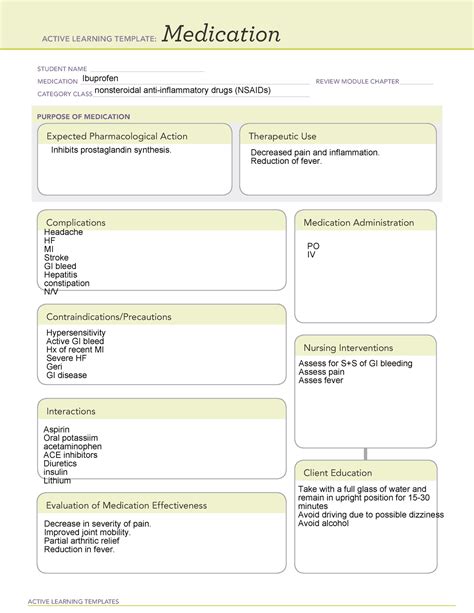
Antipsychotic medications, such as those used to treat schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, have been associated with a range of side effects, including extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS), which can be distressing and debilitating for patients. One approach to minimizing the risk of EPS is the use of atypical antipsychotics, which have been found to have a more favorable side effect profile compared to typical antipsychotics. However, despite their advantages, atypical antipsychotics can still cause significant side effects, including weight gain, metabolic changes, and sedation.
Introduction to Atypical Antipsychotics
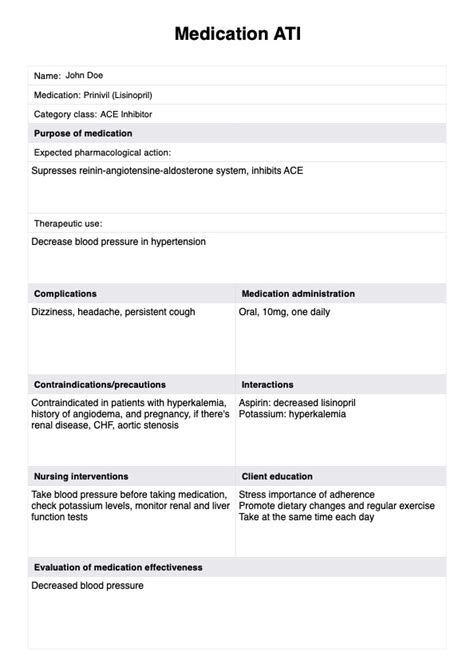
Atypical antipsychotics, also known as second-generation antipsychotics, are a class of medications that have been developed to treat psychiatric disorders, including schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. These medications are thought to work by modulating the activity of neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and serotonin, which are involved in mood regulation and other cognitive processes. Examples of atypical antipsychotics include risperidone, olanzapine, and quetiapine, among others. While atypical antipsychotics have been found to be effective in reducing symptoms of psychosis, they can also cause a range of side effects, including weight gain, metabolic changes, and sedation.
Common Side Effects of Atypical Antipsychotics
One of the most significant side effects of atypical antipsychotics is weight gain, which can be substantial and lead to an increased risk of metabolic disorders, such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease. According to a study published in the Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology, the average weight gain associated with atypical antipsychotics is approximately 4-6 kg (8.8-13.2 lbs) over a period of 12 weeks. Additionally, atypical antipsychotics can cause changes in metabolic parameters, including increased triglycerides and LDL cholesterol, which can further increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
| Atypical Antipsychotic | Weight Gain (kg) | Metabolic Changes |
|---|---|---|
| Risperidone | 2.1-3.5 | Increased triglycerides and LDL cholesterol |
| Olanzapine | 4.2-6.1 | Increased triglycerides, LDL cholesterol, and glucose |
| Quetiapine | 1.8-3.2 | Increased triglycerides and LDL cholesterol |
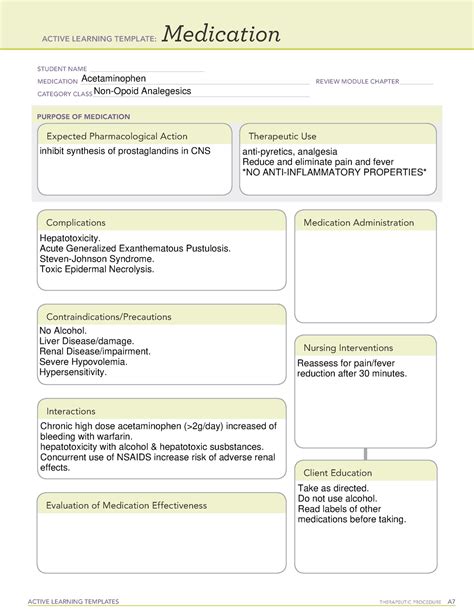
Medication Management and Monitoring

Effective medication management and monitoring are critical to minimizing the risks associated with atypical antipsychotics. Clinicians should carefully assess patients for any pre-existing medical conditions, such as diabetes or cardiovascular disease, and monitor them regularly for signs of weight gain, metabolic changes, and other side effects. Additionally, clinicians should consider alternative treatments, such as lifestyle interventions or other medications, to mitigate the risks associated with atypical antipsychotics.
Alternative Treatments and Lifestyle Interventions
There are several alternative treatments and lifestyle interventions that can help mitigate the risks associated with atypical antipsychotics. For example, lifestyle interventions, such as diet and exercise, can help reduce weight gain and improve metabolic parameters. Additionally, other medications, such as metformin, can help reduce the risk of metabolic disturbances. Clinicians should carefully consider these alternatives and discuss them with patients as part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
Key Points
- Atypical antipsychotics are associated with a range of side effects, including weight gain and metabolic changes.
- Clinicians should carefully monitor patients for signs of weight gain and metabolic disturbances.
- Alternative treatments, such as lifestyle interventions and other medications, can help mitigate the risks associated with atypical antipsychotics.
- Effective medication management and monitoring are critical to minimizing the risks associated with atypical antipsychotics.
- Clinicians should consider the potential risks and benefits of atypical antipsychotics and discuss them with patients as part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, atypical antipsychotics are a class of medications that have been developed to treat psychiatric disorders, including schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. While these medications have been found to be effective in reducing symptoms of psychosis, they can also cause a range of side effects, including weight gain and metabolic changes. Clinicians should carefully consider the potential risks and benefits of atypical antipsychotics and discuss them with patients as part of a comprehensive treatment plan. Future research should focus on developing new treatments and interventions that can help mitigate the risks associated with atypical antipsychotics and improve patient outcomes.
What are atypical antipsychotics?
+Atypical antipsychotics are a class of medications that have been developed to treat psychiatric disorders, including schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
What are the common side effects of atypical antipsychotics?
+The common side effects of atypical antipsychotics include weight gain, metabolic changes, and sedation.
How can clinicians minimize the risks associated with atypical antipsychotics?
+Clinicians can minimize the risks associated with atypical antipsychotics by carefully monitoring patients for signs of weight gain and metabolic disturbances, and considering alternative treatments or lifestyle interventions to mitigate these risks.