The Battle of Tours, also known as the Battle of Poitiers, is one of the most pivotal and decisive battles in world history, fought in 732 AD between the Frankish Kingdom and the Umayyad Caliphate. This confrontation not only halted the Islamic conquest of Western Europe but also had far-reaching consequences for the development of European society, politics, and culture. To understand the significance of the Battle of Tours, it's essential to delve into the historical context that led to this clash of powers.
In the early 8th century, the Umayyad Caliphate, under the leadership of Caliph Abd al-Rahman al-Ghafiqi, had been expanding its territories across North Africa and into the Iberian Peninsula. The Muslim forces had conquered Visigothic Hispania (modern-day Spain and Portugal) in 711 AD, and their campaign of expansion continued northwards into Gaul (modern-day France). The Frankish Kingdom, led by Charles Martel, was the primary power standing in the way of further Islamic conquest. The Franks were a Germanic tribe that had established themselves as a dominant force in Western Europe, with their kingdom stretching across what is now France, Germany, and parts of Italy.
Background and Causes of the Battle

The background to the Battle of Tours is complex and multifaceted, involving not just the clash of two major powers but also the internal dynamics of the Frankish Kingdom and the Umayyad Caliphate. The Umayyads were driven by a desire to spread Islam and expand their empire, which had been rapidly growing since the death of the Prophet Muhammad in 632 AD. The Frankish Kingdom, on the other hand, was motivated by a need to defend its territories and the Christian faith against the advancing Muslim forces. The battle was also precipitated by the alliances and rivalries within the region, including the relationship between the Franks and the Aquitanians, who were resisting Frankish rule and seeking Muslim support.
Preparations and Strategies
Both sides prepared extensively for the battle, though the exact nature of their strategies and the size of their armies are subjects of historical debate. Charles Martel, known for his military prowess and strategic thinking, chose to confront the Umayyad forces in a location that would give him a tactical advantage. The battlefield near Tours, with its dense forests and narrow valleys, allowed the Franks to employ their infantry to great effect, negating the traditional Muslim advantage in cavalry. The Umayyads, under Abd al-Rahman al-Ghafiqi, were accustomed to swift cavalry maneuvers and might have underestimated the defensive capabilities of the Frankish army.
| Military Aspect | Frankish Forces | Umayyad Forces |
|---|---|---|
| Size of Army | Estimated 15,000 to 20,000 | Estimated 20,000 to 25,000 |
| Tactics | Defensive phalanx formation | Mobile cavalry attacks |
| Leadership | Charles Martel | Abd al-Rahman al-Ghafiqi |

The Battle and Its Aftermath
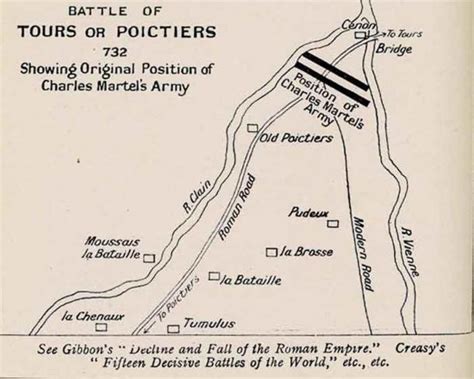
The Battle of Tours itself was a bloody and decisive confrontation. The Frankish army, deployed in a dense phalanx formation, was able to withstand the repeated cavalry charges of the Umayyad forces. The Umayyads, unable to break through the Frankish lines, suffered heavy casualties, including the death of their leader, Abd al-Rahman al-Ghafiqi. The defeat marked a significant turning point in the Islamic conquest of Europe, as it halted the Umayyad advance into Western Europe and protected the Frankish Kingdom and Christianity from potential overthrow.
Historical Significance and Legacy
The historical significance of the Battle of Tours cannot be overstated. It preserved Western Europe from Islamic conquest, allowing for the continuation of Christian culture and the eventual development of feudalism, the Renaissance, and other hallmark periods of European history. The battle also cemented Charles Martel’s legacy as a hero of Christendom and laid the foundation for the Carolingian dynasty, which would play a crucial role in shaping medieval Europe. Furthermore, the battle highlights the complex and often fraught relationship between Christianity and Islam, a theme that would continue to evolve over the centuries.
Key Points
- The Battle of Tours was fought in 732 AD between the Frankish Kingdom and the Umayyad Caliphate, resulting in a decisive Frankish victory that halted Islamic expansion into Western Europe.
- Charles Martel's strategic leadership and the Frankish army's defensive tactics were crucial in securing the victory.
- The battle had significant long-term consequences, including the preservation of Christianity in Western Europe and the development of feudal society.
- The legacy of the Battle of Tours continues to be felt, with implications for modern political, cultural, and religious discourse.
- Understanding the historical context and military strategies of the battle provides insights into the complexities of medieval warfare and the evolution of European society.
In conclusion, the Battle of Tours stands as a pivotal moment in world history, a clash of civilizations that shaped the course of European and Islamic relations for centuries to come. Through its examination, we gain a deeper understanding not only of the military strategies and political alliances of the time but also of the enduring impact of this battle on the development of Western civilization.
What were the primary causes of the Battle of Tours?
+The primary causes of the Battle of Tours included the Umayyad Caliphate’s expansion into Europe, the Frankish Kingdom’s desire to defend its territories, and the complex alliances and rivalries within the region, including the relationship between the Franks and the Aquitanians.
How did the Battle of Tours impact the development of European society?
+The Battle of Tours had a profound impact on the development of European society, preserving Christianity and allowing for the continuation of Christian culture, the development of feudalism, and the eventual evolution of Western civilization as we know it today.
What is the legacy of Charles Martel following the Battle of Tours?
+Charles Martel is remembered as a hero of Christendom and a pivotal figure in European history, whose victory at the Battle of Tours laid the foundation for the Carolingian dynasty and cemented his place as one of the most important leaders of the Middle Ages.