Aluminum, with its atomic number of 13, is a versatile and widely used metal in various industries, including construction, transportation, and packaging. Its unique properties, such as lightweight, corrosion resistance, and high thermal conductivity, make it an essential material in modern technology. One key aspect of aluminum's chemical behavior is its valence electrons, which play a crucial role in determining its reactivity and interaction with other elements. In this article, we will delve into the world of aluminum valence electrons, exploring their arrangement, configuration, and significance in chemical reactions.
Key Points
- Aluminum has three valence electrons in its outermost energy level.
- The valence electron configuration of aluminum is 3s² 3p¹.
- Aluminum's valence electrons determine its reactivity and ability to form compounds with other elements.
- The metal's valence electrons are involved in the formation of aluminum oxides, which provide corrosion resistance.
- Understanding aluminum's valence electrons is essential for predicting its chemical behavior and optimizing its applications.
Introduction to Valence Electrons
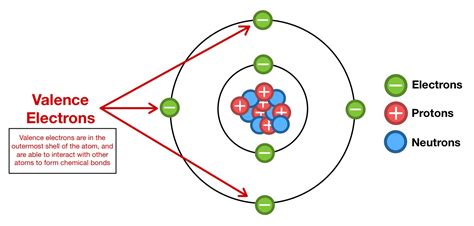
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom, which participate in chemical bonding and reactions. These electrons are responsible for the chemical properties of an element, including its reactivity, electronegativity, and ability to form compounds with other elements. In the case of aluminum, its valence electrons are located in the third energy level, which is the outermost energy level of the atom.
Valence Electron Configuration of Aluminum
The valence electron configuration of aluminum is 3s² 3p¹, which means that the outermost energy level contains three electrons: two in the 3s orbital and one in the 3p orbital. This configuration is responsible for aluminum’s chemical properties, including its reactivity and ability to form compounds with other elements. The 3s electrons are paired, while the 3p electron is unpaired, which makes aluminum a reactive metal that readily forms bonds with other elements.
| Energy Level | Electron Configuration |
|---|---|
| 1s | 1s² |
| 2s | 2s² 2p⁶ |
| 3s | 3s² 3p¹ |

Significance of Valence Electrons in Aluminum Chemistry

The valence electrons of aluminum play a vital role in its chemical reactions and interactions with other elements. Aluminum’s reactivity is largely determined by its valence electrons, which are readily available for bonding with other atoms. The metal’s ability to form compounds with other elements, such as oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon, is a result of its valence electrons participating in chemical bonding.
Formation of Aluminum Oxides
One of the most significant applications of aluminum’s valence electrons is in the formation of aluminum oxides, which provide corrosion resistance to the metal. When aluminum reacts with oxygen, its valence electrons participate in the formation of a thin layer of aluminum oxide, which protects the metal from further corrosion. This oxide layer is responsible for aluminum’s resistance to corrosion and its ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions.
What is the valence electron configuration of aluminum?
+The valence electron configuration of aluminum is 3s² 3p¹, which means that the outermost energy level contains three electrons: two in the 3s orbital and one in the 3p orbital.
Why are valence electrons important in aluminum chemistry?
+Valence electrons are important in aluminum chemistry because they determine the metal's reactivity and ability to form compounds with other elements. The valence electrons of aluminum participate in chemical bonding, which is essential for the metal's applications in various industries.
How do valence electrons contribute to the corrosion resistance of aluminum?
+The valence electrons of aluminum participate in the formation of a thin layer of aluminum oxide, which provides corrosion resistance to the metal. This oxide layer protects the metal from further corrosion and is responsible for aluminum's ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions.
In conclusion, the valence electrons of aluminum play a crucial role in determining its chemical properties and reactivity. Understanding the arrangement and configuration of these electrons is essential for predicting the metal’s behavior and optimizing its applications in various industries. By recognizing the significance of valence electrons in aluminum chemistry, we can appreciate the importance of this metal in modern technology and its potential for future innovations.