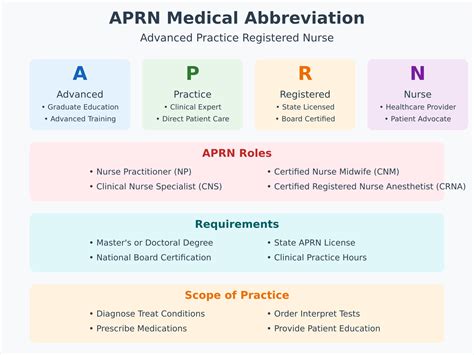
The term "APRN" is an abbreviation that stands for Advanced Practice Registered Nurse. In the medical field, APRNs are registered nurses who have acquired advanced education, training, and skills in a specific area of healthcare. They are authorized to provide high-quality patient care in a variety of settings, including hospitals, clinics, and community health organizations. APRNs are essential members of the healthcare team, working collaboratively with physicians and other healthcare professionals to deliver comprehensive and patient-centered care.
Role and Responsibilities of APRNs

APRNs are trained to perform a wide range of tasks, including diagnosing and treating illnesses, prescribing medications, ordering diagnostic tests, and developing treatment plans. They may specialize in a particular area of healthcare, such as pediatrics, gerontology, or oncology, and may work in a variety of settings, including primary care, acute care, or specialty care. APRNs are also involved in health promotion, disease prevention, and health education, and may provide guidance and support to patients and their families.
Types of APRNs
There are several types of APRNs, including Nurse Practitioners (NPs), Certified Nurse Midwives (CNMs), Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetists (CRNAs), and Clinical Nurse Specialists (CNSs). Each type of APRN has its own unique role and responsibilities, and may require specialized education and training. For example, NPs may provide primary and specialty care to patients, while CNMs may provide prenatal, delivery, and postpartum care to women. CRNAs, on the other hand, may provide anesthesia care to patients undergoing surgery or other medical procedures.
| Type of APRN | Description |
|---|---|
| Nurse Practitioner (NP) | Provides primary and specialty care to patients |
| Certified Nurse Midwife (CNM) | Provides prenatal, delivery, and postpartum care to women |
| Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA) | Provides anesthesia care to patients undergoing surgery or other medical procedures |
| Clinical Nurse Specialist (CNS) | Provides specialized care to patients with complex health needs |

In order to become an APRN, one must first earn a bachelor's degree in nursing and obtain a registered nurse (RN) license. APRNs must then complete a master's or doctoral degree program in nursing, which includes advanced coursework and clinical training in a specific area of healthcare. APRNs must also obtain certification in their area of specialty, which requires passing a national certification exam.
Benefits of APRNs in Healthcare

The benefits of APRNs in healthcare are numerous. APRNs are able to provide high-quality patient care, improve health outcomes, and reduce healthcare costs. They are also able to provide guidance and support to patients and their families, and may help to reduce the burden on primary care physicians. Additionally, APRNs may be more likely to work in underserved areas, where access to healthcare may be limited.
Challenges Facing APRNs
Despite the many benefits of APRNs in healthcare, there are also several challenges that they may face. One of the main challenges is the variability in scope of practice laws and regulations, which can limit their ability to provide care to patients. APRNs may also face barriers to reimbursement, which can make it difficult for them to sustain their practices. Additionally, APRNs may experience role confusion and lack of recognition, which can impact their ability to provide high-quality patient care.
Key Points
- APRNs are advanced practice registered nurses who provide high-quality patient care in a variety of settings
- APRNs may specialize in a particular area of healthcare, such as pediatrics or oncology
- There are several types of APRNs, including NPs, CNMs, CRNAs, and CNSs
- APRNs must complete a master's or doctoral degree program in nursing and obtain certification in their area of specialty
- APRNs play a critical role in the healthcare system, improving health outcomes and reducing healthcare costs
In conclusion, APRNs are essential members of the healthcare team, providing high-quality patient care and improving health outcomes. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, the demand for APRNs is likely to increase, making them an essential part of the healthcare team. By understanding the role and responsibilities of APRNs, as well as the challenges they may face, we can work to support and empower these advanced practice registered nurses to provide the best possible care to patients.
What is the role of an APRN in healthcare?
+APRNs are advanced practice registered nurses who provide high-quality patient care in a variety of settings. They may diagnose and treat illnesses, prescribe medications, order diagnostic tests, and develop treatment plans.
What types of APRNs are there?
+There are several types of APRNs, including Nurse Practitioners (NPs), Certified Nurse Midwives (CNMs), Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetists (CRNAs), and Clinical Nurse Specialists (CNSs).
What education and training is required to become an APRN?
+To become an APRN, one must first earn a bachelor's degree in nursing and obtain a registered nurse (RN) license. APRNs must then complete a master's or doctoral degree program in nursing, which includes advanced coursework and clinical training in a specific area of healthcare.
By providing high-quality patient care and improving health outcomes, APRNs are essential members of the healthcare team. As the demand for APRNs continues to grow, it is essential that we support and empower these advanced practice registered nurses to provide the best possible care to patients.
Meta Description: Learn about the role and responsibilities of Advanced Practice Registered Nurses (APRNs) in healthcare, including their types, education, and benefits. Discover how APRNs improve health outcomes and reduce healthcare costs. (149 characters)