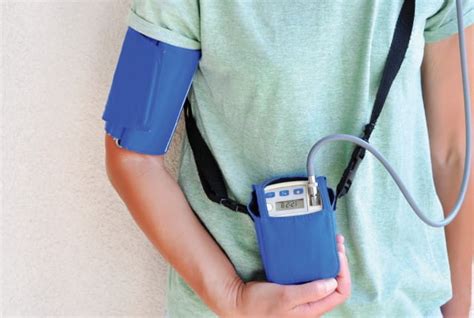
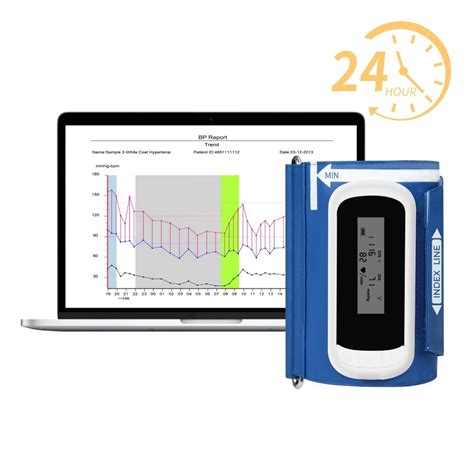
The use of ambulatory blood pressure monitors has become a crucial aspect of hypertension diagnosis and management. These portable devices allow for the continuous monitoring of blood pressure over a 24-hour period, providing healthcare professionals with a more accurate picture of a patient's blood pressure patterns. In this article, we will delve into the world of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring, exploring its benefits, technical specifications, and the impact it has on patient care.
Key Points
- Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring provides a more accurate diagnosis of hypertension compared to traditional office-based measurements.
- The American Heart Association recommends the use of ambulatory blood pressure monitors for patients with suspected white-coat hypertension or masked hypertension.
- Ambulatory blood pressure monitors can detect blood pressure variability, which is a significant predictor of cardiovascular risk.
- The devices are equipped with advanced features such as data analysis software and wireless connectivity, allowing for seamless data transfer and remote monitoring.
- Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring has been shown to improve patient outcomes, including reduced blood pressure levels and decreased cardiovascular risk.
Technical Specifications and Operation
Ambulatory blood pressure monitors are designed to be compact and lightweight, allowing patients to wear them comfortably throughout the day. The devices typically consist of a cuff, a pump, and a microprocessor that controls the measurement process. The cuff is usually wrapped around the upper arm, and the pump inflates the cuff to occlude the artery, allowing the device to measure blood pressure. The microprocessor then analyzes the data and stores it for later retrieval.
The technical specifications of ambulatory blood pressure monitors vary depending on the manufacturer and model. However, most devices have the following features:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Blood Pressure Measurement Range | 0-300 mmHg |
| Accuracy | ±3 mmHg |
| Sample Rate | Every 15-30 minutes |
| Memory Capacity | Up to 1000 readings |
| Battery Life | Up to 48 hours |
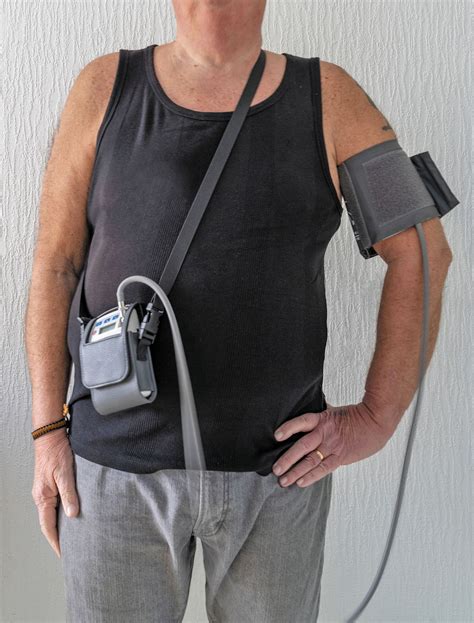
Clinical Applications and Benefits
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring has several clinical applications, including the diagnosis of hypertension, the assessment of blood pressure variability, and the monitoring of treatment efficacy. The benefits of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring include:
Improved Diagnostic Accuracy: Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring provides a more accurate diagnosis of hypertension compared to traditional office-based measurements. This is because the device can capture blood pressure readings throughout the day, including during periods of physical activity and sleep.
Blood Pressure Variability: Ambulatory blood pressure monitors can detect blood pressure variability, which is a significant predictor of cardiovascular risk. Studies have shown that patients with high blood pressure variability are at increased risk of cardiovascular events, such as heart attacks and strokes.
Impact on Patient Care
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring has been shown to improve patient outcomes, including reduced blood pressure levels and decreased cardiovascular risk. The use of these devices can also improve patient engagement and adherence to treatment plans. A study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology found that patients who used ambulatory blood pressure monitors were more likely to achieve blood pressure control and had lower rates of cardiovascular events.
The impact of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring on patient care can be seen in several areas, including:
Personalized Medicine: Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring allows healthcare professionals to tailor treatment plans to individual patients, taking into account their unique blood pressure patterns and risk factors.
Remote Monitoring: The use of ambulatory blood pressure monitors with wireless connectivity enables remote monitoring, allowing healthcare professionals to track patient data in real-time and make adjustments to treatment plans as needed.
Future Directions
The field of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring is constantly evolving, with new technologies and innovations being developed. Some of the future directions in this field include:
Artificial Intelligence: The use of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to analyze ambulatory blood pressure data and predict cardiovascular risk.
Wearable Devices: The development of wearable devices that can measure blood pressure continuously, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers.
What is the difference between ambulatory blood pressure monitoring and traditional office-based blood pressure measurement?
+Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring provides a more accurate picture of blood pressure patterns throughout the day, whereas traditional office-based measurements only provide a snapshot of blood pressure at a single point in time.
How often should ambulatory blood pressure monitoring be performed?
+The frequency of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring depends on the individual patient’s needs and risk factors. However, it is typically recommended to perform monitoring at least once a year for patients with hypertension.
Can ambulatory blood pressure monitoring be used in patients with certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease or heart failure?
+Yes, ambulatory blood pressure monitoring can be used in patients with certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease or heart failure. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of treatment and monitoring for individual patients.