The concept of acids and bases has been a cornerstone of chemistry for centuries, with various definitions and theories emerging over time to explain their properties and behavior. One of the most influential and enduring definitions of an acid is the Arrhenius acid definition, proposed by Swedish chemist Svante Arrhenius in 1887. This definition, which focuses on the dissociation of acids in water, has had a profound impact on our understanding of acid-base chemistry and continues to be widely used today.
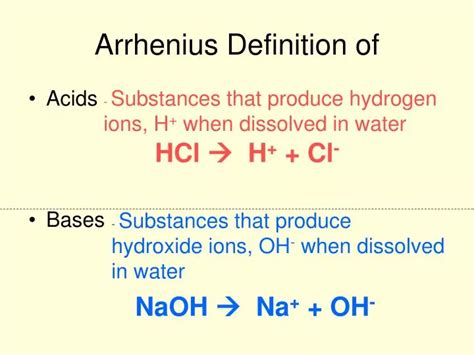
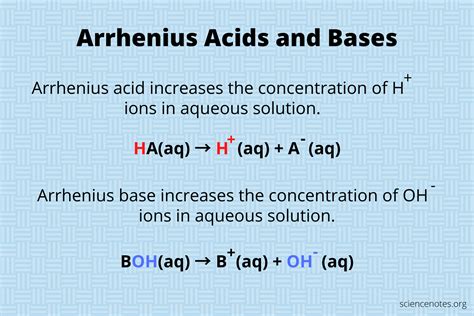
According to the Arrhenius acid definition, an acid is a substance that increases the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution. This definition is based on the idea that acids are substances that donate H+ ions when dissolved in water, resulting in an increase in the acidity of the solution. For example, when hydrochloric acid (HCl) is dissolved in water, it dissociates into H+ and Cl- ions, increasing the concentration of H+ ions in the solution and making it more acidic. The Arrhenius definition also recognizes that bases are substances that increase the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-) in a solution, which is the converse of acid behavior.
Key Points
- The Arrhenius acid definition focuses on the dissociation of acids in water, resulting in an increase in H+ ion concentration.
- Acids are substances that donate H+ ions when dissolved in water, while bases are substances that increase the concentration of OH- ions.
- The Arrhenius definition is widely used in chemistry and has had a significant impact on our understanding of acid-base behavior.
- This definition is limited to aqueous solutions and does not account for non-aqueous acid-base behavior.
- Other definitions, such as the Bronsted-Lowry and Lewis definitions, have expanded our understanding of acid-base chemistry beyond the Arrhenius definition.
A Detailed Explanation of the Arrhenius Acid Definition
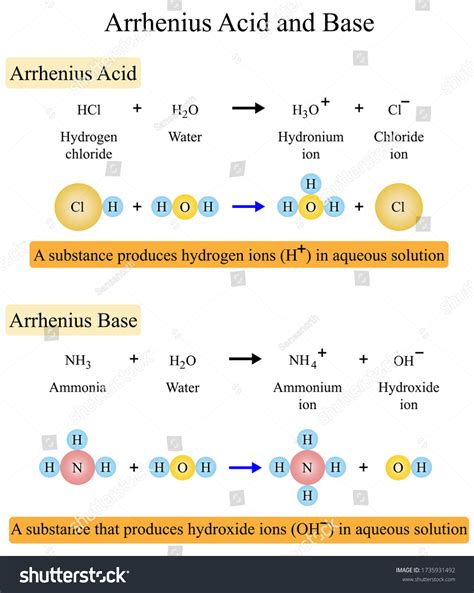
The Arrhenius acid definition is based on the idea that acids are substances that donate H+ ions when dissolved in water. This definition is supported by the fact that many acids, such as HCl, H2SO4, and HNO3, dissociate into H+ and anion ions when dissolved in water, resulting in an increase in the acidity of the solution. The Arrhenius definition also recognizes that the strength of an acid is related to its ability to donate H+ ions, with stronger acids donating more H+ ions than weaker acids.
Limitations of the Arrhenius Acid Definition
While the Arrhenius acid definition has been widely used and has contributed significantly to our understanding of acid-base chemistry, it has some limitations. One of the main limitations is that it only applies to aqueous solutions and does not account for non-aqueous acid-base behavior. This means that the Arrhenius definition does not provide a complete understanding of acid-base chemistry, particularly in non-aqueous solvents such as organic solvents or ionic liquids.
| Acid | Dissociation Reaction | Concentration of H+ Ions |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) | HCl → H+ + Cl- | High |
| Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4) | H2SO4 → 2H+ + SO42- | High |
| Nitric Acid (HNO3) | HNO3 → H+ + NO3- | High |
Comparison with Other Acid Definitions
The Arrhenius acid definition is not the only definition of an acid, and other definitions have been proposed to expand our understanding of acid-base chemistry. The Bronsted-Lowry definition, for example, defines an acid as a substance that donates a proton (H+), while the Lewis definition defines an acid as a substance that accepts an electron pair. These definitions are more general than the Arrhenius definition and can be applied to non-aqueous solutions and other types of acid-base behavior.
Broader Implications of the Arrhenius Acid Definition
The Arrhenius acid definition has had a significant impact on our understanding of acid-base chemistry and has far-reaching implications in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and medicine. The definition has been used to develop new theories and models of acid-base behavior, such as the concept of acid dissociation constants (Ka) and the theory of acid-base titration. Additionally, the Arrhenius definition has been applied in various practical contexts, such as the development of new materials and the design of chemical processes.
What is the main limitation of the Arrhenius acid definition?
+The main limitation of the Arrhenius acid definition is that it only applies to aqueous solutions and does not account for non-aqueous acid-base behavior.
How does the Arrhenius acid definition differ from the Bronsted-Lowry definition?
+The Arrhenius acid definition focuses on the dissociation of acids in water, while the Bronsted-Lowry definition defines an acid as a substance that donates a proton (H+). The Bronsted-Lowry definition is more general and can be applied to non-aqueous solutions.
What is the significance of the Arrhenius acid definition in chemistry?
+The Arrhenius acid definition has had a significant impact on our understanding of acid-base chemistry and has been widely used in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and medicine. It has been used to develop new theories and models of acid-base behavior and has been applied in various practical contexts.
In conclusion, the Arrhenius acid definition has been a cornerstone of acid-base chemistry for over a century and continues to be widely used today. While it has some limitations, it has provided a fundamental understanding of acid-base behavior and has been instrumental in shaping our understanding of chemistry. By considering the Arrhenius acid definition in conjunction with other definitions, such as the Bronsted-Lowry and Lewis definitions, we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of acid-base chemistry and its applications in various fields.