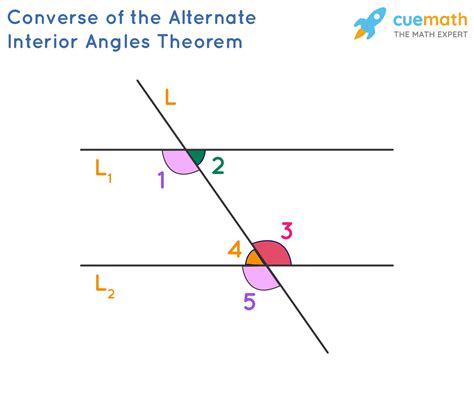
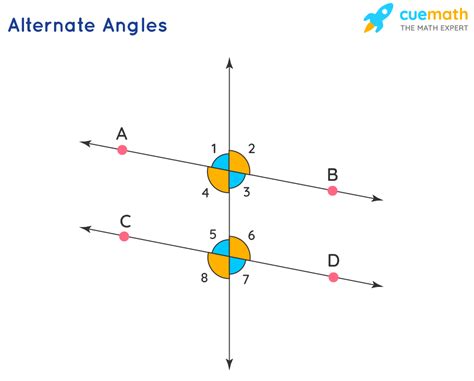
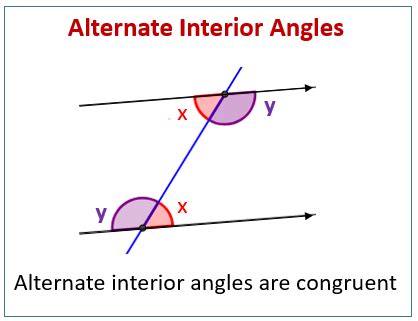
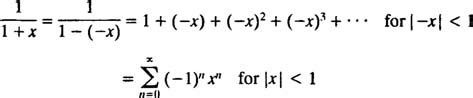Alternate interior angles are a fundamental concept in geometry, particularly when dealing with parallel lines and transversals. To understand this concept, it's essential to start with the basics. When two parallel lines are intersected by a third line, known as a transversal, several angles are formed. These angles can be categorized into different types based on their positions relative to the transversals and the parallel lines. The alternate interior angles are those angles that are on opposite sides of the transversal and inside the two parallel lines.
The significance of alternate interior angles lies in their relationship with parallel lines. According to the properties of parallel lines, when a transversal intersects two parallel lines, the alternate interior angles are congruent. This means that if you have two parallel lines cut by a transversal, the angles on opposite sides of the transversal and inside the lines will be equal in measure. This property is a key characteristic that distinguishes parallel lines from other types of lines and is crucial in various geometric proofs and theorems.
Key Points
- Alternate interior angles are formed when a transversal intersects two parallel lines and are located on opposite sides of the transversal and inside the lines.
- These angles are congruent, meaning they have the same measure, which is a fundamental property of parallel lines.
- The concept of alternate interior angles is essential in geometry for proving theorems and solving problems related to parallel lines and transversals.
- Understanding alternate interior angles helps in identifying and working with parallel lines in various geometric contexts.
- The property of alternate interior angles being congruent is used in real-world applications, such as architecture, engineering, and design, where parallel lines and angles play a critical role.
Nature of Alternate Interior Angles
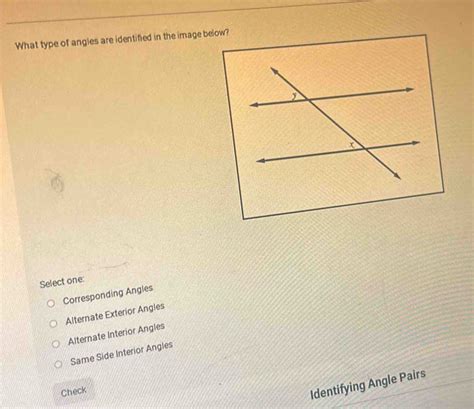
Alternate interior angles are not just a product of the intersection of parallel lines and a transversal; they also have specific characteristics that make them useful in geometric analysis. For instance, if the two parallel lines are intersected by more than one transversal, the concept of alternate interior angles can be applied multiple times, providing a way to relate angles across different parts of the geometric figure. This property is particularly useful in proving that lines are parallel based on angle relationships.
Moreover, the concept of alternate interior angles is closely related to other angle properties, such as corresponding angles and alternate exterior angles. While alternate interior angles are inside the parallel lines and on opposite sides of the transversal, alternate exterior angles are outside the parallel lines and on opposite sides of the transversal. Understanding the distinctions and relationships between these angle types is crucial for applying geometric principles accurately.
Applications and Examples
The concept of alternate interior angles has numerous applications in geometry and real-world problems. For example, in designing roads or railway tracks, engineers must ensure that certain sections of the track are parallel to each other. By applying the property of alternate interior angles, they can verify the parallelism of these sections based on the angles formed when a transversal (like a road or a bridge) intersects the tracks.
In architectural design, the principle of alternate interior angles is used to create symmetrical and balanced structures. By carefully planning the angles at which walls, beams, or other structural elements intersect, architects can achieve desired aesthetic effects while ensuring the stability and functionality of the building.
| Angle Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Alternate Interior Angles | Angles inside parallel lines and on opposite sides of a transversal | Angles A and D in a diagram where line 1 is parallel to line 2 and both are intersected by a transversal |
| Corresponding Angles | Angles in the same relative position in two different intersections | Angles A and E in the same diagram, assuming another transversal intersects the parallel lines |
| Alternate Exterior Angles | Angles outside parallel lines and on opposite sides of a transversal | Angles B and C in the initial diagram |
Conclusion and Further Considerations
In conclusion, alternate interior angles play a vital role in geometry, serving as a fundamental property of parallel lines and a tool for solving problems and proving theorems. Their application extends beyond the realm of pure geometry, influencing fields such as engineering, architecture, and design. As with any geometric concept, understanding the principles and properties of alternate interior angles requires a combination of theoretical knowledge and practical application.
Further considerations in the study and application of alternate interior angles include exploring their role in more complex geometric figures, such as polygons and polyhedra, and examining how they interact with other geometric elements, like circles and ellipses. Additionally, recognizing the historical development of geometric concepts and their impact on modern science and technology can provide a deeper appreciation for the significance of alternate interior angles and related principles.
What is the primary characteristic of alternate interior angles?
+The primary characteristic of alternate interior angles is that they are congruent when formed by a transversal intersecting two parallel lines.
How are alternate interior angles used in real-world applications?
+Alternate interior angles are used in various real-world applications, including architecture, engineering, and design, to verify the parallelism of lines and to achieve desired structural and aesthetic effects.
What is the difference between alternate interior angles and alternate exterior angles?
+Alternate interior angles are inside the parallel lines and on opposite sides of the transversal, while alternate exterior angles are outside the parallel lines and on opposite sides of the transversal.