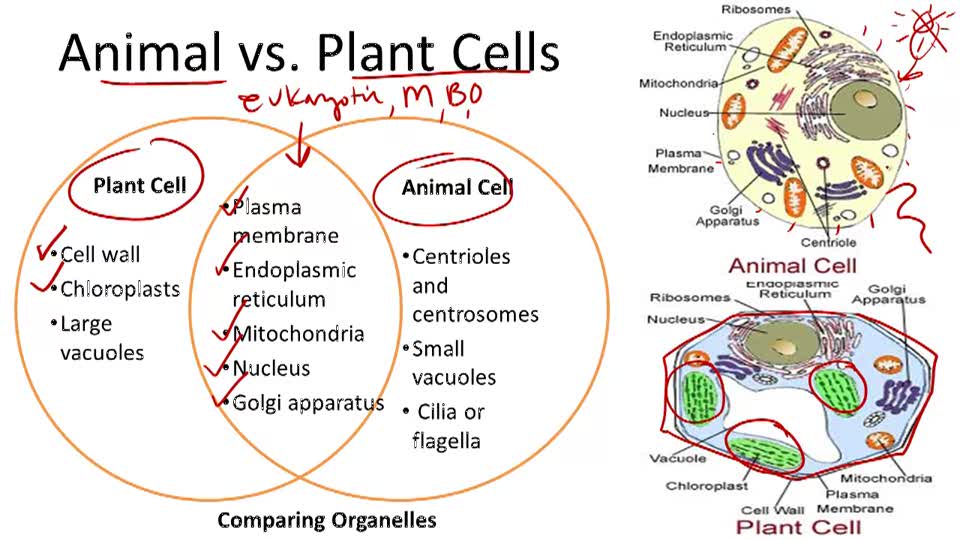
Plant cells, the fundamental building blocks of plants, are a type of eukaryotic cell. Eukaryotic cells are characterized by the presence of a true nucleus, which is surrounded by a nuclear envelope, and other membrane-bound organelles. This distinguishes them from prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria, which lack these features. The eukaryotic nature of plant cells is significant because it allows for a high degree of complexity and specialization, enabling plants to carry out a wide range of functions necessary for their survival and reproduction.
The structure of plant cells is highly specialized, with various organelles working together to perform specific tasks. The cell wall, composed primarily of cellulose, provides support and protection to the cell. The plasma membrane, also known as the cell membrane, regulates the movement of materials in and out of the cell. Inside the cell, the cytoplasm is home to various organelles, including the nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and vacuoles. Each of these organelles plays a crucial role in the functioning of the plant cell, from energy production and photosynthesis to storage and waste removal.
Key Points
- Plant cells are eukaryotic, meaning they have a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
- The cell wall provides support and protection to the cell.
- Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants produce energy from sunlight.
- Vacuoles are involved in storage and waste removal within the cell.
- The nucleus contains the cell's genetic material and is responsible for controlling the cell's activities.
Characteristics of Eukaryotic Plant Cells
Eukaryotic plant cells exhibit several key characteristics that distinguish them from prokaryotic cells. These include the presence of a true nucleus, the division of the cell into distinct organelles, and the use of a process called mitosis to reproduce. Mitosis is a type of cell division that results in two daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This ensures that the genetic material is duplicated accurately and that the new cells receive a complete set of chromosomes.
In addition to these characteristics, plant cells also have a number of specialized features that allow them to carry out their unique functions. For example, chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells that are responsible for photosynthesis. These organelles contain the pigment chlorophyll, which absorbs sunlight and uses it to power the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. This process is essential for the survival of plants and, by extension, for the survival of many other organisms that rely on plants for food and oxygen.
Importance of Chloroplasts in Plant Cells
Chloroplasts are a critical component of plant cells, and their function is essential for the survival of plants. These organelles are responsible for absorbing sunlight and using it to power the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. This process, known as photosynthesis, is the primary means by which plants produce energy. Without chloroplasts, plants would be unable to carry out photosynthesis and would therefore be unable to produce the energy they need to survive.
| Organelle | Function |
|---|---|
| Nucleus | Contains the cell's genetic material and controls the cell's activities. |
| Chloroplasts | Responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants produce energy from sunlight. |
| Mitochondria | Involved in the production of energy for the cell through the process of cellular respiration. |
| Vacuoles | Involved in storage and waste removal within the cell. |

Practical Applications of Eukaryotic Plant Cell Knowledge

Understanding the structure and function of eukaryotic plant cells has a number of practical applications. For example, knowledge of photosynthesis and the role of chloroplasts has led to the development of more efficient methods of crop production and has improved our understanding of the impact of environmental factors on plant growth. Additionally, the study of plant cells has led to the development of new technologies, such as genetic engineering, which allows for the introduction of desirable traits into plants.
In conclusion, the eukaryotic nature of plant cells is a critical factor in their ability to carry out a wide range of functions necessary for their survival and reproduction. The unique characteristics of these cells, including the presence of chloroplasts and the ability to carry out photosynthesis, have allowed plants to thrive in a wide range of environments and have played a critical role in the development of life on Earth. By continuing to study and understand the structure and function of eukaryotic plant cells, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and diversity of life on our planet.
What is the primary function of chloroplasts in plant cells?
+The primary function of chloroplasts is to carry out photosynthesis, the process by which plants produce energy from sunlight.
What is the role of the nucleus in a eukaryotic plant cell?
+The nucleus contains the cell’s genetic material and is responsible for controlling the cell’s activities.
What is the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
+Eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, while prokaryotic cells lack these features.