Sinus infections, also known as sinusitis, are a common health issue affecting millions of people worldwide. The question of whether sinus infections are contagious is a topic of interest for many, especially during cold and flu seasons when the risk of infection transmission is higher. To answer this question, it's essential to understand the causes and types of sinus infections, as well as the mechanisms by which they can be spread.
Understanding Sinus Infections

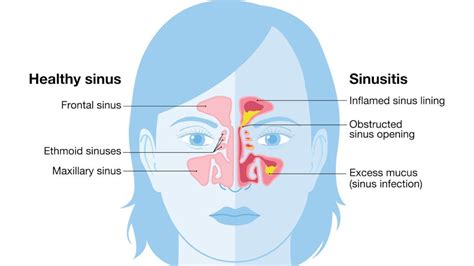
Sinus infections occur when the sinuses, which are air-filled cavities located behind the forehead, cheeks, and eyes, become inflamed or infected. This inflammation can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or fungi, and it often leads to symptoms such as nasal congestion, facial pain, and thick, yellow or green nasal discharge. Sinus infections can be acute, lasting less than four weeks, or chronic, persisting for more than 12 weeks.
Causes of Sinus Infections
The primary causes of sinus infections include viral upper respiratory tract infections, such as the common cold or flu, which can lead to secondary bacterial infections. Allergies, environmental factors like air pollution, and anatomical issues, such as a deviated septum, can also contribute to the development of sinusitis. Understanding these causes is crucial for determining the potential for contagion.
Key Points
- Sinus infections can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or fungi.
- The primary cause of sinus infections is often a viral upper respiratory tract infection.
- Allergies and environmental factors can increase the risk of developing sinusitis.
- Anatomical issues, such as a deviated septum, can also contribute to sinus infections.
- The contagiousness of sinus infections depends on the underlying cause.
Are Sinus Infections Contagious?
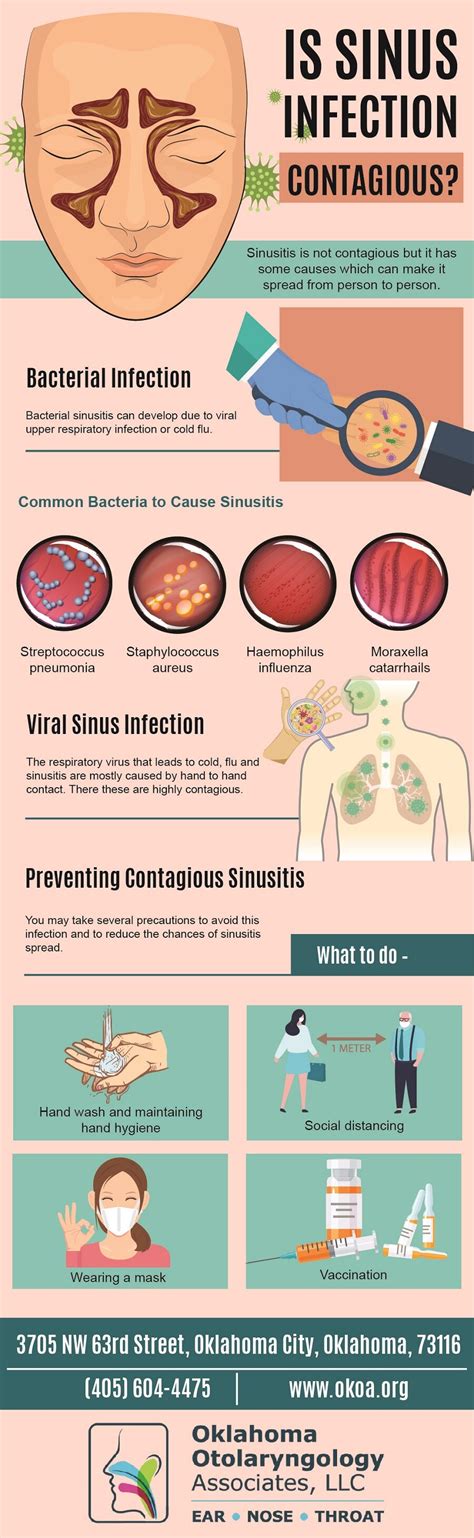
The contagiousness of sinus infections largely depends on the underlying cause. Viral sinus infections, which are the most common type, can be contagious because they are caused by viruses that can be spread from person to person. This typically occurs through respiratory droplets that are released when an infected person talks, coughs, or sneezes. Bacterial sinus infections, on the other hand, are generally not contagious, as they are not caused by a contagious agent but rather by the overgrowth of bacteria in the sinuses, often following a viral infection.
Transmission of Sinus Infections
The transmission of viral sinus infections can occur through close contact with an infected person, such as shaking hands or sharing utensils, and through airborne transmission when the virus is present in respiratory droplets. Practicing good hygiene, such as frequent hand washing and avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick, can help reduce the risk of transmission. For bacterial sinus infections, while they are not contagious, addressing the underlying causes, such as allergies or anatomical issues, and treating any secondary infections is crucial for recovery.
| Type of Sinus Infection | Contagious | Transmission Method |
|---|---|---|
| Viral | Yes | Respiratory droplets, close contact |
| Bacterial | No | Not applicable |
| Fungal | No | Not applicable |
Prevention and Treatment
Preventing the spread of sinus infections involves practices that reduce the transmission of viral infections, such as frequent hand washing, avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick, and not sharing personal items. For individuals who have a sinus infection, practicing good hygiene, staying hydrated, and using a humidifier to relieve congestion can help manage symptoms. Treatment for sinus infections depends on the cause and may include medications to alleviate symptoms, antibiotics for bacterial infections, and in some cases, surgery to address anatomical issues or to drain the sinuses.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for sinus infections are varied and depend on the severity and cause of the infection. For mild cases, over-the-counter medications and home remedies may suffice. However, for more severe or chronic infections, prescription medications or surgical interventions may be necessary. It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
How can I prevent getting a sinus infection?
+To prevent getting a sinus infection, practice good hygiene by washing your hands frequently, avoid close contact with individuals who are sick, and keep your environment clean. Also, managing allergies and avoiding irritants can help reduce your risk.
What are the symptoms of a sinus infection?
+The symptoms of a sinus infection can include nasal congestion, facial pain, thick, yellow or green nasal discharge, and a reduced sense of smell. The severity of these symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity of the infection.
Can sinus infections be treated without antibiotics?
+Yes, many sinus infections can be treated without antibiotics, especially if they are viral in nature. Treatment may focus on relieving symptoms with over-the-counter medications, using a humidifier, and staying hydrated. However, bacterial sinus infections may require antibiotic treatment.
In conclusion, while not all sinus infections are contagious, understanding the cause of the infection is crucial for determining the risk of transmission. By practicing good hygiene, managing allergies, and seeking appropriate medical care when symptoms persist or worsen, individuals can reduce their risk of developing sinus infections and prevent the spread of contagious types. The key to effective management and prevention lies in a comprehensive approach that includes awareness of the infection’s cause, adherence to preventive measures, and timely medical intervention when necessary.