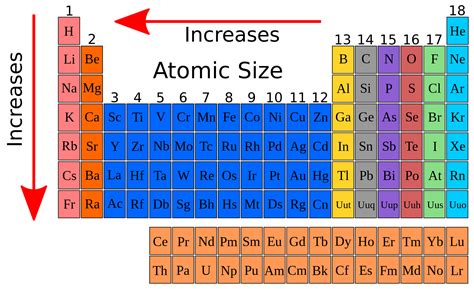
The concept of atomic size is a fundamental aspect of chemistry, playing a crucial role in understanding the properties and behavior of elements in the periodic table. Atomic size, also known as atomic radius, refers to the distance from the nucleus of an atom to the outermost electron. This concept is essential in explaining various phenomena, including the trends and patterns observed in the periodic table. In this article, we will delve into the concept of atomic size, its significance, and how it varies across different elements in the periodic table.
Key Points
- The atomic size of an element decreases as we move from left to right across a period due to the increase in effective nuclear charge.
- Atomic size increases as we move down a group in the periodic table due to the addition of new energy levels and the decrease in effective nuclear charge.
- The atomic size of an element can significantly influence its chemical properties, such as reactivity and electronegativity.
- Understanding atomic size is crucial in explaining various chemical phenomena, including bond formation and the behavior of molecules.
- Atomic size can be measured using various methods, including X-ray diffraction and spectroscopy.
Understanding Atomic Size

Atomic size is a critical parameter in chemistry, as it influences various chemical properties and behaviors. The size of an atom is determined by the distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron, which is also known as the valence electron. The atomic size of an element can be measured using various methods, including X-ray diffraction and spectroscopy. These methods provide valuable insights into the structure and properties of atoms, allowing us to better understand the behavior of elements in the periodic table.
Factors Influencing Atomic Size
Several factors influence the atomic size of an element, including the effective nuclear charge, the number of energy levels, and the electron configuration. The effective nuclear charge refers to the net positive charge experienced by an electron in an atom, which is influenced by the number of protons in the nucleus and the number of electrons in the inner energy levels. As we move from left to right across a period, the effective nuclear charge increases, resulting in a decrease in atomic size. In contrast, as we move down a group, the number of energy levels increases, and the effective nuclear charge decreases, resulting in an increase in atomic size.
| Element | Atomic Number | Atomic Size (pm) |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 1 | 37 |
| Helium | 2 | 32 |
| Lithium | 3 | 152 |
| Beryllium | 4 | 112 |
| Boron | 5 | 87 |
| Carbon | 6 | 67 |
| Nitrogen | 7 | 56 |
| Oxygen | 8 | 48 |
| Fluorine | 9 | 42 |
| Neon | 10 | 38 |
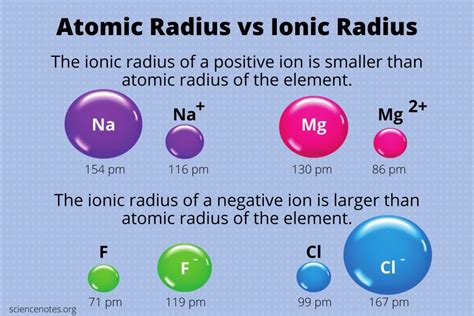
Trends in Atomic Size
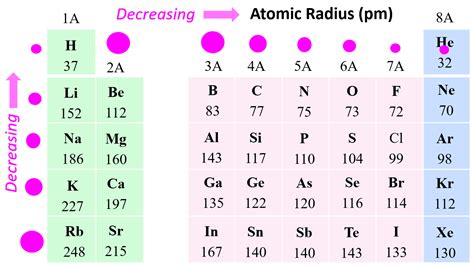
The atomic size of elements in the periodic table exhibits several trends and patterns. As we move from left to right across a period, the atomic size decreases due to the increase in effective nuclear charge. In contrast, as we move down a group, the atomic size increases due to the addition of new energy levels and the decrease in effective nuclear charge. These trends are essential in understanding the chemical properties and behaviors of elements, including their reactivity, electronegativity, and ability to form bonds with other elements.
Importance of Atomic Size
The atomic size of an element plays a significant role in determining its chemical properties and behaviors. The size of an atom influences its ability to form bonds with other elements, which is critical in understanding the structure and properties of molecules. Additionally, the atomic size of an element can influence its reactivity, with smaller atoms tend to be more reactive due to their higher effective nuclear charge. Understanding the relationship between atomic size and chemical properties is essential in explaining various chemical phenomena and predicting the behavior of elements and their compounds.
What is the relationship between atomic size and chemical properties?
+The atomic size of an element plays a significant role in determining its chemical properties and behaviors. The size of an atom influences its ability to form bonds with other elements, which is critical in understanding the structure and properties of molecules.
How does atomic size vary across different elements in the periodic table?
+The atomic size of elements in the periodic table exhibits several trends and patterns. As we move from left to right across a period, the atomic size decreases due to the increase in effective nuclear charge. In contrast, as we move down a group, the atomic size increases due to the addition of new energy levels and the decrease in effective nuclear charge.
What methods can be used to measure atomic size?
+Atomic size can be measured using various methods, including X-ray diffraction and spectroscopy. These methods provide valuable insights into the structure and properties of atoms, allowing us to better understand the behavior of elements in the periodic table.
Meta Description: Understanding atomic size is crucial in chemistry, as it influences various chemical properties and behaviors. Learn about the trends and patterns in atomic size, its significance, and how it varies across different elements in the periodic table.