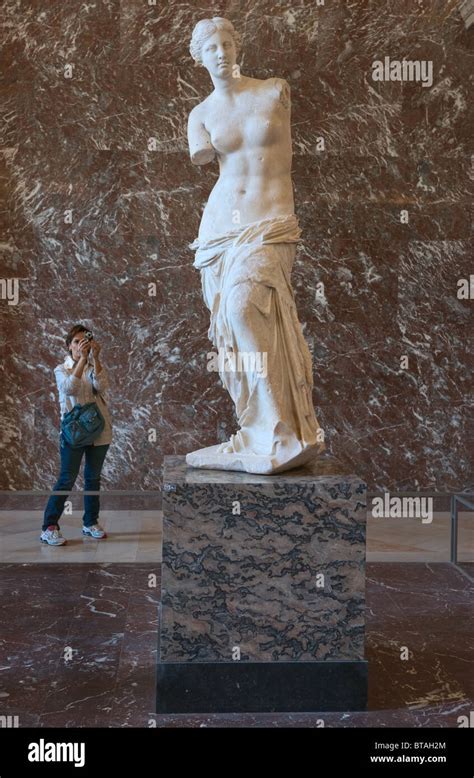
Aphrodite, the Greek goddess of love, beauty, and desire, has been a subject of fascination for centuries. Her mythological significance extends beyond her role in ancient Greek mythology, influencing art, literature, and culture to this day. Here are five key facts about Aphrodite, exploring her origins, powers, and impact on Western cultural heritage.
Key Points
- Aphrodite's origins are complex, with two distinct myths surrounding her birth, one involving her emergence from the sea and the other linking her to the Titans.
- She is renowned for her extraordinary beauty and her ability to inspire love and desire in both gods and mortals, often using her magical girdle to achieve this.
- Aphrodite's marital life is marked by her union with Hephaestus, although she is perhaps more famously known for her numerous affairs, including her long-standing relationship with Ares.
- Despite her association with love, Aphrodite's role in mythology also encompasses aspects of war and violence, particularly through her involvement with Ares.
- The worship of Aphrodite was widespread in the ancient Greek world, with significant cult centers in Cythera and Corinth, reflecting her importance in the religious and cultural practices of the time.
The Mythological Birth of Aphrodite

Aphrodite’s birth is a topic of dual mythology. In one version, she is born from the foam of the sea after the genitals of the Titan Uranus are thrown into the ocean by his son Cronus. This mythological account not only underscores her connection to the sea but also hints at her association with the primal forces of nature. In another myth, Aphrodite is described as the daughter of Zeus and Dione, although this version is less commonly cited in classical sources.
Aphrodite’s Powers and Symbols
Aphrodite is perhaps best known for her incredible beauty and her power to arouse desire in all who lay eyes on her. Her most famous symbol, the mirror, reflects not just her vanity but also her ability to see into the hearts of those who desire love. The rose and the myrtle are also associated with her, representing love and fidelity, respectively. Her magical girdle, given to her by Hephaestus, has the power to make anyone fall in love with the wearer, showcasing her control over the realm of love and desire.
| Mythological Figure | Association with Aphrodite |
|---|---|
| Hephaestus | Husband of Aphrodite, despite her numerous infidelities. |
| Ares | Aphrodite's most famous lover, highlighting her complex and often tumultuous love life. |
| Eros (Cupid) | Sometimes considered Aphrodite's son, symbolizing the arrow that strikes the heart and inspires love. |
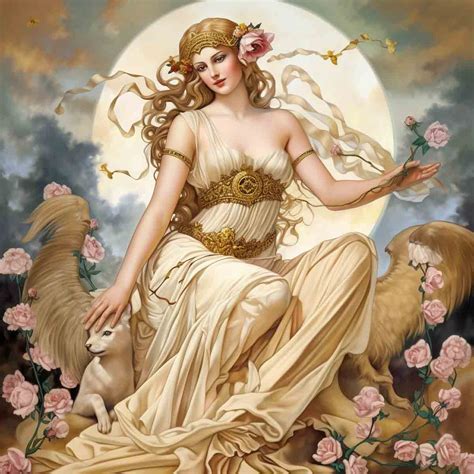

Aphrodite’s Marital Life and Affairs
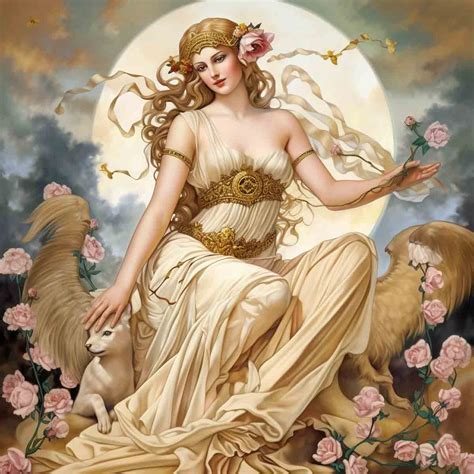

Despite being married to Hephaestus, the god of the forge, Aphrodite’s marital life was marked by her numerous affairs. Her most notable relationship outside of her marriage was with Ares, the god of war, reflecting the often-violent and passionate nature of their love. This affair, however, was not without consequence, as it was discovered by Hephaestus, leading to a dramatic and public shaming of the lovers. Aphrodite’s son with Ares, Phobos (Fear), further underscores the complex interplay between love, war, and the human psyche.
Cultural Impact and Worship
Aphrodite’s influence extends far beyond the confines of ancient Greek mythology. She has been a subject of countless works of art, from sculpture to literature, symbolizing the ideals of beauty and love. The worship of Aphrodite was significant in ancient Greece, with her cults often associated with fertility and prostitution, reflecting the multifaceted nature of her divine role. The island of Cythera and the city of Corinth were particularly important centers of her worship, highlighting her importance in the religious and cultural practices of the time.
What is Aphrodite's role in Greek mythology?
+Aphrodite is the goddess of love, beauty, and desire, known for her extraordinary beauty and her ability to inspire love in both gods and mortals.
How was Aphrodite born according to mythology?
+Aphrodite was born from the foam of the sea after the genitals of Uranus were thrown into the ocean, or alternatively, as the daughter of Zeus and Dione, though the former account is more commonly cited.
What symbols are associated with Aphrodite?
+Aphrodite is associated with several symbols, including the mirror, which reflects her beauty and insight into the hearts of those who desire love, and the rose and myrtle, representing love and fidelity, respectively.
In conclusion, Aphrodite’s enduring presence in Western cultural heritage is a testament to the timeless themes of love, beauty, and desire that she embodies. Through her complex character and multifaceted roles in mythology, Aphrodite continues to captivate and inspire, reflecting the deepest aspects of human emotion and experience.