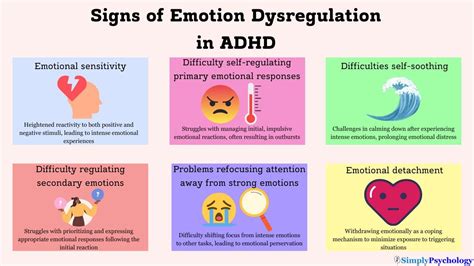
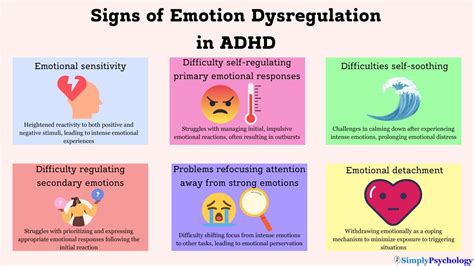
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a complex neurodevelopmental disorder that affects both children and adults, manifesting in a range of symptoms including inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. One of the lesser-discussed yet critical aspects of ADHD is emotional dysregulation, which refers to the difficulty in managing and regulating emotions. This challenge can lead to intense emotional experiences, mood swings, and impulsive behaviors, significantly impacting an individual's daily life, relationships, and overall well-being.
Key Points
- Emotional dysregulation in ADHD involves difficulties in managing emotional responses, leading to heightened emotional sensitivity and reactivity.
- Understanding the neurobiological underpinnings of ADHD and emotional dysregulation is crucial for developing effective management strategies.
- Strategies for managing emotional dysregulation include mindfulness, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), emotional regulation techniques, and, in some cases, medication.
- Support from family, friends, and mental health professionals plays a vital role in helping individuals with ADHD cope with emotional dysregulation.
- Recognizing the signs of emotional dysregulation, such as irritability, mood swings, and explosive behavior, is essential for timely intervention.
Understanding Emotional Dysregulation in ADHD

Emotional dysregulation in ADHD is characterized by an increased sensitivity to emotional stimuli and a decreased ability to regulate emotional responses. This can result in intense feelings of anger, frustration, sadness, or anxiety, which may be disproportionate to the situation at hand. The neurobiological basis of emotional dysregulation in ADHD is complex and involves alterations in brain regions responsible for emotional processing, such as the amygdala and prefrontal cortex, as well as imbalances in neurotransmitter systems like dopamine and serotonin.
The Impact of Emotional Dysregulation on Daily Life
The effects of emotional dysregulation can be far-reaching, affecting not only the individual with ADHD but also their family, friends, and colleagues. Mood swings, explosive behavior, and emotional outbursts can strain relationships and make everyday interactions challenging. Furthermore, the constant struggle to manage emotions can lead to feelings of guilt, shame, and low self-esteem, exacerbating the challenges faced by individuals with ADHD.
| Emotional Dysregulation Symptoms | Description |
|---|---|
| Mood Swings | Rapid shifts in emotional states, such as moving from calm to angry or from happy to sad without an apparent reason. |
| Emotional Overreactivity | Responding to situations with intense emotional reactions that are out of proportion to the circumstances. |
| Irritability | Feeling easily annoyed or frustrated, which can lead to explosive behavior or outbursts. |
| Emotional Sensitivity | Being highly sensitive to emotional stimuli, including criticism, rejection, or perceived slights. |
Strategies for Managing Emotional Dysregulation
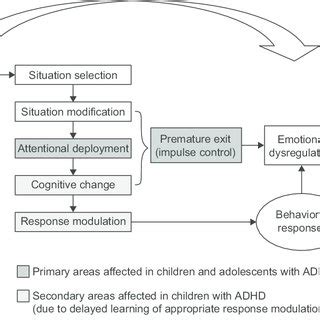
Managing emotional dysregulation in ADHD requires a multifaceted approach that includes psychological therapies, lifestyle modifications, and, in some cases, pharmacological interventions. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is particularly effective in helping individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns and develop more adaptive coping strategies. Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can also help in reducing stress and improving emotional regulation. Additionally, establishing a regular sleep schedule, engaging in physical activity, and maintaining a balanced diet can contribute to better emotional well-being.
The Role of Medication in Managing Emotional Dysregulation
While medication is primarily used to manage the core symptoms of ADHD, certain medications may also help with emotional dysregulation. For example, stimulants and non-stimulants can improve focus and reduce impulsivity, which in turn may help in managing emotional outbursts. However, the use of medication should be carefully considered and monitored by a healthcare professional, as it may have varying effects on different individuals and can interact with other medications.
In conclusion, emotional dysregulation is a significant aspect of ADHD that affects individuals in profound ways. By understanding its causes, recognizing its symptoms, and employing effective management strategies, individuals with ADHD can better navigate their emotional landscape and improve their overall quality of life. It is essential to approach emotional dysregulation with empathy and understanding, acknowledging that it is an inherent part of the ADHD experience for many, rather than a personal weakness.
What is the primary challenge in managing emotional dysregulation in ADHD?
+The primary challenge is recognizing and acknowledging the emotional dysregulation as part of ADHD, rather than a personal failing, and then seeking appropriate help and strategies to manage it.
How can mindfulness help in managing emotional dysregulation?
+Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and deep breathing, can help reduce stress, improve emotional awareness, and enhance the ability to manage emotions more effectively.
Is medication effective in treating emotional dysregulation in ADHD?
+While medication primarily targets the core symptoms of ADHD, certain medications can also help alleviate symptoms of emotional dysregulation. However, the decision to use medication should be made under the guidance of a healthcare professional.