The human body is a complex and fascinating entity, and the female body is no exception. With its unique characteristics and functions, the female body is a remarkable example of nature's ingenuity. In this article, we will delve into the anatomy of the female body, exploring its various systems, organs, and structures, and examining the intricacies of its functions.
Key Points
- The female body is composed of several systems, including the skeletal, muscular, nervous, circulatory, respiratory, digestive, endocrine, and reproductive systems.
- The female reproductive system is a complex and highly specialized system, responsible for producing eggs, supporting fetal development, and giving birth.
- The female body is capable of undergoing significant changes throughout life, including puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause.
- Understanding the anatomy of the female body is essential for maintaining good health, preventing diseases, and promoting overall well-being.
- The female body is subject to various health risks, including breast cancer, cervical cancer, and osteoporosis, which can be mitigated through regular check-ups, screenings, and healthy lifestyle choices.
Introduction to the Female Body

The female body is a dynamic and intricate system, comprising various organs, tissues, and cells that work together to maintain overall health and function. The female body is characterized by its unique reproductive system, which is designed to produce eggs, support fetal development, and give birth. In addition to its reproductive functions, the female body is also equipped with a range of other systems, including the skeletal, muscular, nervous, circulatory, respiratory, digestive, and endocrine systems.
The Skeletal System
The skeletal system is the framework of the body, providing support, protection, and movement. The female skeletal system is composed of 206 bones, which are connected by joints, ligaments, and tendons. The skeletal system plays a crucial role in maintaining posture, facilitating movement, and protecting internal organs. In females, the skeletal system is generally smaller and less dense than in males, which can increase the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
The Muscular System
The muscular system is responsible for movement, contraction, and relaxation. The female muscular system is composed of three types of muscles: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Skeletal muscles are attached to bones and facilitate movement, while smooth muscles are found in the walls of hollow organs and facilitate contraction and relaxation. Cardiac muscle is found in the heart and is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body.
The Nervous System
The nervous system is a complex system that controls and coordinates the body’s functions. The female nervous system is composed of the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS includes the brain and spinal cord, while the PNS includes nerves that connect the CNS to the rest of the body. The nervous system plays a crucial role in controlling movement, sensation, and cognition.
The Reproductive System
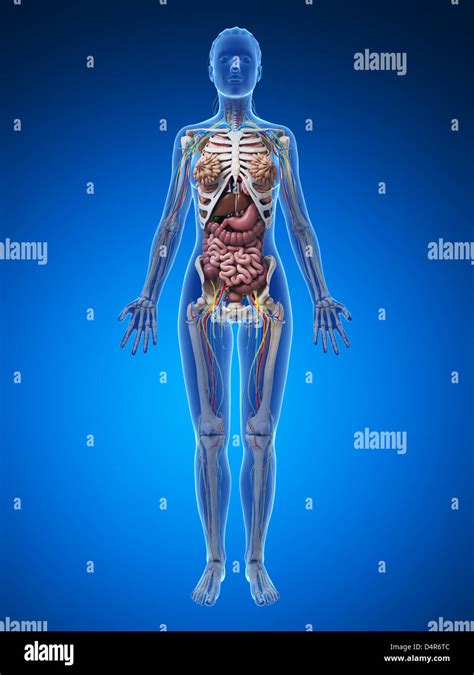
The female reproductive system is a complex and highly specialized system, responsible for producing eggs, supporting fetal development, and giving birth. The reproductive system is composed of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and vagina. The ovaries produce eggs, which are released into the fallopian tubes and fertilized by sperm. The fertilized egg then implants in the uterus, where it develops into a fetus. The reproductive system is controlled by a complex interplay of hormones, including estrogen and progesterone.
| Reproductive Organ | Function |
|---|---|
| Ovaries | Produce eggs and hormones |
| Fallopian Tubes | Transport eggs from ovaries to uterus |
| Uterus | Supports fetal development and gives birth |
| Cervix | Connects uterus to vagina and regulates menstrual flow |
| Vagina | Receives sperm and serves as birth canal |
Pregnancy and Childbirth
Pregnancy and childbirth are significant events in a woman’s life, requiring a range of physical, emotional, and psychological changes. During pregnancy, the female body undergoes significant changes, including the expansion of the uterus, the production of hormones, and the preparation of the breasts for lactation. Childbirth is a complex process, involving the dilation of the cervix, the rupture of membranes, and the delivery of the baby.
Health Risks and Prevention
The female body is subject to various health risks, including breast cancer, cervical cancer, and osteoporosis. Breast cancer is a leading cause of death in women, while cervical cancer can be prevented through regular screenings and vaccinations. Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by the thinning of bones, which can increase the risk of fractures. Regular check-ups, screenings, and healthy lifestyle choices can help mitigate these risks and promote overall health and well-being.
What are the most common health risks facing women?
+The most common health risks facing women include breast cancer, cervical cancer, osteoporosis, and heart disease. Regular check-ups, screenings, and healthy lifestyle choices can help mitigate these risks and promote overall health and well-being.
How can women maintain good reproductive health?
+Women can maintain good reproductive health by practicing safe sex, getting regular check-ups and screenings, and making healthy lifestyle choices, such as exercising regularly, eating a balanced diet, and managing stress.
What are the symptoms of menopause?
+The symptoms of menopause include hot flashes, night sweats, mood changes, and vaginal dryness. Women can manage these symptoms through hormone replacement therapy, lifestyle changes, and natural remedies, such as exercise, meditation, and herbal supplements.
Meta Description: “Explore the anatomy of the female body, including its unique characteristics, functions, and health risks. Learn about the skeletal, muscular, nervous, and reproductive systems, and discover how to maintain good health and well-being.” (149 characters)



