The world of academic writing is governed by a set of rules and guidelines that dictate how research papers, essays, and other written works should be formatted. Two of the most widely used formatting styles are APA (American Psychological Association) and MLA (Modern Language Association). While both styles share some similarities, they also have distinct differences that set them apart. In this article, we will delve into the world of APA and MLA formatting, exploring their history, key features, and applications.
Introduction to APA Formatting

The APA formatting style was first introduced in 1929 by the American Psychological Association. Initially, it was designed to provide a standardized format for writing and publishing research papers in the field of psychology. Over the years, the APA style has evolved to become one of the most widely used formatting styles in the social sciences, education, and business. The APA style is known for its clarity, concision, and emphasis on precision, making it an ideal choice for researchers and scholars who need to present complex data and research findings in a clear and concise manner.
Key Features of APA Formatting
Some of the key features of APA formatting include:
- Font and Spacing: APA recommends using a legible font, such as Times New Roman, in size 12 points, with double spacing throughout the paper.
- Headings: APA uses a hierarchical system of headings, with five levels of headings, each with its own formatting style.
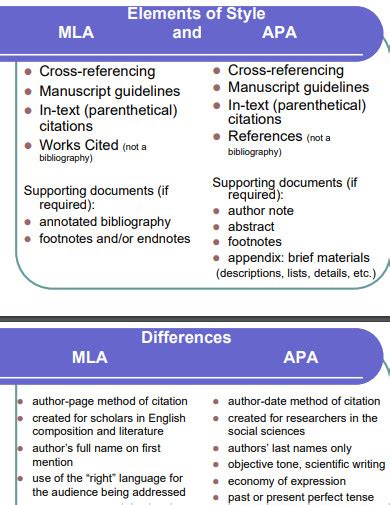
- In-Text Citations: APA uses an author-date system for in-text citations, with the author’s last name and year of publication included in the text.
- Reference List: APA requires a reference list at the end of the paper, which includes a list of all sources cited in the text, formatted according to specific guidelines.
Introduction to MLA Formatting

The MLA formatting style was first introduced in 1951 by the Modern Language Association. Initially, it was designed to provide a standardized format for writing and publishing research papers in the field of literature and language. Over the years, the MLA style has evolved to become one of the most widely used formatting styles in the humanities, arts, and social sciences. The MLA style is known for its emphasis on simplicity, clarity, and readability, making it an ideal choice for researchers and scholars who need to present complex ideas and arguments in a clear and concise manner.
Key Features of MLA Formatting
Some of the key features of MLA formatting include:
- Font and Spacing: MLA recommends using a legible font, such as Times New Roman, in size 12 points, with double spacing throughout the paper.
- Headings: MLA uses a simple system of headings, with no specific formatting style required.
- In-Text Citations: MLA uses a parenthetical system for in-text citations, with the author’s last name and page number included in the text.
- Works Cited: MLA requires a Works Cited page at the end of the paper, which includes a list of all sources cited in the text, formatted according to specific guidelines.
Key Points
- The APA style is widely used in the social sciences, education, and business, while the MLA style is widely used in the humanities, arts, and social sciences.
- APA formatting emphasizes clarity, concision, and precision, while MLA formatting emphasizes simplicity, clarity, and readability.
- APA uses an author-date system for in-text citations, while MLA uses a parenthetical system.
- APA requires a reference list at the end of the paper, while MLA requires a Works Cited page.
- Both APA and MLA formatting styles have specific guidelines for font, spacing, and headings.
Comparison of APA and MLA Formatting
While both APA and MLA formatting styles share some similarities, they also have distinct differences. The APA style is more commonly used in fields that require precise and technical writing, such as psychology, education, and business. The MLA style, on the other hand, is more commonly used in fields that require creative and interpretive writing, such as literature, language, and the arts.
| Formatting Style | APA | MLA |
|---|---|---|
| Font and Spacing | Times New Roman, 12 points, double spacing | Times New Roman, 12 points, double spacing |
| Headings | Hierarchical system of headings | Simple system of headings |
| In-Text Citations | Author-date system | Parenthetical system |
| Reference List | Reference list at the end of the paper | Works Cited page at the end of the paper |
Conclusion
In conclusion, APA and MLA formatting styles are two of the most widely used formatting styles in academic writing. While both styles share some similarities, they also have distinct differences that set them apart. The APA style is more commonly used in fields that require precise and technical writing, while the MLA style is more commonly used in fields that require creative and interpretive writing. By understanding the key features and differences between APA and MLA formatting styles, researchers and scholars can choose the best style for their research paper or essay and present their ideas and arguments in a clear and concise manner.
What is the main difference between APA and MLA formatting styles?
+The main difference between APA and MLA formatting styles is the way they handle in-text citations and reference lists. APA uses an author-date system for in-text citations and a reference list at the end of the paper, while MLA uses a parenthetical system for in-text citations and a Works Cited page at the end of the paper.
Which formatting style is more commonly used in the social sciences?
+The APA formatting style is more commonly used in the social sciences, including fields such as psychology, education, and business.
What is the purpose of using a specific formatting style in academic writing?
+The purpose of using a specific formatting style in academic writing is to provide a standardized format for presenting research findings and ideas, and to ensure that the writer’s work is credible, reliable, and easy to understand.



