The Bee-eater and Stork are two fascinating bird species that belong to different families and exhibit unique characteristics. While they may not be directly related, understanding their behaviors, habitats, and distinctive features can provide valuable insights into the diverse world of ornithology. In this article, we will delve into five interesting facts about the Stork, exploring its biology, ecology, and conservation status, and occasionally drawing comparisons with the Bee-eater to highlight their differences and similarities.
Key Points
- The Stork is a large wading bird with a distinctive feeding behavior, unlike the Bee-eater, which is a near-passerine bird that primarily feeds on insects.
- Storks are known for their impressive migrations, with some species traveling over 12,000 kilometers each year, while Bee-eaters are also migratory but cover shorter distances.
- Storks have a unique way of communicating through bill-clattering, a behavior not observed in Bee-eaters, which instead use a variety of calls and songs.
- Storks are monogamous birds, with many species forming long-term pair bonds, similar to some Bee-eater species, which also exhibit monogamy during the breeding season.
- Unfortunately, many Stork species are facing threats such as habitat loss and hunting, which has led to a decline in their populations, a concern also shared by some Bee-eater species.
Introduction to Stork Biology

Storks are part of the family Ciconiidae and are characterized by their large size, long legs, and distinctive bills. They are found in a variety of habitats, including wetlands, grasslands, and forests, and are known for their unique feeding behaviors. Unlike Bee-eaters, which are brightly colored and known for their agility, Storks have a more subdued plumage and are often seen wading in shallow waters in search of prey.
Stork Migration Patterns
One of the most fascinating aspects of Stork biology is their migratory behavior. Many species of Storks migrate over long distances each year, with some species traveling from their breeding grounds in Europe and Asia to their wintering grounds in Africa. This migration can be up to 12,000 kilometers long and is an impressive feat of endurance. In comparison, Bee-eaters also migrate, but their journeys are generally shorter, and they often travel in smaller groups.
| Species | Migration Distance |
|---|---|
| White Stork | Up to 12,000 km |
| Black Stork | Up to 10,000 km |
| European Bee-eater | Up to 5,000 km |
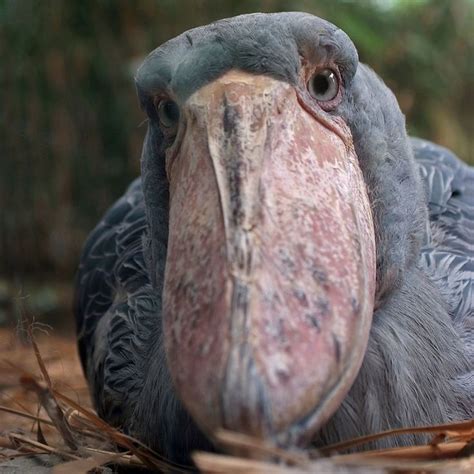

Stork Communication and Social Behavior

Storks are known for their unique way of communicating through bill-clattering, a behavior where they rapidly open and close their bills to produce a loud, clattering sound. This behavior is often used for mating and territorial displays and is an important aspect of Stork social behavior. In contrast, Bee-eaters use a variety of calls and songs to communicate, and their social behavior is often more complex, with many species forming large colonies.
Stork Conservation Status
Unfortunately, many species of Storks are facing threats such as habitat loss, hunting, and climate change, which has led to a decline in their populations. Conservation efforts are underway to protect Stork habitats and reduce human-Stork conflicts, but more needs to be done to ensure the long-term survival of these magnificent birds. Similarly, some Bee-eater species are also facing conservation challenges, highlighting the need for a comprehensive approach to bird conservation that addresses the diverse needs of different species.
What is the main difference between Storks and Bee-eaters?
+The main difference between Storks and Bee-eaters is their feeding behavior and habitat preferences. Storks are large wading birds that feed on a variety of prey, including fish, frogs, and small mammals, while Bee-eaters are near-passerine birds that primarily feed on insects.
How do Storks communicate with each other?
+Storks communicate with each other through a unique behavior called bill-clattering, where they rapidly open and close their bills to produce a loud, clattering sound. This behavior is often used for mating and territorial displays.
What is the conservation status of Storks?
+Many species of Storks are facing threats such as habitat loss, hunting, and climate change, which has led to a decline in their populations. Conservation efforts are underway to protect Stork habitats and reduce human-Stork conflicts, but more needs to be done to ensure the long-term survival of these magnificent birds.
In conclusion, the Stork is a fascinating bird species that exhibits unique characteristics and behaviors. Through their impressive migrations, distinctive feeding behaviors, and complex social structures, Storks continue to captivate ornithologists and bird enthusiasts alike. By comparing and contrasting Storks with Bee-eaters, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the diversity of bird species and the importance of conservation efforts to protect these magnificent creatures.