Appendicitis is a medical emergency that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent serious complications. One of the most effective diagnostic tools for appendicitis is a computed tomography (CT) scan. A CT scan uses a combination of X-rays and computer technology to produce detailed cross-sectional images of the body, allowing doctors to visualize the appendix and surrounding tissues. In this article, we will explore the role of CT scans in diagnosing appendicitis, their benefits and limitations, and what patients can expect during the scanning process.
Key Points
- CT scans are a highly accurate diagnostic tool for appendicitis, with a sensitivity of 95-100% and a specificity of 95-100%.
- The scanning process typically takes 10-30 minutes, and patients may be required to drink a contrast agent to help visualize the appendix.
- CT scans can help doctors diagnose appendicitis by visualizing the appendix and surrounding tissues, and can also help identify other potential causes of abdominal pain.
- Radiation exposure from CT scans is a concern, particularly for younger patients, and alternative diagnostic tools such as ultrasound or MRI may be used in some cases.
- Early diagnosis and treatment of appendicitis are critical to preventing serious complications, and CT scans play a vital role in this process.
How CT Scans Diagnose Appendicitis
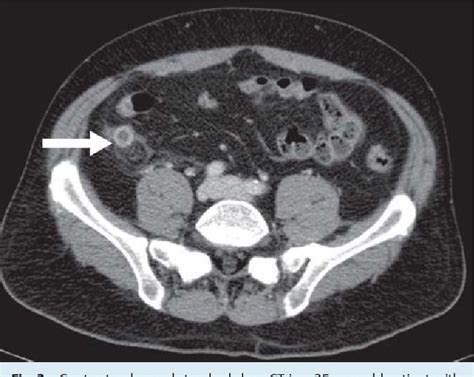
A CT scan can help diagnose appendicitis by visualizing the appendix and surrounding tissues. The scan can show if the appendix is inflamed, ruptured, or blocked, and can also help identify other potential causes of abdominal pain, such as kidney stones or diverticulitis. During the scanning process, patients lie on a table that slides into a large, doughnut-shaped machine, which takes X-ray images of the body from different angles. The images are then reconstructed into detailed cross-sectional images, which are interpreted by a radiologist.
Benefits of CT Scans for Appendicitis Diagnosis
CT scans have several benefits when it comes to diagnosing appendicitis. They are highly accurate, with a sensitivity of 95-100% and a specificity of 95-100%, meaning that they can correctly diagnose appendicitis in the vast majority of cases. CT scans are also quick and non-invasive, taking only 10-30 minutes to complete, and can be performed in an emergency setting. Additionally, CT scans can help doctors identify other potential causes of abdominal pain, which can help guide treatment and prevent unnecessary surgery.
| Diagnostic Tool | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|
| CT Scan | 95-100% | 95-100% |
| Ultrasound | 80-90% | 90-95% |
| MRI | 95-100% | 95-100% |
Limitations and Risks of CT Scans for Appendicitis Diagnosis
While CT scans are a highly effective diagnostic tool for appendicitis, they do have some limitations and risks. One of the main concerns is radiation exposure, particularly for younger patients, who are more susceptible to the effects of radiation. Additionally, CT scans may not be suitable for patients with certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease or allergies to contrast agents. In some cases, alternative diagnostic tools such as ultrasound or MRI may be used instead of CT scans.
Alternatives to CT Scans for Appendicitis Diagnosis
There are several alternative diagnostic tools that can be used to diagnose appendicitis, including ultrasound and MRI. Ultrasound is a non-invasive and radiation-free imaging modality that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the body. While ultrasound is not as accurate as CT scans for diagnosing appendicitis, it can be a useful diagnostic tool, particularly in patients who are pregnant or have certain medical conditions. MRI is another diagnostic tool that can be used to diagnose appendicitis, and has the advantage of being radiation-free and highly accurate. However, MRI scans are typically more expensive and time-consuming than CT scans, and may not be available in all emergency settings.
Early diagnosis and treatment of appendicitis are critical to preventing serious complications, and CT scans play a vital role in this process. By providing highly accurate and detailed images of the appendix and surrounding tissues, CT scans can help doctors diagnose appendicitis quickly and effectively, and guide treatment and surgery. While CT scans do have some limitations and risks, they remain a essential diagnostic tool in emergency medicine, and can help save lives by facilitating prompt and effective treatment of this medical emergency.
What is the purpose of a CT scan in diagnosing appendicitis?
+A CT scan is used to visualize the appendix and surrounding tissues, and to diagnose appendicitis by showing if the appendix is inflamed, ruptured, or blocked.
How accurate are CT scans in diagnosing appendicitis?
+CT scans are highly accurate in diagnosing appendicitis, with a sensitivity of 95-100% and a specificity of 95-100%.
What are the risks and limitations of CT scans for appendicitis diagnosis?
+The main risks and limitations of CT scans include radiation exposure, particularly for younger patients, and the potential for allergic reactions to contrast agents. Additionally, CT scans may not be suitable for patients with certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease.
What are the alternatives to CT scans for appendicitis diagnosis?
+Alternative diagnostic tools for appendicitis include ultrasound and MRI. Ultrasound is a non-invasive and radiation-free imaging modality that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the body, while MRI is a highly accurate and radiation-free diagnostic tool that can be used to diagnose appendicitis.
How long does a CT scan take to complete?
+A CT scan typically takes 10-30 minutes to complete, depending on the type of scan and the individual patient’s needs.



