The concept of essential elements is a crucial aspect of various domains, including chemistry, biology, and nutrition. In the context of these fields, essential elements refer to the fundamental components that are necessary for the growth, development, and maintenance of living organisms. In this article, we will delve into the three essential elements that are commonly recognized across different disciplines, exploring their characteristics, functions, and significance.
Primary Essential Element: Carbon
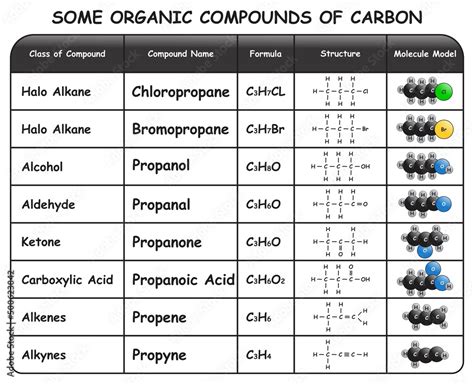
Carbon is widely regarded as the primary essential element due to its unique properties and versatility. With an atomic number of 6, carbon has the ability to form complex molecules and bonds with numerous other elements, making it the backbone of organic chemistry. The presence of carbon is essential for life as we know it, as it forms the basis of biomolecules such as carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids. The chemical properties of carbon, including its high electronegativity and ability to form stable covalent bonds, enable it to play a central role in the structure and function of living organisms.
Secondary Essential Element: Oxygen
Oxygen, with an atomic number of 8, is another crucial essential element that is necessary for the survival of most living organisms. As a highly reactive element, oxygen is involved in numerous biological processes, including cellular respiration, photosynthesis, and the metabolism of nutrients. The presence of oxygen is essential for the production of energy in cells, as it serves as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain. Additionally, oxygen is necessary for the maintenance of proper cellular function, as it helps to regulate the balance of fluids and electrolytes within the body.
| Element | Atomic Number | Biological Function |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon | 6 | Forms the basis of biomolecules and provides structural support |
| Oxygen | 8 | Involved in cellular respiration, photosynthesis, and metabolism |
| Nitrogen | 7 | Essential for the synthesis of amino acids, nucleotides, and chlorophyll |
Tertiary Essential Element: Nitrogen

Nitrogen, with an atomic number of 7, is a vital essential element that plays a critical role in the synthesis of biomolecules and the maintenance of proper cellular function. As a key component of amino acids, nucleotides, and chlorophyll, nitrogen is necessary for the production of proteins, nucleic acids, and other essential biomolecules. The presence of nitrogen is also essential for the regulation of various biological processes, including the metabolism of nutrients and the maintenance of proper pH balance within the body.
Key Points
- Carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen are the three essential elements that are necessary for life.
- These elements form the basis of biomolecules and are involved in various biological processes.
- The unique combination and interaction of these elements give rise to the diverse range of biomolecules and biological processes that are necessary for life.
- The presence of these essential elements is critical for the maintenance of proper cellular function and the regulation of various biological processes.
- Understanding the characteristics, functions, and significance of these essential elements is crucial for appreciating the complexity and diversity of life.
In conclusion, the three essential elements of carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen are the fundamental components that are necessary for the growth, development, and maintenance of living organisms. Their unique properties and interactions give rise to the diverse range of biomolecules and biological processes that are necessary for life, and their presence is critical for the regulation of various biological processes and the maintenance of proper cellular function.
What are the three essential elements necessary for life?
+The three essential elements necessary for life are carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen. These elements form the basis of biomolecules and are involved in various biological processes.
Why is carbon considered the primary essential element?
+Carbon is considered the primary essential element due to its unique properties and versatility. It has the ability to form complex molecules and bonds with numerous other elements, making it the backbone of organic chemistry.
What is the role of oxygen in biological processes?
+Oxygen is involved in numerous biological processes, including cellular respiration, photosynthesis, and the metabolism of nutrients. It serves as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain and helps to regulate the balance of fluids and electrolytes within the body.