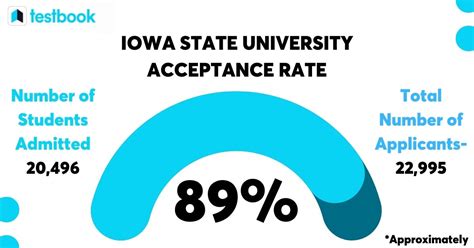
When it comes to citing sources in academic writing, the American Psychological Association (APA) style is one of the most widely used formats. APA citation is crucial for acknowledging the work of other authors, researchers, and experts in the field, thereby maintaining the integrity and credibility of one's own research or academic paper. The APA style provides guidelines for formatting papers, referencing sources, and structuring citations to ensure clarity, consistency, and professionalism in scholarly communication. In this article, we will delve into three primary ways APA citation is utilized, exploring the reasons behind its importance, the different types of citations, and how to apply them correctly.
Understanding APA Citation Basics

To appreciate the nuances of APA citation, it’s essential to understand its core principles. APA style is particularly prevalent in the social sciences, including psychology, education, business, and healthcare. The primary goal of APA citation is to provide a standardized method of crediting sources, which helps readers identify and retrieve the referenced material. This is achieved through in-text citations and a reference list at the end of the document. The APA style has undergone several revisions, with the 7th edition being the most current, offering updated guidelines to reflect modern communication platforms and research practices.
In-Text Citations
In-text citations are a fundamental component of APA citation, allowing authors to acknowledge sources within the body of their work. These citations typically include the author’s last name and the year of publication, separated by a comma. For example, a citation for a source written by Jane Doe in 2020 would appear as (Doe, 2020). If the source has two authors, both names are included, separated by an ampersand (&) when in parentheses, such as (Doe & Smith, 2020). For sources with three or more authors, the first citation includes all names, but subsequent citations use the first author’s name followed by “et al.,” for instance, (Doe et al., 2020). Understanding and applying these rules correctly is vital for maintaining the academic integrity of a paper.
| Citation Type | Example |
|---|---|
| Single Author | (Doe, 2020) |
| Two Authors | (Doe & Smith, 2020) |
| Three or More Authors | (Doe et al., 2020) |

Reference List Citations
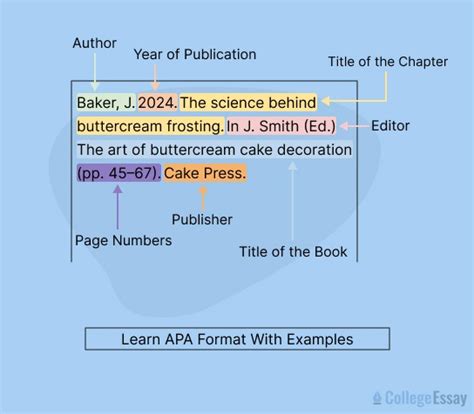
Beyond in-text citations, APA style also requires a detailed reference list at the end of the document. This list includes full citations for all sources mentioned in the text, formatted according to specific guidelines. For instance, a book citation would typically include the author’s last name, first initial, publication year, book title (in title case and italicized), and publication information. An example would be: Doe, J. (2020). The psychology of learning. New York, NY: Penguin Books. Journal articles, on the other hand, require the author’s name, publication year, article title, journal name (in title case and italicized), volume number, and page numbers. The correct citation for a journal article might look like this: Smith, A. (2020). Learning strategies. Journal of Educational Psychology, 112(3), 456–463.
Direct Quotes and Paraphrasing
When incorporating the words or ideas of others into one’s writing, it’s crucial to distinguish between direct quotes and paraphrasing. Direct quotes involve using the exact words of the original source, enclosed in quotation marks, and must be cited with the page number(s) where the quote can be found. For example, (Doe, 2020, p. 123). Paraphrasing, however, involves restating the information in one’s own words, still requiring a citation but without quotation marks. Both methods are valuable tools for incorporating external knowledge into academic writing, but they must be used judiciously to avoid plagiarism.
Key Points
- APA citation is essential for academic integrity and clarity in scholarly writing.
- In-text citations and a reference list are the two primary components of APA citation.
- Understanding the differences between direct quotes and paraphrasing is crucial for avoiding plagiarism.
- APA style guidelines evolve to accommodate new forms of communication and research practices.
- Correct application of APA citation rules enhances the credibility and readability of academic papers.
In conclusion, mastering APA citation is a fundamental skill for anyone engaged in academic or research writing. By understanding the basics of in-text citations, reference lists, and the proper use of direct quotes and paraphrasing, authors can ensure their work is not only well-referenced but also respectful of the intellectual property and contributions of others in their field. As academic and research landscapes continue to evolve, adhering to established citation styles like APA will remain indispensable for maintaining the high standards of scholarly communication.
What is the primary purpose of APA citation in academic writing?
+The primary purpose of APA citation is to provide a standardized method for crediting sources, thereby maintaining academic integrity and facilitating the retrieval of referenced material.
How do I properly cite a source with two authors in APA style?
+For sources with two authors, include both names in the in-text citation, separated by an ampersand (&), such as (Doe & Smith, 2020).
What is the difference between a direct quote and paraphrasing in APA citation?
+A direct quote involves using the exact words of the original source, enclosed in quotation marks, and must include the page number(s) in the citation. Paraphrasing involves restating the information in one’s own words, without quotation marks, but still requires a citation.