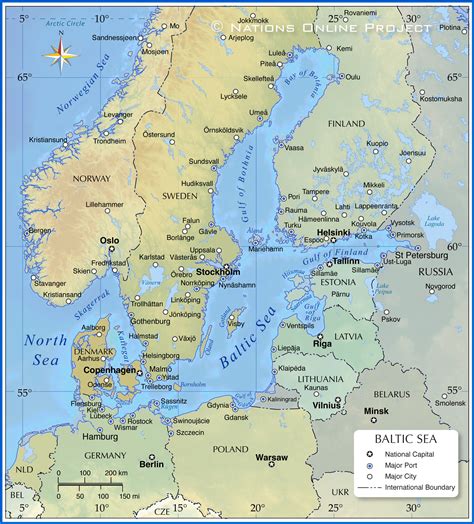
The Baltic Sea, located in Northern Europe, is a vital body of water that borders several countries, including Sweden, Finland, Russia, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Germany, and Denmark. With a rich history, diverse culture, and unique geography, the Baltic Sea is an attractive destination for travelers, sailors, and those interested in exploring its many wonders. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various aspects of the Baltic Sea, providing a detailed map guide, historical background, and practical information for visitors.
Key Points
- The Baltic Sea is the largest brackish water body in the world, covering an area of approximately 377,000 square kilometers.
- The sea is connected to the North Sea by the Skagerrak and Kattegat straits, and its coastline stretches for about 8,000 kilometers.
- The Baltic Sea is home to over 2,000 islands, with the largest being Gotland, Öland, and Saaremaa.
- The sea's unique geography and climate support a diverse range of flora and fauna, including over 100 species of fish and numerous bird species.
- The Baltic Sea has played a significant role in the region's history, with many important trade routes, ports, and cultural exchange centers located along its shores.
Geography and Climate of the Baltic Sea
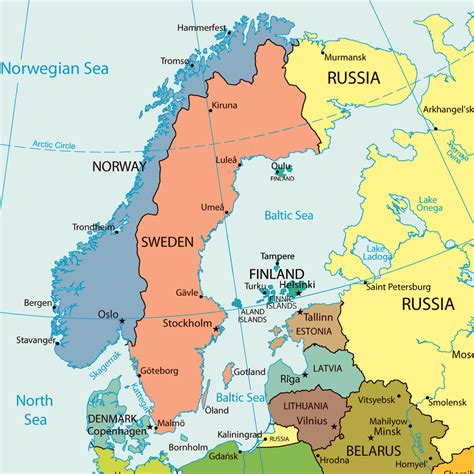
The Baltic Sea is a semi-enclosed sea, with a mix of fresh and saltwater, resulting from the combination of freshwater input from numerous rivers and the limited exchange of water with the North Sea. The sea’s geography is characterized by a complex system of bays, fjords, and straits, with the largest being the Gulf of Finland, the Gulf of Riga, and the Bay of Gdańsk. The climate in the region is temperate, with cold winters and mild summers, influenced by the sea’s proximity to the Arctic Circle and the warmth of the Gulf Stream.
Map of the Baltic Sea Region
A detailed map of the Baltic Sea region is essential for understanding the geography, climate, and cultural significance of the area. The map should include the following features:
- The coastline and borders of the surrounding countries
- The location of major ports, cities, and cultural attractions
- The distribution of islands, bays, and straits
- The network of rivers and waterways that flow into the sea
- The climate zones and weather patterns in the region
| Country | Coastline Length (km) | Major Ports |
|---|---|---|
| Sweden | 3,220 | Stockholm, Gothenburg, Malmö |
| Finland | 809 | Helsinki, Turku, Vaasa |
| Russia | 1,350 | St. Petersburg, Kaliningrad, Vyborg |
| Estonia | 1,370 | Tallinn, Pärnu, Haapsalu |
| Latvia | 498 | Riga, Liepāja, Ventspils |
| Lithuania | 90 | Klaipėda, Palanga, Šilutė |
| Poland | 491 | Gdańsk, Gdynia, Szczecin |
| Germany | 2,240 | Rostock, Kiel, Lübeck |
| Denmark | 7,314 | Copenhagen, Aarhus, Odense |
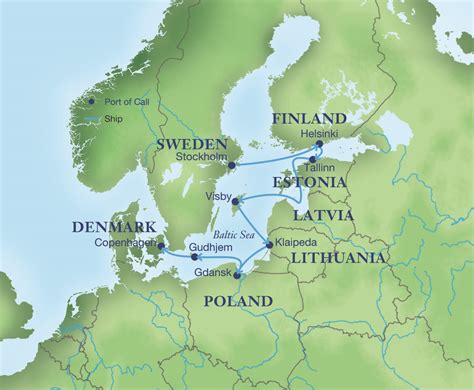
Cultural Significance and History of the Baltic Sea
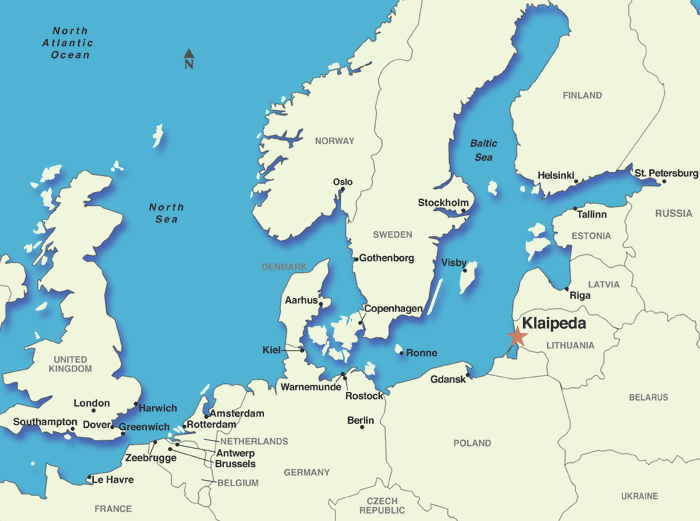
The Baltic Sea has played a significant role in the region’s history, with many important trade routes, ports, and cultural exchange centers located along its shores. The Hanseatic League, a powerful trading federation, dominated the region’s commerce from the 13th to the 16th century, leaving a lasting legacy in the architecture, language, and customs of the surrounding countries. The sea has also been the site of numerous conflicts, including the Swedish-Russian Wars and the Napoleonic Wars, which have shaped the region’s politics, economy, and culture.
Major Cities and Ports in the Baltic Sea Region
The Baltic Sea region is home to many vibrant cities and ports, each with its unique character, history, and cultural attractions. Some of the major cities and ports include:
- Stockholm, Sweden: Known for its stunning architecture, vibrant nightlife, and picturesque Old Town.
- Helsinki, Finland: Famous for its modern design, innovative technology, and stunning natural beauty.
- St. Petersburg, Russia: A city of grandeur and opulence, with its impressive palaces, museums, and canals.
- Tallinn, Estonia: A medieval town with a rich history, stunning architecture, and a thriving tech industry.
- Gdańsk, Poland: A historic port city with a rich cultural heritage, stunning architecture, and a vibrant nightlife.
What is the best time to visit the Baltic Sea?
+The best time to visit the Baltic Sea is during the summer months (June to August) when the weather is warm and sunny. However, the shoulder season (April to May and September to October) can also be a great time to visit, with fewer tourists and lower prices.
What are the most popular activities in the Baltic Sea region?
+The most popular activities in the Baltic Sea region include sailing, hiking, cycling, and exploring the region's rich cultural heritage. Visitors can also enjoy water sports, such as kayaking, paddleboarding, and windsurfing, as well as explore the region's stunning natural beauty, including its many islands, forests, and national parks.
What are the most important historical sites in the Baltic Sea region?
+The Baltic Sea region is home to many important historical sites, including the Hanseatic cities of Lübeck, Hamburg, and Danzig, the medieval town of Tallinn, and the stunning palaces and museums of St. Petersburg. Visitors can also explore the region's many castles, fortresses, and churches, which offer a glimpse into the region's rich history and cultural heritage.
In conclusion, the Baltic Sea is a unique and fascinating region, with a rich history, diverse culture, and stunning natural beauty. Whether you’re a sailor, a historian, or simply a curious traveler, the Baltic Sea has something to offer everyone. With its complex geography, vibrant cities, and rich cultural heritage, the region is a must-visit destination for anyone looking to explore the best of Northern Europe.