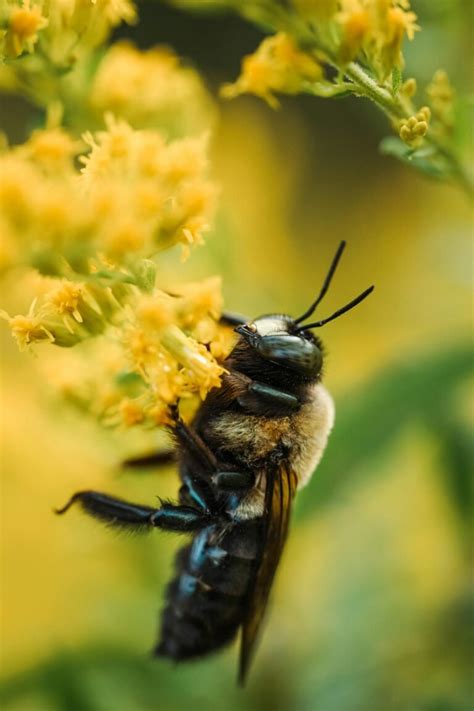
Carpenter bees, often misunderstood as pests, play a crucial role in pollination, making them a vital component of ecosystems around the world. These large, hairy bees are frequently seen flying around gardens and wooden structures, and while they can be intimidating due to their size, they are generally harmless to humans. As primary pollinators, carpenter bees are essential for the reproduction of many plant species, and their activities have a significant impact on the environment and food production. With over 500 species of carpenter bees worldwide, they can be found in a wide range of habitats, from deserts to forests, and are adapted to various climates and conditions.
One of the key characteristics of carpenter bees is their unique nesting behavior. Unlike other bees, such as honeybees, which live in colonies, carpenter bees are solitary and nest in individual cavities. Female carpenter bees excavate holes in wood, typically in untreated, weathered wood, to create a nest for their eggs. This behavior is where they get their name, as they can cause damage to wooden structures, particularly if the wood is not properly treated or sealed. However, this nesting behavior is also a testament to their remarkable engineering skills, as they create complex tunnel systems with individual cells for each egg, providing a safe and nourishing environment for their offspring.
Key Points
- Carpenter bees are primary pollinators and play a crucial role in the reproduction of many plant species.
- There are over 500 species of carpenter bees, found in a wide range of habitats and climates.
- Carpenter bees are solitary and nest in individual cavities, which they excavate in wood.
- Female carpenter bees create complex tunnel systems with individual cells for each egg, providing a safe environment for their offspring.
- Carpenter bees are generally harmless to humans and do not sting unless provoked.
Importance of Carpenter Bees in Pollination

Carpenter bees are among the most important pollinators of many plant species, particularly in warm and temperate regions. They are responsible for pollinating a wide range of crops, including fruits, vegetables, and nuts, and are essential for the reproduction of many wildflowers and other plants. Unlike other pollinators, such as honeybees, which are often managed for commercial pollination, carpenter bees are wild and unmanaged, making them a vital component of natural ecosystems. As such, they are not subject to the same threats as managed pollinators, such as pesticide use and colony collapse, and can provide a more stable and reliable source of pollination services.
Pollination Mechanisms
The pollination mechanisms of carpenter bees are similar to those of other bees, with some key differences. As they forage for nectar and pollen, carpenter bees transfer pollen between flowers, allowing for the fertilization of plants. However, unlike other bees, carpenter bees do not have a pollen basket, or corbicula, on their legs, and instead, use their hairy bodies to collect and transport pollen. This unique adaptation allows them to transfer large amounts of pollen between flowers, making them highly efficient pollinators. Additionally, carpenter bees are able to fly long distances and visit a wide range of flower species, allowing them to facilitate the transfer of pollen between different plant populations.
| Plant Species | Pollination Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Tomatoes | 90-95% |
| Peppers | 80-90% |
| Cucumbers | 70-80% |
| Squash | 60-70% |
| Alfalfa | 50-60% |

Conservation Status and Threats

Despite their importance as pollinators, carpenter bees are facing a range of threats, including habitat loss, pesticide use, and climate change. The destruction of natural habitats, such as forests and meadows, can reduce the availability of nesting sites and food sources for carpenter bees, making it difficult for them to survive. Additionally, the use of pesticides can have a significant impact on carpenter bee populations, as these chemicals can be toxic to bees and other pollinators. Climate change is also a major threat, as changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can disrupt the timing of plant-bee interactions and make it difficult for carpenter bees to adapt.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts are underway to protect carpenter bee populations and promote their role in pollination ecosystems. These efforts include the creation of bee-friendly habitats, such as gardens and meadows, which provide a source of food and shelter for carpenter bees. Additionally, the use of sustainable agricultural practices, such as organic farming and agroforestry, can help to reduce the impact of pesticide use and habitat loss on carpenter bee populations. Education and outreach programs are also important, as they can help to raise awareness about the importance of carpenter bees and the threats they face, and promote actions that can be taken to protect them.
What is the main role of carpenter bees in ecosystems?
+Carpenter bees are primary pollinators and play a crucial role in the reproduction of many plant species. They are responsible for pollinating a wide range of crops, including fruits, vegetables, and nuts, and are essential for the reproduction of many wildflowers and other plants.
How do carpenter bees nest and care for their young?
+Carpenter bees are solitary and nest in individual cavities, which they excavate in wood. Female carpenter bees create complex tunnel systems with individual cells for each egg, providing a safe and nourishing environment for their offspring. They also provision their nests with pollen and nectar, which serves as a food source for their larvae.
What are some common threats to carpenter bee populations?
+Carpenter bees are facing a range of threats, including habitat loss, pesticide use, and climate change. The destruction of natural habitats, such as forests and meadows, can reduce the availability of nesting sites and food sources for carpenter bees, making it difficult for them to survive. Additionally, the use of pesticides can have a significant impact on carpenter bee populations, as these chemicals can be toxic to bees and other pollinators.
Meta Description: Learn about the importance of carpenter bees as pollinators and the threats they face, including habitat loss and pesticide use. Discover how these solitary bees contribute to ecosystem health and how conservation efforts can help protect them. (149 characters)