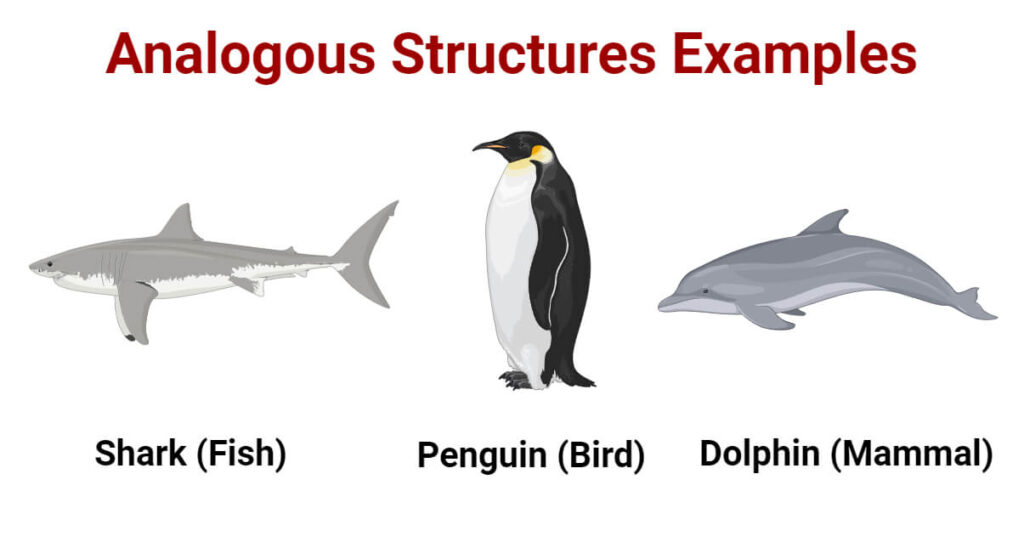
Analogous structures refer to the similarities in form or function between different entities, which can be observed in various domains such as biology, architecture, engineering, and even social systems. These similarities often arise due to convergent evolution, where different systems develop similar solutions to common problems, despite not being directly related. Understanding analogous structures can provide valuable insights into the principles of design, efficiency, and adaptation. Here, we will explore five examples of analogous structures across different fields.
Biological and Engineering Analogies

In biology, the structure of the human eye and the camera share an analogous relationship. Both have a lens that focuses light onto a sensitive surface (the retina in the eye and the digital sensor in a camera), an aperture that controls the amount of light entering (the pupil in the eye and the camera aperture), and a mechanism for adjusting focus to ensure clear images at varying distances. This analogy highlights how different systems can develop similar solutions to the problem of capturing and processing visual information.
Aerodynamic and Hydrodynamic Similarities
The shapes of airplanes and fish also exhibit analogous structures. Both are designed to move efficiently through their respective mediums (air and water), with streamlined bodies that reduce drag. The wing of an airplane and the pectoral fin of a fish have similar cross-sectional shapes, utilizing the principle of lift to counteract the forces of gravity and buoyancy, respectively. These similarities demonstrate how the principles of fluid dynamics can lead to analogous solutions in seemingly disparate systems.
| System | Analogous Structure | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Human Eye | Camera | Light Focus and Image Formation |
| Airplane Wing | Fish Pectoral Fin | Lift Generation |
| Tree Roots | River Branching | Optimized Resource Distribution |
| Brain Neural Networks | Internet Routing | Efficient Information Transmission |
| Bird Wings | Airplane Wings | Aerodynamic Lift |
Social and Biological Networks
Another example of analogous structures can be found in the comparison between social networks and biological networks. The structure of the internet, with its nodes and connections, bears a resemblance to the neural networks in the brain, where neurons are connected by synapses. Both systems are designed for efficient information transmission and have developed similar strategies, such as clustering and hubs, to manage and distribute information effectively.
Ecological and Urban Planning Analogies
The branching patterns of trees and rivers also show analogous structures. Both systems have evolved to optimize the distribution of resources (water and nutrients for trees, and water flow for rivers) through a network of branches that divide and subdivide into smaller, more specialized units. This principle can be applied to urban planning, where the design of road networks and public transportation systems can benefit from understanding how natural systems efficiently distribute resources.
Key Points
- Analogous structures are found across different domains, including biology, engineering, and social systems.
- These structures often arise due to convergent evolution, where different systems develop similar solutions to common problems.
- Understanding analogous structures can provide insights into design principles, efficiency, and adaptation.
- Examples include the human eye and camera, airplane and fish shapes, tree roots and river branching, brain neural networks and internet routing, and bird wings and airplane wings.
- Studying analogous structures can inspire innovation and inform the design of more efficient technologies and systems.
In conclusion, the study of analogous structures offers a fascinating glimpse into how different systems, whether natural or engineered, can develop similar solutions to common challenges. By recognizing and understanding these analogies, we can not only appreciate the ingenuity of nature but also leverage this knowledge to create more efficient, adaptable, and innovative technologies and systems.
What are analogous structures, and why are they important?
+Analogous structures refer to the similarities in form or function between different entities. They are important because they highlight how different systems can develop similar solutions to common problems, offering insights into design principles, efficiency, and adaptation.
Can the study of analogous structures inspire innovation?
+Yes, understanding how nature and different systems solve complex problems can inspire the development of more efficient and adaptable technologies. By applying the principles observed in analogous structures, engineers and designers can create innovative solutions to real-world challenges.
What are some examples of analogous structures in nature and engineering?
+Examples include the human eye and camera, airplane and fish shapes, tree roots and river branching, brain neural networks and internet routing, and bird wings and airplane wings. These examples demonstrate how different domains can exhibit similar structural and functional analogies.