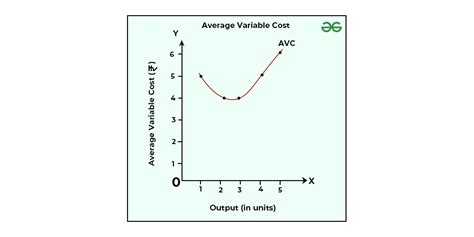
The concept of average variable cost (AVC) is a fundamental principle in microeconomics, playing a crucial role in a firm's decision-making process regarding production and pricing strategies. Average variable cost refers to the total variable costs incurred by a firm divided by the quantity of output produced. It essentially measures the average cost of producing one additional unit of a good or service, excluding fixed costs. Understanding AVC is vital for businesses to optimize their production levels, minimize costs, and maximize profits. Here, we will delve into five key aspects of average variable cost and its implications for firms.
Key Points
- Definition and calculation of average variable cost
- Relationship between average variable cost and marginal cost
- Impact of average variable cost on production decisions
- Role of average variable cost in pricing strategies
- Factors influencing average variable cost
Understanding Average Variable Cost
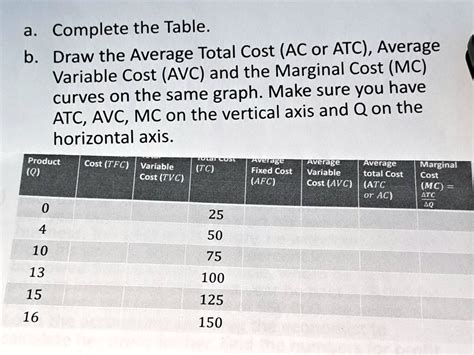
Average variable cost is calculated by dividing the total variable costs by the quantity of output. The formula for AVC is: AVC = TVC / Q, where TVC represents total variable costs and Q represents the quantity produced. For instance, if a firm incurs total variable costs of 1,000 to produce 100 units of a product, the average variable cost would be 10 per unit. This metric provides valuable insights into the efficiency of a firm’s production process and helps in identifying areas where costs can be minimized.
Relationship Between Average Variable Cost and Marginal Cost
The relationship between average variable cost and marginal cost (MC) is significant in economic analysis. Marginal cost represents the change in total cost that arises from producing one additional unit of output. When marginal cost is less than average variable cost, the production of an additional unit reduces the average variable cost. Conversely, when marginal cost exceeds average variable cost, producing more units increases the average variable cost. This relationship is crucial for firms to determine the optimal production level where MC equals AVC, ensuring that production is at its most efficient point.
| Production Level | Total Variable Cost | Average Variable Cost | Marginal Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 units | $1,000 | $10 | $9 |
| 200 units | $1,800 | $9 | $8 |
| 300 units | $2,700 | $9 | $9 |
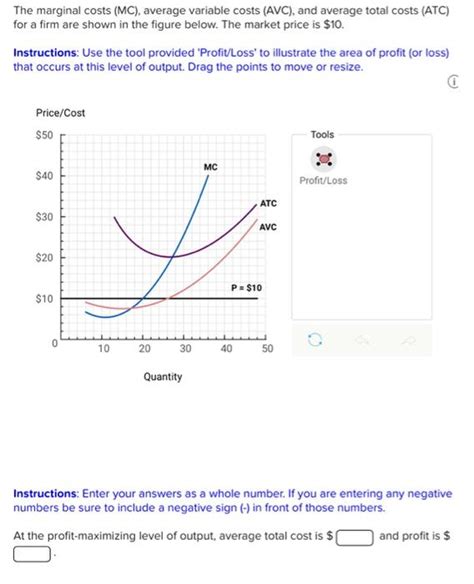
Impact of Average Variable Cost on Production Decisions

The average variable cost has a direct impact on a firm’s production decisions. Firms aim to produce at a level where the marginal revenue (MR) equals the marginal cost (MC), which also implies that the average variable cost is minimized at this production level. By understanding AVC, firms can adjust their production levels to achieve the most cost-efficient output. For instance, if the market price of a product is higher than the average variable cost, a firm may increase production to capitalize on the profit opportunity, assuming that fixed costs are covered.
Role of Average Variable Cost in Pricing Strategies
Average variable cost plays a crucial role in a firm’s pricing strategy. In competitive markets, firms may use the average variable cost as a benchmark to set prices. If the market price is below the average variable cost, producing and selling the product would result in a loss for each unit sold. Therefore, firms must ensure that their selling price is at least equal to or greater than the average variable cost to avoid losses. In less competitive markets, firms may have more flexibility in setting prices, but understanding AVC remains essential to ensure profitability.
Factors Influencing Average Variable Cost
Several factors can influence a firm’s average variable cost, including the cost of raw materials, labor costs, and the efficiency of the production process. Technological advancements can reduce AVC by increasing productivity and reducing waste. Economies of scale can also play a role, as larger production volumes can lead to lower average costs due to the spreading of fixed costs over more units. However, external factors such as changes in market prices of inputs or regulatory changes can increase AVC, necessitating firms to adjust their strategies accordingly.
How does average variable cost influence a firm's pricing strategy?
+Average variable cost is a critical factor in a firm's pricing strategy, especially in competitive markets. Firms must ensure that their selling price covers at least the average variable cost to avoid losses. In less competitive markets, firms may have more flexibility but still need to consider AVC for profitability.
What is the relationship between average variable cost and marginal cost?
+The relationship between average variable cost and marginal cost is significant. When marginal cost is less than average variable cost, producing more units reduces AVC. Conversely, when marginal cost exceeds average variable cost, producing more units increases AVC. The optimal production level is where MC equals AVC.
How do technological advancements affect average variable cost?
+Technological advancements can significantly reduce average variable cost by increasing productivity, reducing waste, and improving the efficiency of the production process. This allows firms to produce more units at a lower cost, potentially increasing profitability.
In conclusion, average variable cost is a pivotal concept in economics that guides firms in their production and pricing decisions. By understanding and analyzing AVC, businesses can optimize their operations, minimize costs, and maximize profits. The interplay between average variable cost, marginal cost, and market conditions underscores the complexity of economic decision-making and the importance of strategic planning in achieving business objectives.