of the squares of the other two sides. This property is a direct consequence of the angle-side relationship in triangles and is a key factor in distinguishing acute triangles from other types.
Another important aspect of acute triangles is their circumcircle and incircle properties. The circumcircle of a triangle is a circle that passes through the three vertices of the triangle, while the incircle is the largest circle that fits inside the triangle and touches all three sides. In acute triangles, the circumcenter (the center of the circumcircle) and the incenter (the center of the incircle) lie inside the triangle. This is in contrast to obtuse triangles, where the circumcenter lies outside the triangle.
Applications of Acute Triangles
Acute triangles have numerous applications in various fields, including architecture, engineering, and design. In architecture, the design of buildings, bridges, and other structures often involves the use of triangles for stability and strength. Acute triangles, with their unique properties, play a crucial role in ensuring the structural integrity of these designs.
In engineering, the principles of geometry, including the properties of acute triangles, are applied in the design and analysis of mechanical systems, electronic circuits, and other complex systems. The understanding of acute triangles and their properties helps engineers to develop efficient and stable designs.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Angle Sum | Always 180 degrees |
| Largest Angle | |
| Circumcenter | Lies inside the triangle |
| Incenter | Lies inside the triangle |
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, acute triangles are a fascinating area of study within geometry, offering insights into the fundamental properties of triangles and their applications. The unique characteristics of acute triangles, such as all angles being less than 90 degrees and the specific relationships between their sides and angles, make them a crucial component of geometric analysis and design.
As geometric principles continue to evolve and find new applications in technology, engineering, and other disciplines, the understanding of acute triangles will remain a cornerstone of these developments. By exploring and applying the properties of acute triangles, researchers and practitioners can push the boundaries of innovation, leading to the creation of more sophisticated and efficient designs in various fields.
What distinguishes an acute triangle from other types of triangles?
+An acute triangle is distinguished by having all three angles less than 90 degrees, which is different from right triangles (one 90-degree angle) and obtuse triangles (one angle greater than 90 degrees).
What are some real-world applications of acute triangles?
+Acute triangles have applications in architecture for designing stable structures, in engineering for developing efficient systems, and in design for creating aesthetically pleasing and functional products.
How do the properties of acute triangles contribute to their stability and strength?
+The properties of acute triangles, such as the relationship between their sides and angles, contribute to their stability and strength by distributing forces evenly and providing a balanced structure.