The Earth's surface is characterized by a diverse range of landforms, each with its unique features and characteristics. Landforms are natural features of the Earth's surface, shaped by a combination of geological processes, including tectonic activity, weathering, erosion, and deposition. Understanding these landforms is essential for various fields, including geography, geology, and environmental science. In this article, we will explore five key landforms, their characteristics, and their significance in the context of the Earth's surface.
Key Points
- Mountains are elevated landforms formed through tectonic activity, weathering, and erosion.
- Plains are vast, flat or gently sloping areas of land, often formed through erosion and deposition.
- Plateaus are elevated areas of land with relatively flat tops and steep sides, formed through volcanic activity or erosion.
- Valleys are low areas of land between hills or mountains, often formed through erosion by rivers or glaciers.
- Coastlines are the boundaries between land and sea, shaped by a combination of geological processes, including erosion, deposition, and tectonic activity.
Mountains
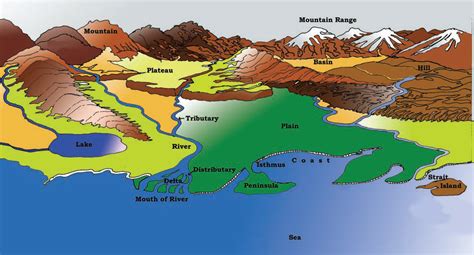
Mountains are elevated landforms that are formed through a combination of geological processes, including tectonic activity, weathering, and erosion. They can be found on every continent and are characterized by their rugged terrain, steep slopes, and diverse range of ecosystems. The formation of mountains is a complex process that involves the movement of tectonic plates, resulting in the folding, faulting, and volcanic activity that shapes the Earth’s surface. For example, the Himalayan mountain range was formed as a result of the collision between the Indian and Eurasian tectonic plates, resulting in the formation of the highest mountain peak in the world, Mount Everest.
Types of Mountains
There are several types of mountains, including fold mountains, volcanic mountains, and block mountains. Fold mountains are formed through the folding of rocks, resulting in the creation of mountain ranges such as the Himalayas and the Rocky Mountains. Volcanic mountains are formed through volcanic activity, resulting in the creation of mountains such as Mount Fuji and Mount St. Helens. Block mountains are formed through the movement of tectonic plates, resulting in the creation of mountains such as the Sierra Nevada and the Appalachian Mountains.
| Mountain Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Fold Mountains | Formed through the folding of rocks |
| Volcanic Mountains | Formed through volcanic activity |
| Block Mountains | Formed through the movement of tectonic plates |
Plains

Plains are vast, flat or gently sloping areas of land that are often formed through erosion and deposition. They can be found on every continent and are characterized by their flat terrain, lack of relief, and diverse range of ecosystems. The formation of plains is a complex process that involves the erosion of rocks, resulting in the creation of a flat or gently sloping surface. For example, the Great Plains of North America were formed as a result of the erosion of rocks by rivers and glaciers, resulting in the creation of a vast, flat area of land.
Types of Plains
There are several types of plains, including coastal plains, interior plains, and river plains. Coastal plains are formed through the erosion of rocks by the sea, resulting in the creation of a flat or gently sloping area of land. Interior plains are formed through the erosion of rocks by rivers and glaciers, resulting in the creation of a vast, flat area of land. River plains are formed through the erosion of rocks by rivers, resulting in the creation of a flat or gently sloping area of land.
Plateaus
Plateaus are elevated areas of land with relatively flat tops and steep sides, formed through volcanic activity or erosion. They can be found on every continent and are characterized by their flat terrain, steep slopes, and diverse range of ecosystems. The formation of plateaus is a complex process that involves the erosion of rocks, resulting in the creation of a flat or gently sloping surface. For example, the Colorado Plateau was formed as a result of the erosion of rocks by rivers and glaciers, resulting in the creation of a vast, elevated area of land.
Types of Plateaus
There are several types of plateaus, including volcanic plateaus, erosion plateaus, and structural plateaus. Volcanic plateaus are formed through volcanic activity, resulting in the creation of mountains such as the Deccan Plateau. Erosion plateaus are formed through the erosion of rocks, resulting in the creation of a flat or gently sloping surface. Structural plateaus are formed through the movement of tectonic plates, resulting in the creation of a flat or gently sloping surface.
Valleys
Valleys are low areas of land between hills or mountains, often formed through erosion by rivers or glaciers. They can be found on every continent and are characterized by their low terrain, steep slopes, and diverse range of ecosystems. The formation of valleys is a complex process that involves the erosion of rocks, resulting in the creation of a low area of land. For example, the Grand Canyon was formed as a result of the erosion of rocks by the Colorado River, resulting in the creation of one of the most spectacular valleys in the world.
Types of Valleys
There are several types of valleys, including river valleys, glacial valleys, and tectonic valleys. River valleys are formed through the erosion of rocks by rivers, resulting in the creation of a low area of land. Glacial valleys are formed through the erosion of rocks by glaciers, resulting in the creation of a low area of land. Tectonic valleys are formed through the movement of tectonic plates, resulting in the creation of a low area of land.
Coastlines

Coastlines are the boundaries between land and sea, shaped by a combination of geological processes, including erosion, deposition, and tectonic activity. They can be found on every continent and are characterized by their diverse range of ecosystems, including beaches, cliffs, and estuaries. The formation of coastlines is a complex process that involves the interaction between the land and sea, resulting in the creation of a unique and dynamic environment. For example, the coastline of California was formed as a result of the interaction between the Pacific Ocean and the North American plate, resulting in the creation of a diverse range of ecosystems, including beaches, cliffs, and estuaries.
What is the difference between a mountain and a hill?
+A mountain is a natural elevation of the Earth's surface, typically with a peak elevation of over 1,000 feet. A hill is a smaller elevation of the Earth's surface, typically with a peak elevation of less than 1,000 feet.
What is the process of erosion and how does it shape landforms?
+Erosion is the process of wearing away or removal of soil, rock, or other materials from the Earth's surface. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including water, wind, ice, and gravity. Erosion shapes landforms by removing material and creating new landforms, such as valleys, canyons, and coastlines.
What is the importance of studying landforms?
+Studying landforms is essential for understanding the Earth's surface and the processes that shape it. By studying landforms, we can gain a deeper understanding of the geological processes that have shaped our planet over millions of years, and how they continue to shape it today. This knowledge can be used to inform decision-making in a variety of fields, including environmental management, urban planning, and natural resource management.
In conclusion, the five key landforms discussed in this article - mountains, plains, plateaus, valleys, and coastlines - are all unique and complex features of the Earth’s surface. Each landform has its own distinct characteristics and is shaped by a combination of geological processes, including tectonic activity, weathering, erosion, and deposition. By studying these landforms, we can gain a deeper understanding of the Earth’s surface and the processes that shape it, and how they continue to shape it today.